|
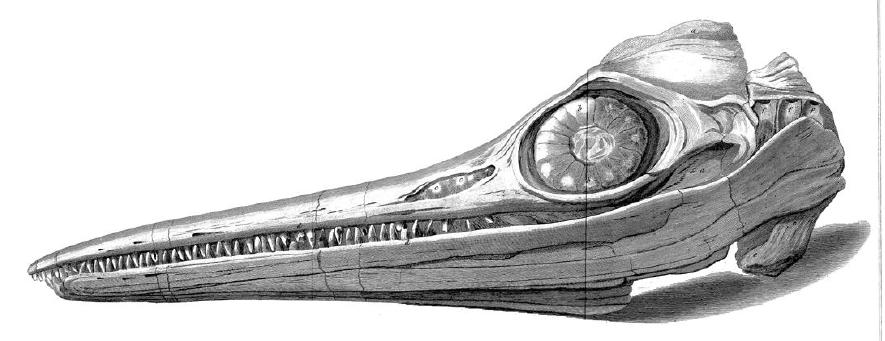
Suevoleviathan
''Suevoleviathan'' is an extinct genus of primitive ichthyosaur found in the Early Jurassic (Toarcian) of Holzmaden, Germany. Taxonomy The genus was named in 1998 by Michael Maisch for ''Leptopterygius disinteger'' and ''Ichthyosaurus integer'', both found in the Toarcian-age Posidonia Shale of Holzmaden.Maisch, W.A., 1998, A new ichthyosaur genus from the Posidonia Shale (Lower Toarcian, Jurassic) of Holzmaden, SW-Germany with comments on the phylogeny of post-Triassic ichthyosaurs. ''Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie, Abhandlungen'', 209: 47–78 The generic name means "Swabian Leviathan". The type species is ''Leptopterygius disinteger'' Huene 1926. ''Ichthyosaurus integer'' Bronn 1844 was also reassigned to the genus by Maisch to create the new combination ''Suevoleviathan integer''. Based on the relocation of the holotype of ''Suevoleviathan integer'' and an updated description of the specimen, Maxwell (2018) concluded that the two ''Suevoleviathan'' species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suevoleviathan Sp 43
''Suevoleviathan'' is an extinct genus of primitive ichthyosaur found in the Early Jurassic (Toarcian) of Holzmaden, Germany. Taxonomy The genus was named in 1998 by Michael Maisch for ''Leptopterygius disinteger'' and ''Ichthyosaurus integer'', both found in the Toarcian-age Posidonia Shale of Holzmaden.Maisch, W.A., 1998, A new ichthyosaur genus from the Posidonia Shale (Lower Toarcian, Jurassic) of Holzmaden, SW-Germany with comments on the phylogeny of post-Triassic ichthyosaurs. ''Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie, Abhandlungen'', 209: 47–78 The generic name means "Swabian Leviathan". The type species is ''Leptopterygius disinteger'' Huene 1926. ''Ichthyosaurus integer'' Bronn 1844 was also reassigned to the genus by Maisch to create the new combination ''Suevoleviathan integer''. Based on the relocation of the holotype of ''Suevoleviathan integer'' and an updated description of the specimen, Maxwell (2018) concluded that the two ''Suevoleviathan'' species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timeline Of Ichthyosaur Research
This timeline of ichthyosaur research is a chronological listing of events in the history of paleontology focused on the ichthyosauromorphs, a group of secondarily aquatic marine reptiles whose later members superficially resembled dolphins, sharks, or swordfish. Scientists have documented ichthyosaur fossils at least as far back as the late 17th century. At that time, a scholar named Edward Lhwyd published a book on British fossils that misattributed some ichthyosaur vertebrae to actual fishes; their true nature was not recognized until the 19th century. In 1811, a boy named Joseph Anning discovered the first ichthyosaur fossils that would come to be scientifically recognized as such. His sister Mary would later find the rest of its skeleton and would go on to become a respected fossil collector and paleontologist in her own right. Early researchers recognized ichthyosaurs as marine reptiles, but major aspects of their anatomy and behavior needed to be resolved. They were freque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyosauria
Ichthyosaurs (Ancient Greek for "fish lizard" – and ) are large extinct marine reptiles. Ichthyosaurs belong to the order known as Ichthyosauria or Ichthyopterygia ('fish flippers' – a designation introduced by Sir Richard Owen in 1842, although the term is now used more for the parent clade of the Ichthyosauria). Ichthyosaurs thrived during much of the Mesozoic era; based on fossil evidence, they first appeared around 250 million years ago ( Ma) and at least one species survived until about 90 million years ago, into the Late Cretaceous. During the Early Triassic epoch, ichthyosaurs and other ichthyosauromorphs evolved from a group of unidentified land reptiles that returned to the sea, in a development similar to how the mammalian land-dwelling ancestors of modern-day dolphins and whales returned to the sea millions of years later, which they gradually came to resemble in a case of convergent evolution. Ichthyosaurs were particularly abundant in the Late Triassic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyosaur
Ichthyosaurs (Ancient Greek for "fish lizard" – and ) are large extinct marine reptiles. Ichthyosaurs belong to the order known as Ichthyosauria or Ichthyopterygia ('fish flippers' – a designation introduced by Sir Richard Owen in 1842, although the term is now used more for the parent clade of the Ichthyosauria). Ichthyosaurs thrived during much of the Mesozoic era; based on fossil evidence, they first appeared around 250 million years ago ( Ma) and at least one species survived until about 90 million years ago, into the Late Cretaceous. During the Early Triassic epoch, ichthyosaurs and other ichthyosauromorphs evolved from a group of unidentified land reptiles that returned to the sea, in a development similar to how the mammalian land-dwelling ancestors of modern-day dolphins and whales returned to the sea millions of years later, which they gradually came to resemble in a case of convergent evolution. Ichthyosaurs were particularly abundant in the Late Triassic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyosaurs Of Europe
Ichthyosaurs (Ancient Greek for "fish lizard" – and ) are large extinct marine reptiles. Ichthyosaurs belong to the order known as Ichthyosauria or Ichthyopterygia ('fish flippers' – a designation introduced by Sir Richard Owen in 1842, although the term is now used more for the parent clade of the Ichthyosauria). Ichthyosaurs thrived during much of the Mesozoic era; based on fossil evidence, they first appeared around 250 million years ago ( Ma) and at least one species survived until about 90 million years ago, into the Late Cretaceous. During the Early Triassic epoch, ichthyosaurs and other ichthyosauromorphs evolved from a group of unidentified land reptiles that returned to the sea, in a development similar to how the mammalian land-dwelling ancestors of modern-day dolphins and whales returned to the sea millions of years later, which they gradually came to resemble in a case of convergent evolution. Ichthyosaurs were particularly abundant in the Late Triassic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |