|
Subderivative
In mathematics, the subderivative, subgradient, and subdifferential generalize the derivative to convex functions which are not necessarily differentiable. Subderivatives arise in convex analysis, the study of convex functions, often in connection to convex optimization. Let f:I \to \mathbb be a real-valued convex function defined on an open interval In mathematics, a (real) interval is a set of real numbers that contains all real numbers lying between any two numbers of the set. For example, the set of numbers satisfying is an interval which contains , , and all numbers in between. Other ... of the real line. Such a function need not be differentiable at all points: For example, the absolute value function ''f''(''x'')=, ''x'', is nondifferentiable when ''x''=0. However, as seen in the graph on the right (where ''f(x)'' in blue has non-differentiable kinks similar to the absolute value function), for any ''x''0 in the domain of the function one can draw a line which goes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subderivative Illustration
In mathematics, the subderivative, subgradient, and subdifferential generalize the derivative to convex functions which are not necessarily differentiable. Subderivatives arise in convex analysis, the study of convex functions, often in connection to convex optimization. Let f:I \to \mathbb be a real-valued convex function defined on an open interval of the real line. Such a function need not be differentiable at all points: For example, the absolute value function ''f''(''x'')=, ''x'', is nondifferentiable when ''x''=0. However, as seen in the graph on the right (where ''f(x)'' in blue has non-differentiable kinks similar to the absolute value function), for any ''x''0 in the domain of the function one can draw a line which goes through the point (''x''0, ''f''(''x''0)) and which is everywhere either touching or below the graph of ''f''. The slope of such a line is called a ''subderivative'' (because the line is under the graph of ''f''). Definition Rigorously, a ''subderivat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
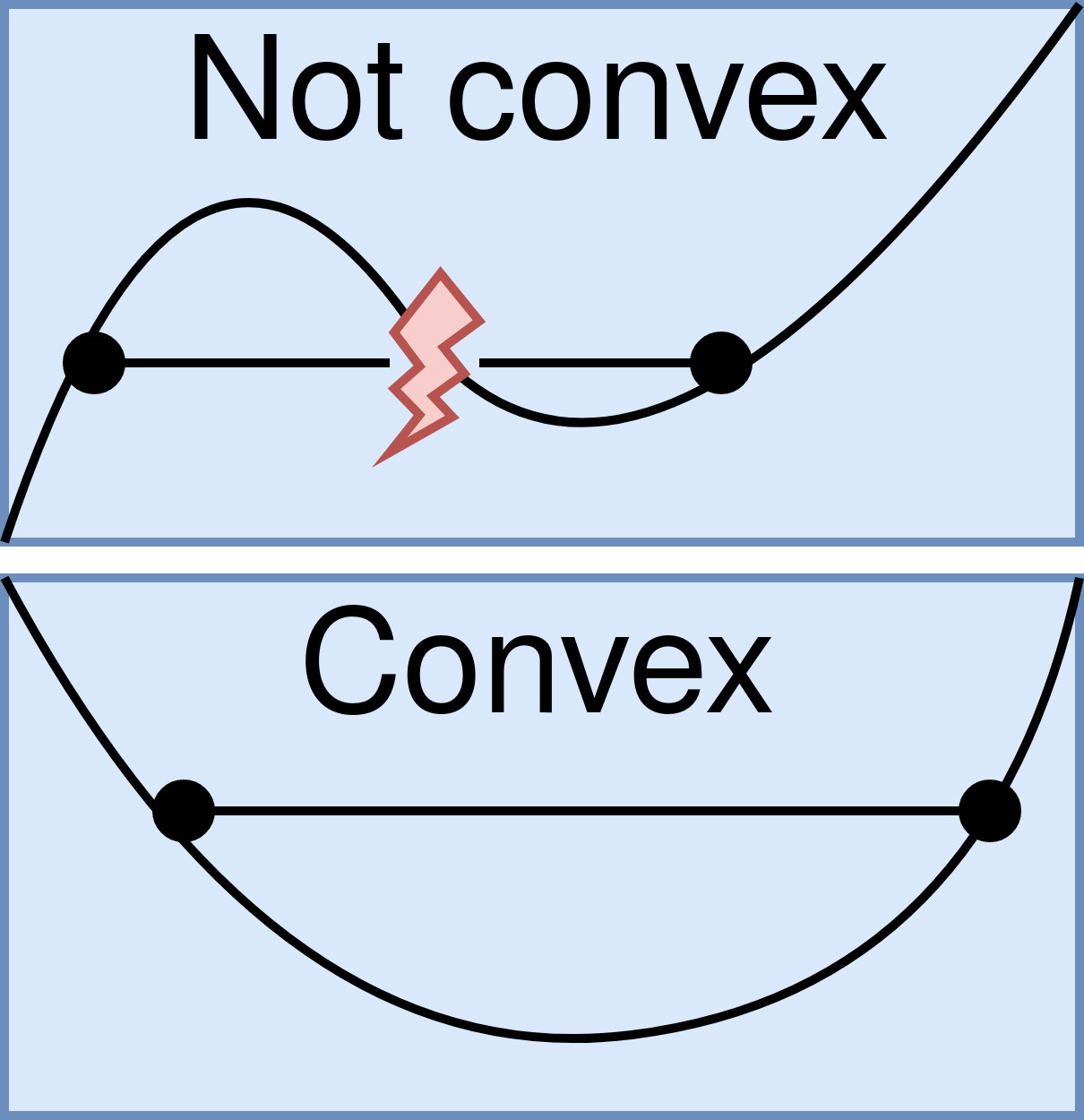
Convex Functions
In mathematics, a real-valued function is called convex if the line segment between any two points on the graph of the function lies above the graph between the two points. Equivalently, a function is convex if its epigraph (the set of points on or above the graph of the function) is a convex set. A twice-differentiable function of a single variable is convex if and only if its second derivative is nonnegative on its entire domain. Well-known examples of convex functions of a single variable include the quadratic function x^2 and the exponential function e^x. In simple terms, a convex function refers to a function whose graph is shaped like a cup \cup, while a concave function's graph is shaped like a cap \cap. Convex functions play an important role in many areas of mathematics. They are especially important in the study of optimization problems where they are distinguished by a number of convenient properties. For instance, a strictly convex function on an open set has n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sign Function
In mathematics, the sign function or signum function (from '' signum'', Latin for "sign") is an odd mathematical function that extracts the sign of a real number. In mathematical expressions the sign function is often represented as . To avoid confusion with the sine function, this function is usually called the signum function. Definition The signum function of a real number is a piecewise function which is defined as follows: \sgn x :=\begin -1 & \text x 0. \end Properties Any real number can be expressed as the product of its absolute value and its sign function: x = , x, \sgn x. It follows that whenever is not equal to 0 we have \sgn x = \frac = \frac\,. Similarly, for ''any'' real number , , x, = x\sgn x. We can also ascertain that: \sgn x^n=(\sgn x)^n. The signum function is the derivative of the absolute value function, up to (but not including) the indeterminacy at zero. More formally, in integration theory it is a weak derivative, and in convex function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Jacques Moreau
Jean Jacques Moreau (31 July 1923 – 9 January 2014) was a French mathematician and mechanician. He normally published under the name J. J. Moreau. Moreau was born in Blaye. He received his doctorate in mathematics from the University of Paris, then became a researcher at the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique. He was appointed Professor of Mathematical Models in Physics at Poitiers University and later Professor of General Mechanics at University of Montpellier II. He was emeritus professor in the Laboratoire de Mécanique et Génie Civil, a joint research unit of the university and the CNRS. Moreau's principal works have been in non-smooth mechanics and convex analysis. He is considered one of the founders of convex analysis, where several fundamental and now classical results have his name (Moreau's lemma of the two cones, Moreau's envelopes, Moreau-Yosida's approximations, Fenchel-Moreau's theorem, etc.). He founded the Convex Analysis Group in the 1970s at Montp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |