|
StyleGAN
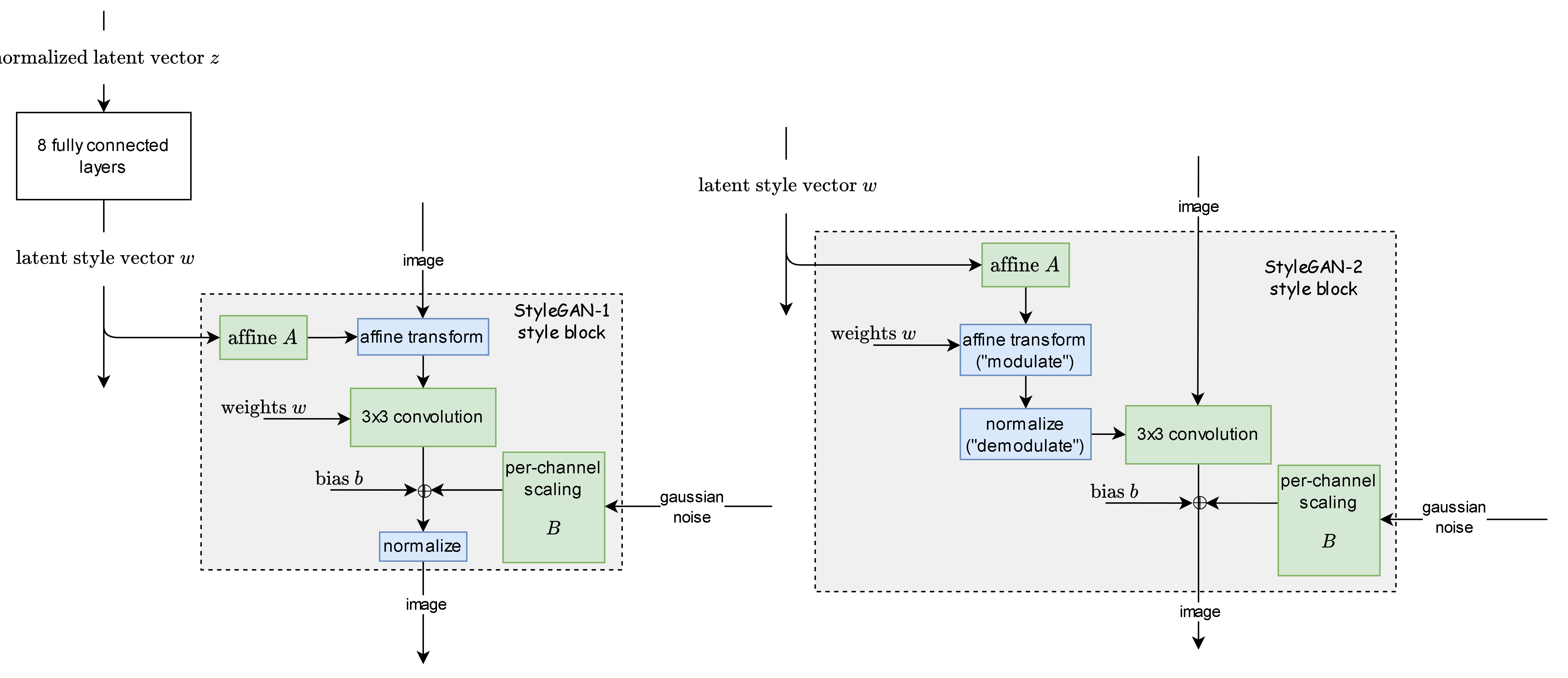
StyleGAN is a generative adversarial network (GAN) introduced by Nvidia researchers in December 2018, and made source available in February 2019. StyleGAN depends on Nvidia's CUDA software, GPUs, and Google's TensorFlow, or Meta AI's PyTorch, which supersedes TensorFlow as the official implementation library in later StyleGAN versions. The second version of StyleGAN, called StyleGAN2, was published on February 5, 2020. It removes some of the characteristic artifacts and improves the image quality. Nvidia introduced StyleGAN3, described as an "alias-free" version, on June 23, 2021, and made source available on October 12, 2021. History In December 2018, Nvidia researchers distributed a preprint with accompanying software introducing StyleGAN, a GAN for producing an unlimited number of (often convincing) portraits of fake human faces. StyleGAN was able to run on Nvidia's commodity GPU processors. In February 2019, Uber engineer Phillip Wang used the software to create ''This P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Adversarial Network
A generative adversarial network (GAN) is a class of machine learning frameworks designed by Ian Goodfellow and his colleagues in June 2014. Two neural networks contest with each other in the form of a zero-sum game, where one agent's gain is another agent's loss. Given a training set, this technique learns to generate new data with the same statistics as the training set. For example, a GAN trained on photographs can generate new photographs that look at least superficially authentic to human observers, having many realistic characteristics. Though originally proposed as a form of generative model for unsupervised learning, GANs have also proved useful for semi-supervised learning, fully supervised learning, and reinforcement learning. The core idea of a GAN is based on the "indirect" training through the discriminator, another neural network that can tell how "realistic" the input seems, which itself is also being updated dynamically. This means that the generator is not trai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Adversarial Network
A generative adversarial network (GAN) is a class of machine learning frameworks designed by Ian Goodfellow and his colleagues in June 2014. Two neural networks contest with each other in the form of a zero-sum game, where one agent's gain is another agent's loss. Given a training set, this technique learns to generate new data with the same statistics as the training set. For example, a GAN trained on photographs can generate new photographs that look at least superficially authentic to human observers, having many realistic characteristics. Though originally proposed as a form of generative model for unsupervised learning, GANs have also proved useful for semi-supervised learning, fully supervised learning, and reinforcement learning. The core idea of a GAN is based on the "indirect" training through the discriminator, another neural network that can tell how "realistic" the input seems, which itself is also being updated dynamically. This means that the generator is not trai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Image Synthesis
Human image synthesis is technology that can be applied to make believable and even photorealistic renditions of human-likenesses, moving or still. It has effectively existed since the early 2000s. Many films using computer generated imagery have featured synthetic images of human-like characters digitally composited onto the real or other simulated film material. Towards the end of the 2010s deep learning artificial intelligence has been applied to synthesize images and video that look like humans, without need for human assistance, once the training phase has been completed, whereas the old school 7D-route required massive amounts of human work. Timeline of human image synthesis * In 1971 Henri Gouraud made the first CG geometry capture and representation of a human face. Modeling was his wife Sylvie Gouraud. The 3D model was a simple wire-frame model and he applied the Gouraud shader he is most known for to produce the first known representation of human-likeness on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Image Synthesis
Human image synthesis is technology that can be applied to make believable and even photorealistic renditions of human-likenesses, moving or still. It has effectively existed since the early 2000s. Many films using computer generated imagery have featured synthetic images of human-like characters digitally composited onto the real or other simulated film material. Towards the end of the 2010s deep learning artificial intelligence has been applied to synthesize images and video that look like humans, without need for human assistance, once the training phase has been completed, whereas the old school 7D-route required massive amounts of human work. Timeline of human image synthesis * In 1971 Henri Gouraud made the first CG geometry capture and representation of a human face. Modeling was his wife Sylvie Gouraud. The 3D model was a simple wire-frame model and he applied the Gouraud shader he is most known for to produce the first known representation of human-likeness on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woman 1
A woman is an adult female human. Prior to adulthood, a female human is referred to as a girl (a female child or adolescent). The plural ''women'' is sometimes used in certain phrases such as "women's rights" to denote female humans regardless of age. Typically, women inherit a pair of X chromosomes, one from each parent, and are capable of pregnancy and giving birth from puberty until menopause. More generally, sex differentiation of the female fetus is governed by the lack of a present, or functioning, SRY-gene on either one of the respective sex chromosomes. Female anatomy is distinguished from male anatomy by the female reproductive system, which includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and vulva. A fully developed woman generally has a wider pelvis, broader hips, and larger breasts than an adult man. Women have significantly less facial and other body hair, have a higher body fat composition, and are on average shorter and less muscular than men. Througho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Graphics
Computer graphics deals with generating images with the aid of computers. Today, computer graphics is a core technology in digital photography, film, video games, cell phone and computer displays, and many specialized applications. A great deal of specialized hardware and software has been developed, with the displays of most devices being driven by computer graphics hardware. It is a vast and recently developed area of computer science. The phrase was coined in 1960 by computer graphics researchers Verne Hudson and William Fetter of Boeing. It is often abbreviated as CG, or typically in the context of film as computer generated imagery (CGI). The non-artistic aspects of computer graphics are the subject of computer science research. Some topics in computer graphics include user interface design, sprite graphics, rendering, ray tracing, geometry processing, computer animation, vector graphics, 3D modeling, shaders, GPU design, implicit surfaces, visualization, scientific c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Learning Software Applications
Deep or The Deep may refer to: Places United States * Deep Creek (Appomattox River tributary), Virginia * Deep Creek (Great Salt Lake), Idaho and Utah * Deep Creek (Mahantango Creek tributary), Pennsylvania * Deep Creek (Mojave River tributary), California * Deep Creek (Pine Creek tributary), Pennsylvania * Deep Creek (Soque River tributary), Georgia * Deep Creek (Texas), a tributary of the Colorado River * Deep Creek (Washington), a tributary of the Spokane River * Deep River (Indiana), a tributary of the Little Calumet River * Deep River (Iowa), a minor tributary of the English River * Deep River (North Carolina) * Deep River (Washington), a minor tributary of the Columbia River * Deep Voll Brook, New Jersey, also known as Deep Brook Elsewhere * Deep Creek (Bahamas) * Deep Creek (Melbourne, Victoria), Australia, a tributary of the Maribyrnong River * Deep River (Western Australia) People * Deep (given name) * Deep (rapper), Punjabi rapper from Houston, Texas * Ravi Deep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filter (signal Processing)
In signal processing, a filter is a device or process that removes some unwanted components or features from a signal. Filtering is a class of signal processing, the defining feature of filters being the complete or partial suppression of some aspect of the signal. Most often, this means removing some frequencies or frequency bands. However, filters do not exclusively act in the frequency domain; especially in the field of image processing many other targets for filtering exist. Correlations can be removed for certain frequency components and not for others without having to act in the frequency domain. Filters are widely used in electronics and telecommunication, in radio, television, audio recording, radar, control systems, music synthesis, image processing, and computer graphics. There are many different bases of classifying filters and these overlap in many different ways; there is no simple hierarchical classification. Filters may be: *non-linear or linear *time-variant or t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faithful Representation
In mathematics, especially in an area of abstract algebra known as representation theory, a faithful representation ρ of a group on a vector space is a linear representation in which different elements of are represented by distinct linear mappings . In more abstract language, this means that the group homomorphism :\rho: G\to GL(V) is injective (or one-to-one). ''Caveat:'' While representations of over a field are ''de facto'' the same as -modules (with denoting the group algebra of the group ), a faithful representation of is not necessarily a faithful module for the group algebra. In fact each faithful -module is a faithful representation of , but the converse does not hold. Consider for example the natural representation of the symmetric group in dimensions by permutation matrices, which is certainly faithful. Here the order of the group is while the matrices form a vector space of dimension . As soon as is at least 4, dimension counting means that some linear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-pass Filter
A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a selected cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The exact frequency response of the filter depends on the filter design. The filter is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble-cut filter in audio applications. A low-pass filter is the complement of a high-pass filter. In optics, high-pass and low-pass may have different meanings, depending on whether referring to frequency or wavelength of light, since these variables are inversely related. High-pass frequency filters would act as low-pass wavelength filters, and vice versa. For this reason it is a good practice to refer to wavelength filters as ''short-pass'' and ''long-pass'' to avoid confusion, which would correspond to ''high-pass'' and ''low-pass'' frequencies. Low-pass filters exist in many different forms, including electronic circuits such as a hiss filter used in audio, anti-aliasing fil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyquist–Shannon Sampling Theorem
The Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem is a theorem in the field of signal processing which serves as a fundamental bridge between continuous-time signals and discrete-time signals. It establishes a sufficient condition for a sample rate that permits a discrete sequence of ''samples'' to capture all the information from a continuous-time signal of finite bandwidth. Strictly speaking, the theorem only applies to a class of mathematical functions having a Fourier transform that is zero outside of a finite region of frequencies. Intuitively we expect that when one reduces a continuous function to a discrete sequence and interpolates back to a continuous function, the fidelity of the result depends on the density (or sample rate) of the original samples. The sampling theorem introduces the concept of a sample rate that is sufficient for perfect fidelity for the class of functions that are band-limited to a given bandwidth, such that no actual information is lost in the sampling proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gramian Matrix
In linear algebra, the Gram matrix (or Gramian matrix, Gramian) of a set of vectors v_1,\dots, v_n in an inner product space is the Hermitian matrix of inner products, whose entries are given by the inner product G_ = \left\langle v_i, v_j \right\rangle., p.441, Theorem 7.2.10 If the vectors v_1,\dots, v_n are the columns of matrix X then the Gram matrix is X^* X in the general case that the vector coordinates are complex numbers, which simplifies to X^\top X for the case that the vector coordinates are real numbers. An important application is to compute linear independence: a set of vectors are linearly independent if and only if the Gram determinant (the determinant of the Gram matrix) is non-zero. It is named after Jørgen Pedersen Gram. Examples For finite-dimensional real vectors in \mathbb^n with the usual Euclidean dot product, the Gram matrix is G = V^\top V, where V is a matrix whose columns are the vectors v_k and V^\top is its transpose whose rows are the vectors v_k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
