|
Sugar Addiction
A food or eating addiction is any behavioral addiction that is primarily characterized by the compulsive consumption of palatable (e.g., high fat and high sugar) food items which markedly activate the reward system in humans and other animals despite adverse consequences. [Baidu] |
Behavioral Addiction
Behavioral addiction is a form of addiction that involves a compulsion to engage in a rewarding non- substance-related behavior – sometimes called a natural reward – despite any negative consequences to the person's physical, mental, social or financial well-being. Addiction canonically refers to substance abuse; however, the term's connotation has been expanded to include behaviors that may lead to a reward (such as gambling, eating, or shopping) since the 1990s. A gene transcription factor known as ΔFosB has been identified as a necessary common factor involved in both behavioral and drug addictions, which are associated with the same set of neural adaptations in the reward system. Psychiatric and medical classifications Diagnostic models do not currently include the criteria necessary to identify behaviors as addictions in a clinical setting. Behavioral addictions have been proposed as a new class in ''DSM-5'', but the only category included is gambling addiction. Interne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
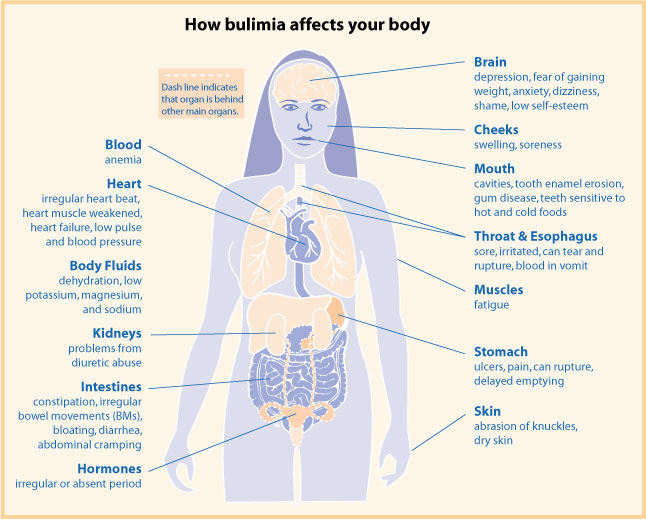
Bulimia Nervosa
Bulimia nervosa, also known as simply bulimia, is an eating disorder characterized by binge eating followed by purging or fasting, and excessive concern with body shape and weight. The aim of this activity is to expel the body of calories eaten from the binging phase of the process. Binge eating refers to eating a large amount of food in a short amount of time. Purging refers to the attempts to get rid of the food consumed. This may be done by vomiting or taking laxatives. Other efforts to lose weight may include the use of diuretics, stimulants, water fasting, or excessive exercise. Most people with bulimia are at a normal weight. The forcing of vomiting may result in thickened skin on the knuckles, breakdown of the teeth and effects on metabolic rate and caloric intake which cause thyroid dysfunction. Bulimia is frequently associated with other mental disorders such as depression, anxiety, borderline personality disorder, bipolar disorder and problems with drugs or alcohol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lisdexamfetamine
Lisdexamfetamine, sold under the brand name Vyvanse among others, is a stimulant medication that is mainly used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in people over the age of five as well as moderate-to-severe binge eating disorder in adults. Lisdexamfetamine is taken by mouth. Its effects generally begin within 2 hours and last for up to 14 hours. In the United Kingdom, it is usually less preferred than methylphenidate for the treatment of children. Common side effects of lisdexamfetamine include loss of appetite, anxiety, diarrhea, trouble sleeping, irritability, and nausea. Rare but serious side effects include mania, sudden cardiac death in those with underlying heart problems, and psychosis. It has a high potential for substance abuse per the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA). Serotonin syndrome may occur if used with certain other medications. Its use during pregnancy may result in harm to the baby and use during breastfeeding is not recommende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walkability
Walkability is a term for planning concepts best understood by the mixed-use of amenities in high-density neighborhoods where people can access said amenities by foot. It is based on the idea that urban spaces should be more than just transport corridors designed for maximum vehicle throughput. Instead, it should be relatively complete livable spaces that serve a variety of uses, users, and transportation modes and reduce the need for cars for travel. The term 'walkability' was primarily invented in the 1960s due to Jane Jacobs' revolution in urban studies. In recent years, walkability has become popular because of its health, economic, and environmental benefits. It is an essential concept of sustainable urban design. Factors influencing walkability include the presence or absence and quality of footpaths, sidewalks or other pedestrian rights-of-way, traffic and road conditions, land use patterns, building accessibility, and safety, among others. Factors One proposed def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches. Headaches can occur as a result of many conditions. There are a number of different classification systems for headaches. The most well-recognized is that of the International Headache Society, which classifies it into more than 150 types of primary and secondary headaches. Causes of headaches may include dehydration; fatigue; sleep deprivation; stress; the effects of medications (overuse) and recreational drugs, including withdrawal; viral infections; loud noises; head injury; rapid ingestion of a very cold food or beverage; and dental or sinus issues (such as sinusitis). Treatment of a headache depends on the underlying cause, but commonly involves pain medication (especially in case of migraine or cluster headache). A headache is one of the most commonly experienced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irritability
Irritability (also called as crankiness) is the excitatory ability that living organisms have to respond to changes in their environment. The term is used for both the physiological reaction to stimuli and for the pathological, abnormal or excessive sensitivity to stimuli. When reflecting human emotion and behavior, it is commonly defined as the tendency to react to stimuli with negative affective states (especially anger) and temper outbursts, which can be aggressive. Distressing or impairing irritability is important from a mental health perspective as a common symptom of concern and predictor of clinical outcomes. Definition Irritability is the excitatory ability that living organisms have to respond to changes in their environment. The term is used for both the physiological reaction to stimuli and for the pathological, abnormal or excessive sensitivity to stimuli. Irritability can be demonstrated in behavioral responses to both physiological and behavioral stimuli, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychomotor Agitation
Psychomotor agitation is a symptom in various disorders and health conditions. It is characterized by unintentional and purposeless motions and restlessness, often but not always accompanied by emotional distress. Typical manifestations include pacing around, wringing of the hands, uncontrolled tongue movement, pulling off clothing and putting it back on, and other similar actions. In more severe cases, the motions may become harmful to the individual, and may involve things such as ripping, tearing, or chewing at the skin around one's fingernails, lips, or other body parts to the point of bleeding. Psychomotor agitation is typically found in major depressive disorder or obsessive-compulsive disorder, and sometimes the manic phase in bipolar disorder, though it can also be a result of an excess intake of stimulants. It can also be caused by severe hyponatremia. The middle-aged and the elderly are more at risk to express it. Psychomotor agitation overlaps with agitation generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insomnia
Insomnia, also known as sleeplessness, is a sleep disorder in which people have trouble sleeping. They may have difficulty falling asleep, or staying asleep as long as desired. Insomnia is typically followed by daytime sleepiness, low energy, irritability, and a depressed mood. It may result in an increased risk of motor vehicle collisions, as well as problems focusing and learning. Insomnia can be short term, lasting for days or weeks, or long term, lasting more than a month. The concept of the word insomnia has two possibilities: insomnia disorder and insomnia symptoms, and many abstracts of randomized controlled trials and systematic reviews often underreport on which of these two possibilities the word insomnia refers to. Insomnia can occur independently or as a result of another problem. Conditions that can result in insomnia include psychological stress, chronic pain, heart failure, hyperthyroidism, heartburn, restless leg syndrome, menopause, certain medications, and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatigue (medical)
Fatigue describes a state of tiredness that does not resolve with rest or sleep. In general usage, fatigue is synonymous with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that normally follows prolonged physical or mental activity. When it does not resolve after rest or sleep, or occurs independently of physical or mental exertion, it may be a symptom of a medical condition that may become severe or progressive. Fatigue can be a feature of a mental disorder such as depression; may be associated with conditions of chronic pain such as fibromyalgia; it may also feature in conditions of chronic low-level inflammation, and be a disease-related symptom in many other conditions. Fatigue often has no known cause, and is recognised as being very complex in nature. Fatigability describes a susceptibility to fatigue. Physical fatigue results from muscle fatigue brought about by intense physical activity. Mental fatigue results from prolonged periods of cognitive activity which impairs cognitive abil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Craving
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is ingested by an organism and assimilated by the organism's cells to provide energy, maintain life, or stimulate growth. Different species of animals have different feeding behaviours that satisfy the needs of their unique metabolisms, often evolved to fill a specific ecological niche within specific geographical contexts. Omnivorous humans are highly adaptable and have adapted to obtain food in many different ecosystems. The majority of the food energy required is supplied by the industrial food industry, which produces food with intensive agriculture and distributes it through complex food processing and food distribution systems. This system of conventional agriculture relies heavily on fossil fuels, which means that the food and agricultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Consumption
Eating (also known as consuming) is the ingestion of food, typically to provide a heterotrophic organism with energy and to allow for growth. Animals and other heterotrophs must eat in order to survive — carnivores eat other animals, herbivores eat plants, omnivores consume a mixture of both plant and animal matter, and detritivores eat detritus. Fungi digest organic matter outside their bodies as opposed to animals that digest their food inside their bodies. For humans, eating is an activity of daily living. Some individuals may limit their amount of nutritional intake. This may be a result of a lifestyle choice, due to hunger or famine, as part of a diet or as religious fasting. Eating practices among humans Many homes have a large kitchen area devoted to preparation of meals and food, and may have a dining room, dining hall, or another designated area for eating. Most societies also have restaurants, food courts, and food vendors so that people may eat when away f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overeating
Overeating occurs when an individual consumes more calories in relation to the energy that is expended via physical activity or expelled via excretion, leading to weight gain and often obesity. Overeating is the defining characteristic of binge eating disorder. This term may also be used to refer to specific episodes of over-consumption. For example, many people overeat during festivals or while on holiday. Overeating can be a symptom of binge eating disorder or bulimia nervosa. Compulsive overeaters depend on food to comfort themselves when they are stressed, suffering bouts of depression, and have feelings of helplessness. In a broader sense, hyperalimentation includes excessive food administration through other means than eating, e.g. through parenteral nutrition. Treatment Cognitive behavioural therapy, individual therapy, and group therapy are often beneficial in helping people keep track of their eating habits and changing the way they cope with difficult situations. Of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |