|
Suchians
Suchia is a clade of archosaurs containing the majority of pseudosuchians ( crocodilians and their extinct relatives). It was defined as the least inclusive clade containing ''Aetosaurus ferratus'', '' Rauisuchus tiradentes'', '' Prestosuchus chiniquensis'', and '' Crocodylus niloticus'' (the living Nile crocodile) by Nesbitt (2011). Generally the only pseudosuchian group which is omitted from Suchia is the family Ornithosuchidae, although at least one analysis classifies ornithosuchids as close relatives of erpetosuchids (which are usually considered suchians) and aetosaurs (which are suchians by definition of the group). Phytosaurs are also excluded from Suchia, although it is not certain whether they qualify as pseudosuchians in the first place. There is some controversy over which traits, if any, can be used to distinguish suchians from non-suchian archosaurs. Anatomical features which evolve at the base of a group, and can thus be used to characterize the group, are know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetosauriformes
Aetosauriformes is an extinct clade of early-diverging pseudosuchians (the group of archosaurs that contains modern crocodylians and their stem group relatives). It includes the aetosaurs, a group of heavily armoured and at least partially herbivorous pseudosuchians, as well as the closely related genera ''Acaenasuchus'', '' Euscolosuchus'' and ''Revueltosaurus''. Classification Aetosauriformes was named in 2021 by William G. Parker and colleagues, as part of a redescription of the species '' Revueltosaurus callenderi''. It is a stem-based taxon, defined as the most inclusive clade that contains '' Acaenasuchus geoffreyi'', '' Aetosaurus ferratus'', ''Desmatosuchus spurensis'' and ''Revueltosaurus callenderi'', but not '' Erpetosuchus granti'', '' Ornithosuchus woodwardi'', ''Poposaurus gracilis'', ''Postosuchus kirkpatricki'', '' Rutiodon carolinensis'', ''Crocodylus niloticus'' (the Nile crocodile) or ''Passer domesticus'' (the house sparrow). Parker and colleagues performed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a unit in chronostratigraphy. The Early Triassic is the oldest epoch of the Mesozoic Era. It is preceded by the Lopingian Epoch (late Permian, Paleozoic Era) and followed by the Middle Triassic Epoch. The Early Triassic is divided into the Induan and Olenekian ages. The Induan is subdivided into the Griesbachian and Dienerian subages and the Olenekian is subdivided into the Smithian and Spathian subages. The Lower Triassic series is coeval with the Scythian Stage, which is today not included in the official timescales but can be found in older literature. In Europe, most of the Lower Triassic is composed of Buntsandstein, a lithostratigraphic unit of continental red beds. The Early Triassic and partly also the Middle Triassic span the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
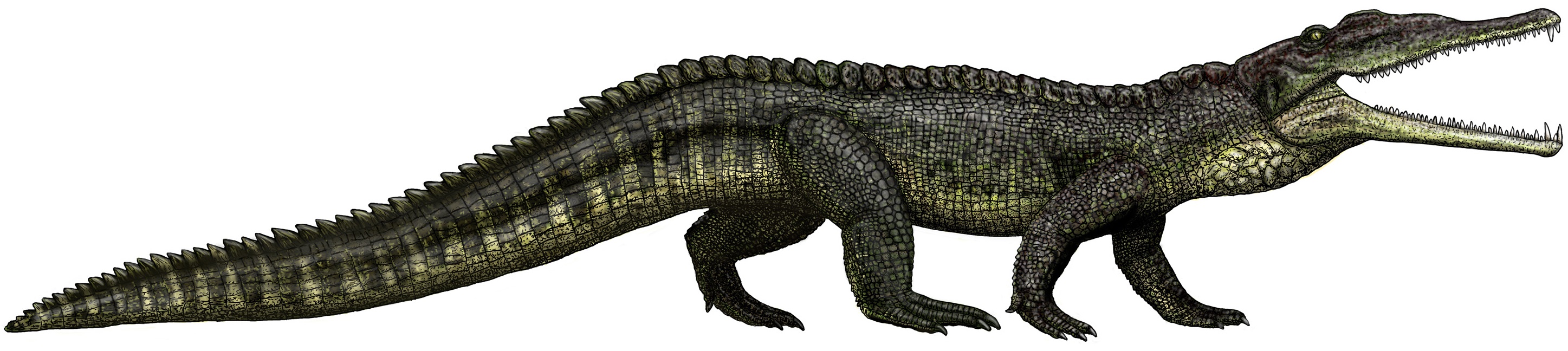
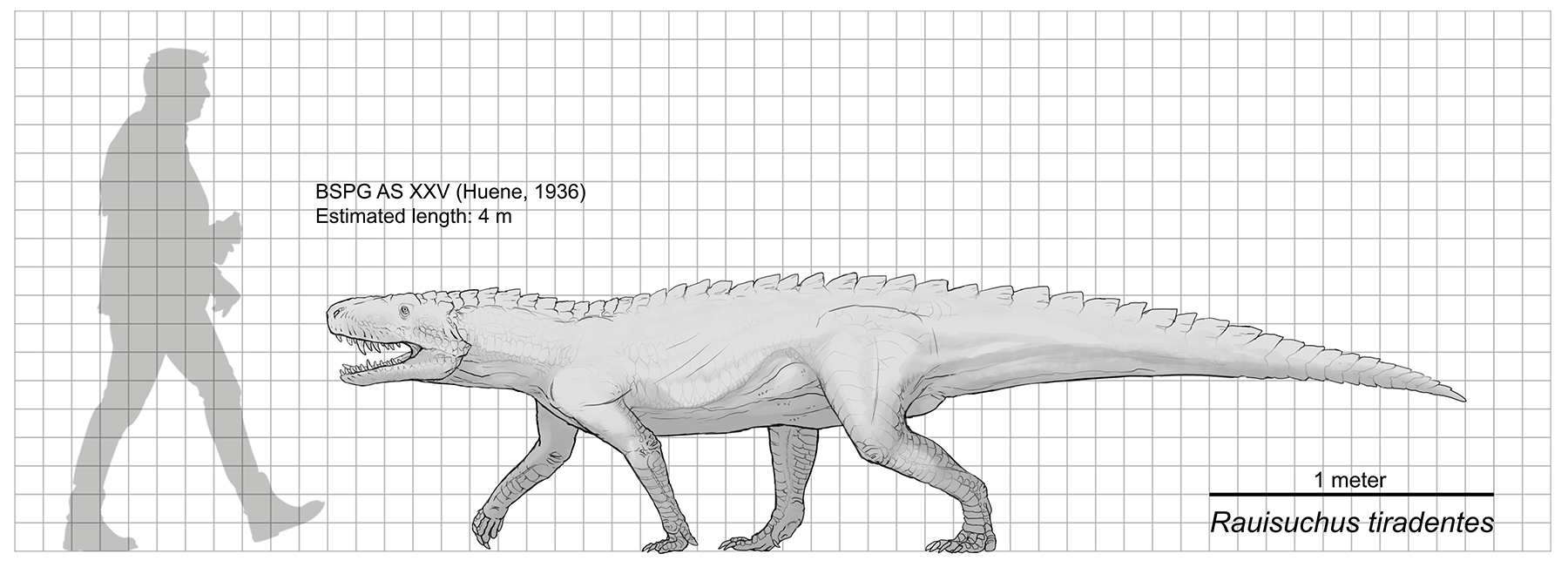
Rauisuchus
''Rauisuchus'' (meaning "Wilhelm Rau's crocodile") is a genus of extinct archosaurs which lived in what is now the Geopark of Paleorrota (Santa María Formation), Brazil, during the Late Triassic period (235–228 million years ago). It contains one species, ''R. tiradentes''.''Rauisuchus'' at Fossilworks.orgF. v. Huene. (1942) ''Die fossilen Reptilien des südamerikanischen Gondwanalandes. Ergebnisse der Sauriergrabung in Südbrasilien 1928/29.'' München: C.H. Beck'sche Verlagsbuchhandlung Discovery and naming In 1928 or 1929, near the road from Sa ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibula
The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint. Structure The bone has the following components: * Lateral malleolus * Interosseous membrane connecting the fibula to the tibia, forming a syndesmosis joint * The superior tibiofibular articulation is an arthrodial joint between the lateral condyle of the tibia and the head of the fibula. * The inferior tibiofibular articulation (tibiofibular syndesmosis) is formed by the rough, convex surface of the medial side of the lower end of the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcaneus
In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus (; from the Latin ''calcaneus'' or ''calcaneum'', meaning heel) or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock. Structure In humans, the calcaneus is the largest of the tarsal bones and the largest bone of the foot. Its long axis is pointed forwards and laterally. The talus bone, calcaneus, and navicular bone are considered the proximal row of tarsal bones. In the calcaneus, several important structures can be distinguished:Platzer (2004), p 216 There is a large calcaneal tuberosity located posteriorly on plantar surface with medial and lateral tubercles on its surface. Besides, there is another peroneal tubecle on its lateral surface. On its lower edge on either side are its lateral and medial processes (serving as the origins of the abductor hallucis and abductor digiti minimi). The Achilles tendon is inserted into a roughened area on its superio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jugal Bone
The jugal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians and birds. In mammals, the jugal is often called the malar or zygomatic. It is connected to the quadratojugal and maxilla, as well as other bones, which may vary by species. Anatomy The jugal bone is located on either side of the skull in the circumorbital region. It is the origin of several masticatory muscles in the skull. The jugal and lacrimal bones are the only two remaining from the ancestral circumorbital series: the prefrontal, postfrontal, postorbital, jugal, and lacrimal bones. During development, the jugal bone originates from dermal bone. In dinosaurs This bone is considered key in the determination of general traits in cases in which the entire skull has not been found intact (for instance, as with dinosaurs in paleontology). In some dinosaur genera the jugal also forms part of the lower margin of either the antorbital fenestra or the infratemporal fenestra, or both. Most commonly, this bone articu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sterling Nesbitt
Sterling Nesbitt (born March 25, 1982, in Mesa, Arizona) is an American paleontologist best known for his work on the origin and early evolutionary patterns of archosaurs. He is currently an associate professor at Virginia Tech in the Department of Geosciences. Biography Sterling Nesbitt received his B.A. in integrative biology with a minor in geology from the University of California Berkeley in 2004. He received his PhD from Columbia University in 2009, completing the majority of his research at the American Museum of Natural History in New York City. He subsequently held postdoctoral researcher positions at the University of Texas at Austin, the University of Washington, and the Field Museum. He is currently an associate professor in thDepartment of Geosciencesat Virginia Tech in Blacksburg, Virginia. He is also a research associate/affiliate of the American Museum of Natural History, the Vertebrate Paleontology Lab at The University of Texas at Austin, the Virginia Museum of Nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batrachotomus Calcaneum Labelled
''Batrachotomus'' is a genus of prehistoric archosaur. Fossils of this animal have been found in southern Germany and dated from the Ladinian stage of the Middle Triassic period, around 242 to 237 million years ago. ''Batrachotomus'' was described by palaeontologist David J. Gower 22 years after its discovery. The locality where ''Batrachotomus'' lived was a swampy region and the name comes from the Greek ''batrachos/βάτραχος'' (frog) and ''tome/τομή'' (cutting, slicing), which refers to its preying on the large amphibian ''Mastodonsaurus''.Gower (1999), p. 6. In contrast with sprawling reptiles, like crocodiles, this large carnivore was very agile with locomotor superiority due to its erect stance. A remarkable feature seen on its back was a row of paired, flattened bony plates. ''Batrachotomus'' was possibly an early relative of ''Postosuchus'',Gower (1999), p. 1. which lived during the dawn of the dinosaurs. Description ''Batrachotomus'' was a heavily bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium and the viscerocranium ( facial skeleton) that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to enable sound localisation of the direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, such as horned ungulates (mammals with hooves), the skull also has a defensive function by providing the mount (on the front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamosal Bone
The squamosal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians, and birds. In fishes, it is also called the pterotic bone. In most tetrapods, the squamosal and quadratojugal bones form the cheek series of the skull. The bone forms an ancestral component of the dermal roof and is typically thin compared to other skull bones. The squamosal bone lies ventral to the temporal series and otic notch, and is bordered anteriorly by the postorbital. Posteriorly, the squamosal articulates with the quadrate and pterygoid bones. The squamosal is bordered anteroventrally by the jugal and ventrally by the quadratojugal. Function in reptiles In reptiles, the quadrate and articular bones of the skull articulate to form the jaw joint. The squamosal bone lies anterior to the quadrate bone. Anatomy in synapsids Non-mammalian synapsids In non-mammalian synapsids, the jaw is composed of four bony elements and referred to as a quadro-articular jaw because the joint is between the articular an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postorbital Bone
The ''postorbital'' is one of the bones in vertebrate skulls which forms a portion of the dermal skull roof and, sometimes, a ring about the orbit. Generally, it is located behind the postfrontal and posteriorly to the orbital fenestra. In some vertebrates, the postorbital is fused with the postfrontal to create a postorbitofrontal. Birds have a separate postorbital as an embryo, but the bone fuses with the frontal Front may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''The Front'' (1943 film), a 1943 Soviet drama film * ''The Front'', 1976 film Music * The Front (band), an American rock band signed to Columbia Records and active in the 1980s and e ... before it hatches. References * Roemer, A. S. 1956. ''Osteology of the Reptiles''. University of Chicago Press. 772 pp. Skull {{Vertebrate anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Sereno
Paul Callistus Sereno (born October 11, 1957) is a professor of paleontology at the University of Chicago and a National Geographic "explorer-in-residence" who has discovered several new dinosaur species on several continents, including at sites in Inner Mongolia, Argentina, Morocco and Niger. One of his most widely publicized discoveries is that of a nearly complete specimen of ''Sarcosuchus imperator'' — popularly known as SuperCroc — at Gadoufaoua in the Tenere desert of Niger. Biography Youth and education The son of a mail carrier and an art teacher at Prairie Elementary, Sereno grew up in Naperville, Illinois and graduated from Naperville Central High School. He was then educated at Northern Illinois University (B.S., Biological Sciences, 1979) and Columbia University (M.A., Vertebrate Paleontology, 1981; M. Phil., Geological Sciences, 1981; Ph.D., Geological Sciences, 1987). Career Sereno was named one of ''People'' magazine's 50 Most Beautiful People (1997). Ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)




