|
Sulfonylurea Receptor
In molecular biology, the sulfonylurea receptors (SUR) are membrane proteins which are the molecular targets of the sulfonylurea class of antidiabetic drugs whose mechanism of action is to promote insulin release from pancreatic beta cells. More specifically, SUR proteins are subunits of the inward-rectifier potassium ion channels Kir6.x (6.1 and 6.2). The association of four Kir6.x and four SUR subunits form an ion conducting channel commonly referred to as the KATP channel. Three forms of the sulfonylurea receptor are known, SUR1 encoded by the ''ABCC8'' gene, and SUR2A and SUR2B, which are splice variants arising from a single ''ABCC9'' gene. Function The primary function of the sulfonylurea receptor is to sense intracellular levels of the nucleotides ATP and ADP and in response facilitate the open or closing its associated Kir6.x potassium channel. Hence, the KATP channel monitors the energy balance within the cell. Depending on the tissue in which the KATP channel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ABCC8
ATP-binding cassette transporter sub-family C member 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ABCC8'' gene. ''ABCC8'' orthologs have been identified in all mammals for which complete genome data are available. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). This protein is a member of the MRP subfamily which is involved in multi-drug resistance. This protein functions as a modulator of ATP-sensitive potassium channels and insulin release. Mutations and deficiencies in this protein have been observed in patients with hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy, an autosomal recessive disorder of unregulated and high insulin secretion. Mutations have also been associated with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus type II (neonatal dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all life-forms on Earth. Nucleotides are obtained in the diet and are also synthesized from common nutrients by the liver. Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates. The four nucleobases in DNA are guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine; in RNA, uracil is used in place of thymine. Nucleotides also play a central role in metabolism at a fundamental, cellular level. They provide chemical energy—in the form of the nucleoside triphosphates, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), guanosine triphosphate (GTP), cytidine triphosphate (CTP) and uridine triphosphate (UTP)—throughout the cell for the many cellular func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
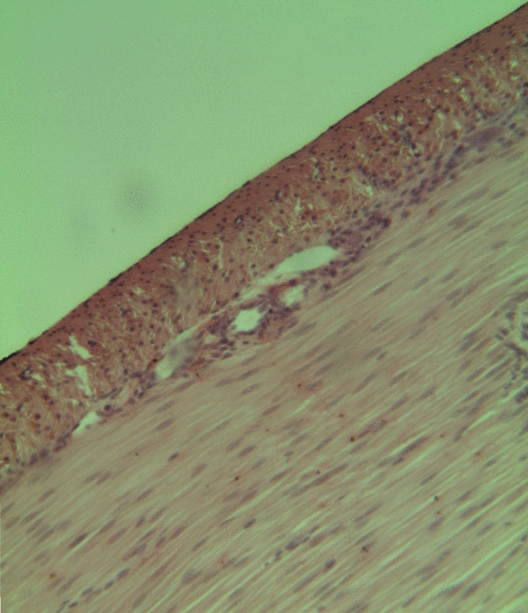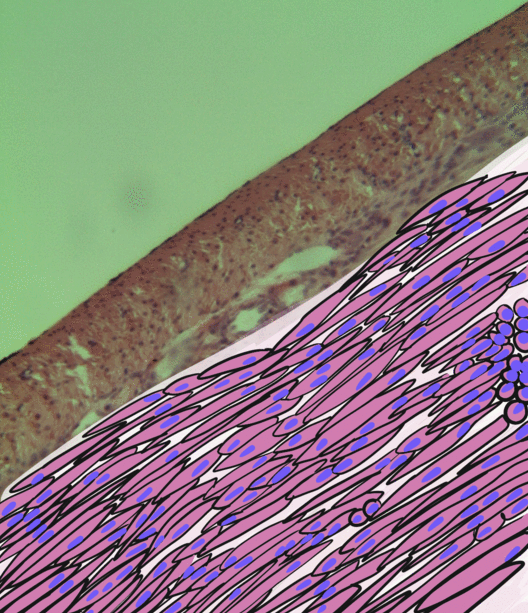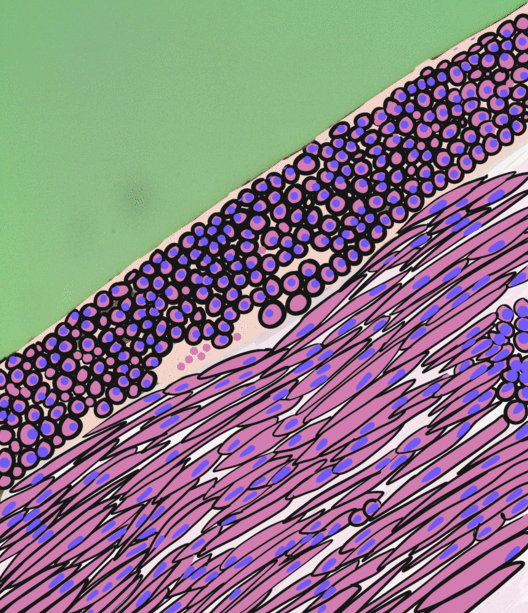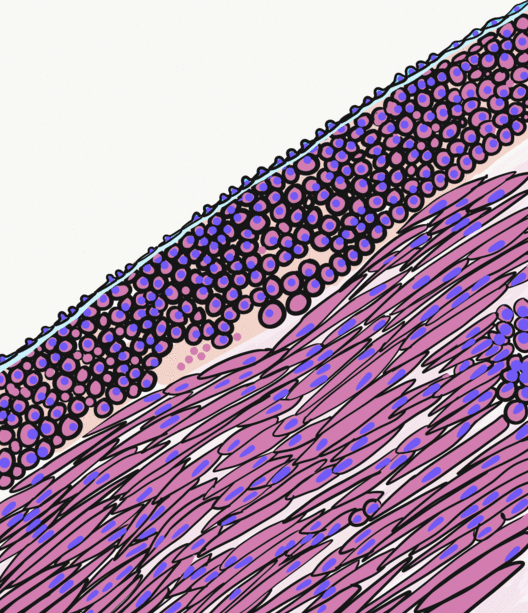
Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts as a syncytium. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines, bladder and uterus; in the walls of passageways, such as blood, and lymph vessels, and in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems. In the eyes, the ciliary muscles, a type of smooth muscle, dilate and contract the iris and alter the shape of the lens. In the skin, smooth muscle cells such as those of the arrector pili cause hair to stand erect in response to cold temperature or fear. Structure Gross anatomy Smooth muscle is grouped into two types: single-unit smooth muscle, also known as visceral smooth muscle, and multiunit smooth muscle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple muscle fascicle, fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the cell fusion, fusion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Myocytes
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate Muscle tissue, muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle tissue, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the Heart#Wall, wall of the heart. The cardiac muscle (myocardium) forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall (the pericardium) and the inner layer (the endocardium), with blood supplied via the coronary circulation. It is composed of individual cardiac muscle cells joined by intercalated discs, and encased by Collagen, collagen fibers and other substances that form the extracellular matrix. Cardiac muscle Muscle contraction, contracts in a similar manner to skeletal muscle, although with some important differences. Electrical stimulation in the form of a cardiac action potential triggers the release of calcium from the cell's internal calci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adipose Tissue
Adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells and a variety of immune cells such as adipose tissue macrophages. Adipose tissue is derived from preadipocytes. Its main role is to store energy in the form of lipids, although it also cushions and insulates the body. Far from being hormonally inert, adipose tissue has, in recent years, been recognized as a major endocrine organ, as it produces hormones such as leptin, estrogen, resistin, and cytokines (especially TNFα). In obesity, adipose tissue is also implicated in the chronic release of pro-inflammatory markers known as adipokines, which are responsible for the development of metabolic syndrome, a constellation of diseases including, but not limited to, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exocytosis
Exocytosis () is a form of active transport and bulk transport in which a cell transports molecules (e.g., neurotransmitters and proteins) out of the cell ('' exo-'' + ''cytosis''). As an active transport mechanism, exocytosis requires the use of energy to transport material. Exocytosis and its counterpart, endocytosis, are used by all cells because most chemical substances important to them are large polar molecules that cannot pass through the hydrophobic portion of the cell membrane by passive means. Exocytosis is the process by which a large amount of molecules are released; thus it is a form of bulk transport. Exocytosis occurs via secretory portals at the cell plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structure at the cell plasma membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell. In exocytosis, membrane-bound secretory vesicles are carried to the cell membrane, where they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage-dependent Calcium Channel
Voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs), also known as voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs), are a group of voltage-gated ion channels found in the membrane of excitable cells (''e.g.'', muscle, glial cells, neurons, etc.) with a permeability to the calcium ion Ca2+. These channels are slightly permeable to sodium ions, so they are also called Ca2+-Na+ channels, but their permeability to calcium is about 1000-fold greater than to sodium under normal physiological conditions. At physiologic or resting membrane potential, VGCCs are normally closed. They are activated (''i.e.'': opened) at depolarized membrane potentials and this is the source of the "voltage-gated" epithet. The concentration of calcium (Ca2+ ions) is normally several thousand times higher outside the cell than inside. Activation of particular VGCCs allows a Ca2+ influx into the cell, which, depending on the cell type, results in activation of calcium-sensitive potassium channels, muscular contraction, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperpolarization (biology)
Hyperpolarization is a change in a cell's membrane potential that makes it more negative. It is the opposite of a depolarization. It inhibits action potentials by increasing the stimulus required to move the membrane potential to the action potential threshold. Hyperpolarization is often caused by efflux of K+ (a cation) through K+ channels, or influx of Cl– (an anion) through Cl– channels. On the other hand, influx of cations, e.g. Na+ through Na+ channels or Ca2+ through Ca2+ channels, inhibits hyperpolarization. If a cell has Na+ or Ca2+ currents at rest, then inhibition of those currents will also result in a hyperpolarization. This voltage-gated ion channel response is how the hyperpolarization state is achieved. In neurons, the cell enters a state of hyperpolarization immediately following the generation of an action potential. While hyperpolarized, the neuron is in a refractory period that lasts roughly 2 milliseconds, during which the neuron is unabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depolarization
In biology, depolarization or hypopolarization is a change within a cell, during which the cell undergoes a shift in electric charge distribution, resulting in less negative charge inside the cell compared to the outside. Depolarization is essential to the function of many cells, communication between cells, and the overall physiology of an organism. Most cells in higher organisms maintain an internal environment that is negatively charged relative to the cell's exterior. This difference in charge is called the cell's membrane potential. In the process of depolarization, the negative internal charge of the cell temporarily becomes more positive (less negative). This shift from a negative to a more positive membrane potential occurs during several processes, including an action potential. During an action potential, the depolarization is so large that the potential difference across the cell membrane briefly reverses polarity, with the inside of the cell becoming positively char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. The human body recycles its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day. It is also a precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (adenine), the sugar ribose, and the Polyphosphate, triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of an adenine attached by the 9-nitrogen atom to the 1′ carbon atom of a sugar (ribose), which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATP-sensitive Potassium Channel
An ATP-sensitive potassium channel (or KATP channel) is a type of potassium channel that is gated by intracellular nucleotides, ATP and ADP. ATP-sensitive potassium channels are composed of Kir6.x-type subunits and sulfonylurea receptor (SUR) subunits, along with additional components. KATP channels are found in the plasma membrane; however some may also be found on subcellular membranes. These latter classes of KATP channels can be classified as being either sarcolemmal ("sarcKATP"), mitochondrial ("mitoKATP"), or nuclear ("nucKATP"). Discovery and structure KATP channels were first identified in cardiac myocytes by the Akinori Noma group in Japan. They have also been found in pancreas where they control insulin secretion, but are in fact widely distributed in plasma membranes. SarcKATP are composed of eight protein subunits (octamer). Four of these are members of the inward-rectifier potassium ion channel family Kir6.x (either Kir6.1 or Kir6.2), while the other four ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |