|
Summermatter Cycle
The Summermatter cycle is a physiological concept describing the complex relationship between physical activity/inactivity and energy expenditure/conservation. The concept explains why dieting fails in most cases and results in a Yo-yo effect. A central element of the Summermatter cycle is that reductions in energy intake, occurring with dieting or starvation, initially successfully induce weight and adipose tissue loss. At the same time, the reduced food availability prompts ambulatory activity, which further accelerates body and fat mass loss and depletes ATP, glycogen and intramyocellular lipids ( IMCL) in skeletal muscle. The scarcity of energy ultimately suppresses thermogenesis in skeletal muscle to conserve energy. As soon as energy becomes available again, this originally adaptive, thrifty program supports the replenishment of energy stores and weight regain. Fat deposition is the most efficient way for the body to store energy. This phenomenon of energy store replenishmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physiological
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical and physical functions in a living system. According to the classes of organisms, the field can be divided into medical physiology, animal physiology, plant physiology, cell physiology, and comparative physiology. Central to physiological functioning are biophysical and biochemical processes, homeostatic control mechanisms, and communication between cells. ''Physiological state'' is the condition of normal function. In contrast, ''pathological state'' refers to abnormal conditions, including human diseases. The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for exceptional scientific achievements in physiology related to the field of medicine. Foundations Cells Although there are differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dieting
Dieting is the practice of eating food in a regulated way to decrease, maintain, or increase body weight, or to prevent and treat diseases such as diabetes and obesity. As weight loss depends on calorie intake, different kinds of calorie-reduced diets, such as those emphasising particular macronutrients (low-fat, low-carbohydrate, etc.), have been shown to be no more effective than one another. As weight regain is common, diet success is best predicted by long-term adherence. Regardless, the outcome of a diet can vary widely depending on the individual. The first popular diet was "Banting", named after William Banting. In his 1863 pamphlet, ''Letter on Corpulence, Addressed to the Public'', he outlined the details of a particular low-carbohydrate, low-calorie diet that led to his own dramatic weight loss. Some guidelines recommend dieting to lose weight for people with weight-related health problems, but not for otherwise healthy people. One survey found that almost half o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yo-yo Effect
Weight cycling, also known as yo-yo dieting, is the repeated loss and gain of weight, resembling the up-down motion of a yo-yo. Many dieters are initially successful in the pursuit of weight loss but unsuccessful in maintaining the loss long-term and gain the weight back. The dieter then seeks to lose the regained weight, and the cycle begins again. Other individuals cycle weight deliberately in service of bodybuilding or athletic goals. It continues to be debated whether weight cycling causes increased risk of later obesity or cardiometabolic disease. Causes Dieting The reasons for yo-yo dieting are varied but often include embarking upon a hypocaloric diet that was initially too extreme. At first the dieter may experience elation at the thought of weight loss and pride in their rejection of food. Over time, however, the limits imposed by such extreme diets cause effects such as depression or fatigue that make the diet impossible to sustain. Ultimately, the dieter reverts to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
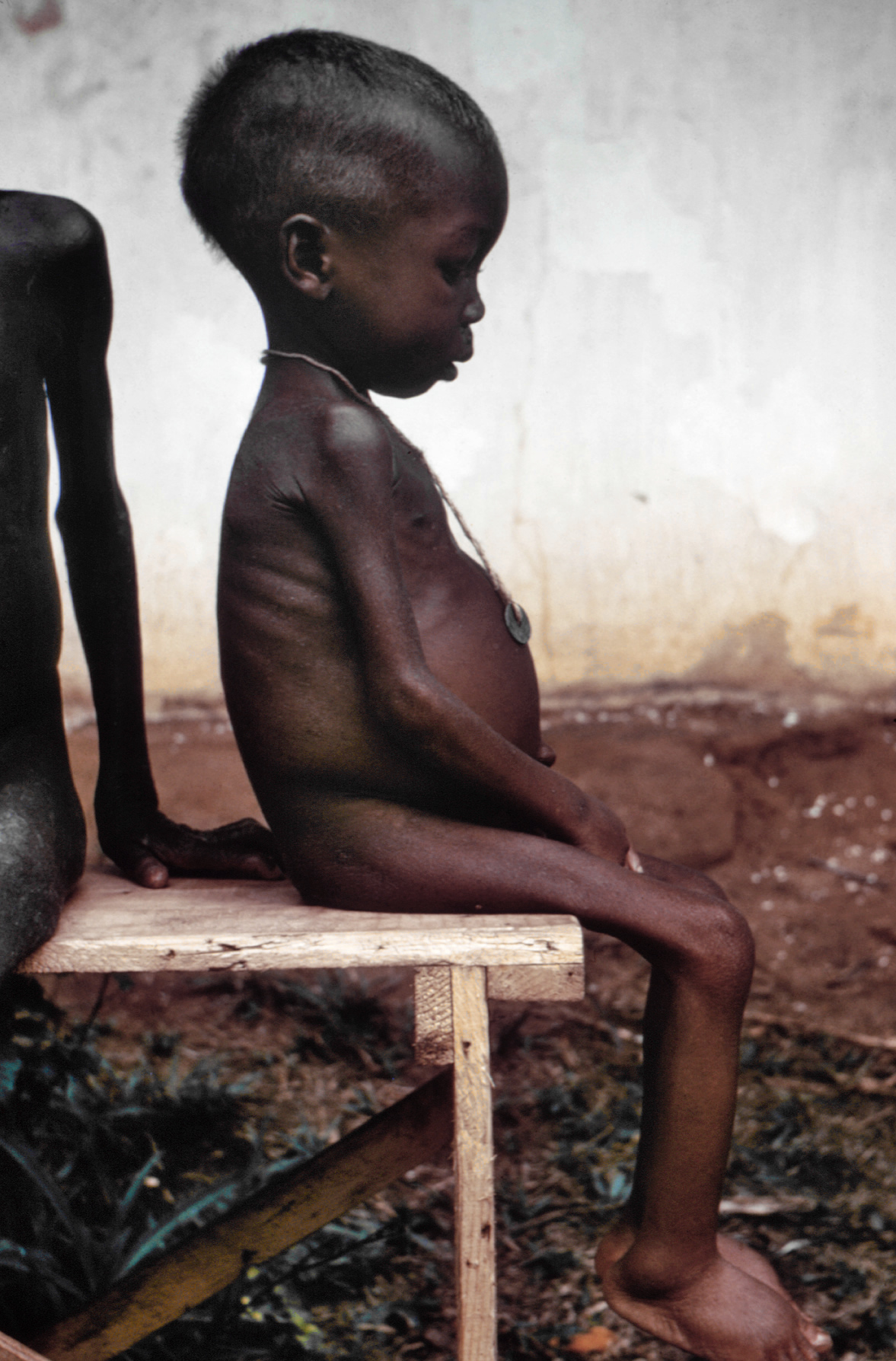
Starvation
Starvation is a severe deficiency in caloric energy intake, below the level needed to maintain an organism's life. It is the most extreme form of malnutrition. In humans, prolonged starvation can cause permanent organ damage and eventually, death. The term ''inanition'' refers to the symptoms and effects of starvation. Starvation may also be used as a means of torture or execution. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), hunger is the single gravest threat to the world's public health.Malnutrition The Starvelings The WHO also states that is by far the biggest contributor to [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |