|
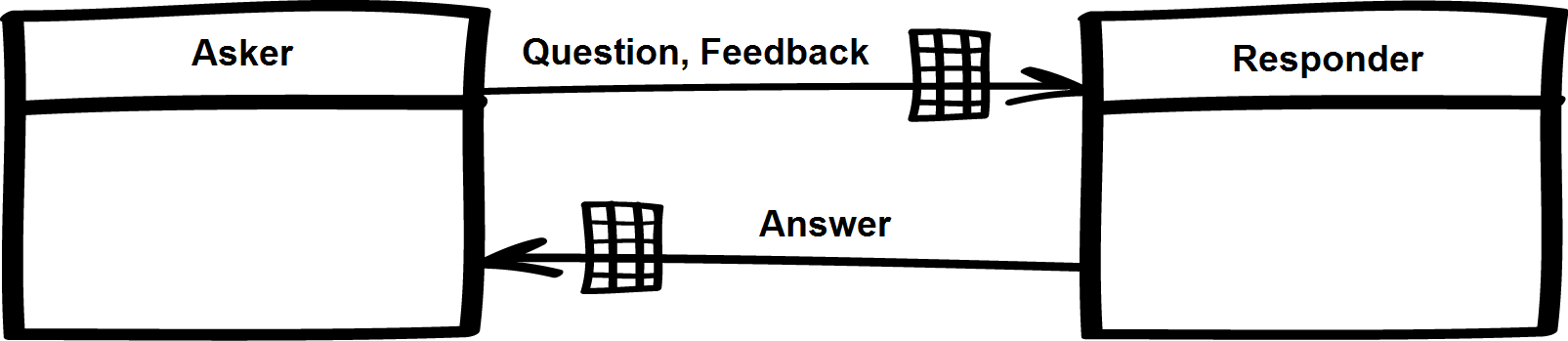
Subject-oriented Business Process Management
Subject-oriented business process management (S-BPM) is a communication based view on actor model, actors (the subjects), which compose a business process orchestration or choreography. The modeling paradigm uses five symbols to model any process and allows direct transformation into executable form. Each business process consists of two or more ''subjects'' which exchange ''messages''. Each subject has an ''internal behavior'' (capsulation), which is defined as a control flow between different states, which are ''receive'' and ''send message'' and ''do something''. For practical usage and for syntactical sugaring there are more elements available, but not necessary. In 2011 and 2012 S-BPM has been included in Gartner's Hype Cycle. Foundations Process calculi The S-BPM methodology in its essence is based on the Calculus of communicating systems, CCS-Calculus of Robin Milner. The main objective of CCS was to provide a mathematical framework to describe communicating systems in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actor Model
The actor model in computer science is a mathematical model of concurrent computation that treats ''actor'' as the universal primitive of concurrent computation. In response to a message it receives, an actor can: make local decisions, create more actors, send more messages, and determine how to respond to the next message received. Actors may modify their own private state, but can only affect each other indirectly through messaging (removing the need for lock-based synchronization). The actor model originated in 1973. It has been used both as a framework for a theoretical understanding of computation and as the theoretical basis for several practical implementations of concurrent systems. The relationship of the model to other work is discussed in actor model and process calculi. History According to Carl Hewitt, unlike previous models of computation, the actor model was inspired by physics, including general relativity and quantum mechanics. It was also influenced by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is an interdisciplinary subfield of linguistics, computer science, and artificial intelligence concerned with the interactions between computers and human language, in particular how to program computers to process and analyze large amounts of natural language data. The goal is a computer capable of "understanding" the contents of documents, including the contextual nuances of the language within them. The technology can then accurately extract information and insights contained in the documents as well as categorize and organize the documents themselves. Challenges in natural language processing frequently involve speech recognition, natural-language understanding, and natural-language generation. History Natural language processing has its roots in the 1950s. Already in 1950, Alan Turing published an article titled "Computing Machinery and Intelligence" which proposed what is now called the Turing test as a criterion of intelligence, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-BPM Model Of Quiz Process
Subject-oriented business process management (S-BPM) is a communication based view on actors (the subjects), which compose a business process orchestration or choreography. The modeling paradigm uses five symbols to model any process and allows direct transformation into executable form. Each business process consists of two or more ''subjects'' which exchange ''messages''. Each subject has an ''internal behavior'' (capsulation), which is defined as a control flow between different states, which are ''receive'' and ''send message'' and ''do something''. For practical usage and for syntactical sugaring there are more elements available, but not necessary. In 2011 and 2012 S-BPM has been included in Gartner's Hype Cycle. Foundations Process calculi The S-BPM methodology in its essence is based on the CCS-Calculus of Robin Milner. The main objective of CCS was to provide a mathematical framework to describe communicating systems in a formal way. Milner states that every intere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-BPM Internal Behaviour
Subject-oriented business process management (S-BPM) is a communication based view on actors (the subjects), which compose a business process orchestration or choreography. The modeling paradigm uses five symbols to model any process and allows direct transformation into executable form. Each business process consists of two or more ''subjects'' which exchange ''messages''. Each subject has an ''internal behavior'' (capsulation), which is defined as a control flow between different states, which are ''receive'' and ''send message'' and ''do something''. For practical usage and for syntactical sugaring there are more elements available, but not necessary. In 2011 and 2012 S-BPM has been included in Gartner's Hype Cycle. Foundations Process calculi The S-BPM methodology in its essence is based on the CCS-Calculus of Robin Milner. The main objective of CCS was to provide a mathematical framework to describe communicating systems in a formal way. Milner states that every intere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Agent
In computer science, a software agent or software AI is a computer program that acts for a user or other program in a relationship of agency, which derives from the Latin ''agere'' (to do): an agreement to act on one's behalf. Such "action on behalf of" implies the authority to decide which, if any, action is appropriate. Agents are colloquially known as ''bots'', from ''robot''. They may be embodied, as when execution is paired with a robot body, or as software such as a chatbot executing on a phone (e.g. Siri) or other computing device. Software agents may be autonomous or work together with other agents or people. Software agents interacting with people (e.g. chatbots, human-robot interaction environments) may possess human-like qualities such as natural language understanding and speech, personality or embody humanoid form (see Asimo). Related and derived concepts include ''intelligent agents'' (in particular exhibiting some aspects of artificial intelligence, such as reas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agent (grammar)
In linguistics, a grammatical agent is the thematic relation of the cause or initiator to an event. The agent is a semantic concept distinct from the subject of a sentence as well as from the topic Topic, topics, TOPIC, topical, or topicality may refer to: Topic / Topics * Topić, a Slavic surname * ''Topics'' (Aristotle), a work by Aristotle * Topic (chocolate bar), a brand of confectionery bar * Topic (DJ), German musician * Topic (g .... Whereas the subject is determined syntactically, primarily through word order, the agent is determined through its relationship to the action expressed by the verb. For example, in the sentence "The little girl was bitten by the dog", "girl" is the subject, but "dog" is the agent. The word "agent" comes from the present participle ''agens, agentis'' ("the one doing") of the Latin verb ''agere'', to "do" or "make". Theory Typically, the situation is denoted by a Sentence (linguistics), sentence, the action by a verb in the sentence, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agent (economics)
In economics, an agent is an actor (more specifically, a decision maker) in a model of some aspect of the economy. Typically, every agent makes decisions by solving a well- or ill-defined optimization or choice problem. For example, ''buyers'' (consumers) and ''sellers'' ( producers) are two common types of agents in partial equilibrium models of a single market. Macroeconomic models, especially dynamic stochastic general equilibrium models that are explicitly based on microfoundations, often distinguish households, firms, and governments or central banks as the main types of agents in the economy. Each of these agents may play multiple roles in the economy; households, for example, might act as consumers, as workers, and as voters in the model. Some macroeconomic models distinguish even more types of agents, such as workers and shoppers or commercial banks. The term ''agent'' is also used in relation to principal–agent models; in this case, it refers specifically to someone de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Object
A business object is an entity within a multi-tiered software application that works in conjunction with the data access and business logic layers to transport data. For example, a "Manager" would be a ''business object'' where its attributes can be "Name", "Second name", "Age", "Area", "Country" and it could hold a ''1-n'' association with its employees (a collection of ''Employee'' instances). Another example would be a concept like "Process" having "Identifier", "Name", "Start date", "End date" and "Kind" attributes and holding an association with the "Employee" (''the responsible'') that started it. Function Whereas a program may implement classes, which typically end in objects managing or executing behaviours, a ''business object'' usually does nothing itself but holds a set of instance variables or properties, also known as ''attributes'', and associations with other business objects, weaving a map of objects representing the business relationships. A domain model whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formal Language
In logic, mathematics, computer science, and linguistics, a formal language consists of words whose letters are taken from an alphabet and are well-formed according to a specific set of rules. The alphabet of a formal language consists of symbols, letters, or tokens that concatenate into strings of the language. Each string concatenated from symbols of this alphabet is called a word, and the words that belong to a particular formal language are sometimes called ''well-formed words'' or ''well-formed formulas''. A formal language is often defined by means of a formal grammar such as a regular grammar or context-free grammar, which consists of its formation rules. In computer science, formal languages are used among others as the basis for defining the grammar of programming languages and formalized versions of subsets of natural languages in which the words of the language represent concepts that are associated with particular meanings or semantics. In computational complexity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gartner's Hype Cycle
The Gartner hype cycle is a graphical presentation developed, used and branded by the American research, advisory and information technology firm Gartner to represent the maturity, adoption, and social application of specific technologies. The hype cycle claims to provide a graphical and conceptual presentation of the maturity of emerging technologies through five phases. The model is not perfect and research so far shows possible improvements for the model. Five phases Each hype cycle drills down into the five key phases of a technology's life cycle. The term "hype cycle" and each of the associated phases are now used more broadly in the marketing of new technologies. Hype in new media Hype (in the more general media sense of the term "hype") plays a large part in the adoption of new media. Analyses of the Internet in the 1990s featured large amounts of hype, and that created "debunking" responses. A longer-term historical perspective on such cycles can be found in the res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subject-oriented Business Process Management
Subject-oriented business process management (S-BPM) is a communication based view on actor model, actors (the subjects), which compose a business process orchestration or choreography. The modeling paradigm uses five symbols to model any process and allows direct transformation into executable form. Each business process consists of two or more ''subjects'' which exchange ''messages''. Each subject has an ''internal behavior'' (capsulation), which is defined as a control flow between different states, which are ''receive'' and ''send message'' and ''do something''. For practical usage and for syntactical sugaring there are more elements available, but not necessary. In 2011 and 2012 S-BPM has been included in Gartner's Hype Cycle. Foundations Process calculi The S-BPM methodology in its essence is based on the Calculus of communicating systems, CCS-Calculus of Robin Milner. The main objective of CCS was to provide a mathematical framework to describe communicating systems in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |