|
Study Of Animal Locomotion
The study of animal locomotion is a branch of biology that investigates and quantifies how animals move. Kinematics Kinematics is the study of how objects move, whether they are mechanical or living. In animal locomotion, kinematics is used to describe the motion of the body and limbs of an animal. The goal is ultimately to understand how the movement of individual limbs relates to the overall movement of an animal within its environment. Below highlights the key kinematic parameters used to quantify body and limb movement for different modes of animal locomotion. Quantifying locomotion Walking Legged locomotion is a dominant form of terrestrial locomotion, the movement on land. The motion of limbs is quantified by intralimb and interlimb kinematic parameters. Intralimb kinematic parameters capture movement aspects of an individual limb, whereas, interlimb kinematic parameters characterize the coordination across limbs. Interlimb kinematic parameters are also referred to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Locomotion
Animal locomotion, in ethology, is any of a variety of methods that animal (biology), animals use to move from one place to another. Some modes of locomotion are (initially) self-propelled, e.g., running, swimming, jumping, flying, hopping, soaring and gliding. There are also many animal species that depend on their environment for transportation, a type of mobility called Passive locomotion in animals, passive locomotion, e.g., sailing (some jellyfish), Ballooning (spider), kiting (spiders), rolling (some beetles and spiders) or riding other animals (phoresis (biology), phoresis). Animals move for a variety of reasons, such as to find Foraging, food, a Mating system, mate, a suitable microhabitat, or to Escape response, escape predators. For many animals, the ability to move is essential for survival and, as a result, natural selection has shaped the locomotion methods and mechanisms used by moving organisms. For example, Animal migration, migratory animals that travel vast dista ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treadmills
A treadmill is a device generally used for walking, running, or climbing while staying in the same place. Treadmills were introduced before the development of powered machines to harness the power of animals or humans to do work, often a type of mill operated by a person or animal treading the steps of a treadwheel to grind grain. In later times, treadmills were used as punishment devices for people sentenced to hard labor in prisons. The terms ''treadmill'' and ''treadwheel'' were used interchangeably for the power and punishment mechanisms. More recently, treadmills have instead been used as exercise machines for running or walking in one place. Rather than the user powering a mill, the device provides a moving platform with a wide conveyor belt driven by an electric motor or a flywheel. The belt moves to the rear, requiring the user to walk or run at a speed matching the belt. The rate at which the belt moves is the rate of walking or running. Thus, the speed of running may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nervous System
In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes that impact the body, then works in tandem with the endocrine system to respond to such events. Nervous tissue first arose in wormlike organisms about 550 to 600 million years ago. In vertebrates it consists of two main parts, the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. The PNS consists mainly of nerves, which are enclosed bundles of the long fibers or axons, that connect the CNS to every other part of the body. Nerves that transmit signals from the brain are called motor nerves or '' efferent'' nerves, while those nerves that transmit information from the body to the CNS are called sensory nerves or '' afferent''. Spinal nerves are mixed nerves that serve both fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy () is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope () allows a physician to see the internal structure and function of a patient, so that the pumping action of the heart or the motion of swallowing, for example, can be watched. This is useful for both diagnosis and therapy and occurs in general radiology, interventional radiology, and image-guided surgery. In its simplest form, a fluoroscope consists of an X-ray source and a fluorescent screen, between which a patient is placed. However, since the 1950s most fluoroscopes have included X-ray image intensifiers and cameras as well, to improve the image's visibility and make it available on a remote display screen. For many decades, fluoroscopy tended to produce live pictures that were not recorded, but since the 1960s, as technology improved, recording and playback became the norm. Fluoroscopy is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonomicrometry
Sonomicrometry is a technique of measuring the distance between piezoelectric crystals based on the speed of acoustic signals through the medium they are embedded in. Typically, the crystals will be coated with an epoxy 'lens' and placed into the material facing each other. An electrical signal sent to either crystal will be transformed into sound, which passes through the medium, eventually reaching the other crystal, which converts the sound into electricity, detected by a receiver. From the time taken for sound to move between the crystals and the speed of sound in the medium, the distance between the crystals can be calculated. History Sonomicrometry was originally applied in the study of cardiac function in research animals by Dean Franklin in 1956, and was quickly adopted by biologists working in biomechanics as well as other physiological organ systems and structures (gastro-intestinal, uro-genital and musculo-skeletal). Medical device companies also use sonomicrometry to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optogenetics
Optogenetics is a biological technique to control the activity of neurons or other cell types with light. This is achieved by expression of light-sensitive ion channels, pumps or enzymes specifically in the target cells. On the level of individual cells, light-activated enzymes and transcription factors allow precise control of biochemical signaling pathways. In systems neuroscience, the ability to control the activity of a genetically defined set of neurons has been used to understand their contribution to decision making, learning, fear memory, mating, addiction, feeding, and locomotion. In a first medical application of optogenetic technology, vision was partially restored in a blind patient. Optogenetic techniques have also been introduced to map the functional connectivity of the brain''.'' By altering the activity of genetically labelled neurons with light and using imaging and electrophysiology techniques to record the activity of other cells, researchers can identify ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an instrument called an electromyograph to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyograph detects the electric potential generated by muscle cells when these cells are electrically or neurologically activated. The signals can be analyzed to detect abnormalities, activation level, or recruitment order, or to analyze the biomechanics of human or animal movement. Needle EMG is an electrodiagnostic medicine technique commonly used by neurologists. Surface EMG is a non-medical procedure used to assess muscle activation by several professionals, including physiotherapists, kinesiologists and biomedical engineers. In Computer Science, EMG is also used as middleware in gesture recognition towards allowing the input of physical action to a computer as a form of human-computer interaction. Clinical uses EMG testing has a variety of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Force Platform
Force platforms or force plates are measuring instruments that measure the ground reaction forces generated by a body standing on or moving across them, to quantify balance, gait and other parameters of biomechanics. Most common areas of application are medicine and sports. Operation The simplest force platform is a plate with a single pedestal, instrumented as a load cell. Better designs have a pair of rectangular plates, although triangular can also work, one over another with load cells or triaxial force transducers between them at the corners. Like single-force platforms, dual-force platforms can be used to assess performance in double leg tests and strength and power asymmetries in unilateral jump and isometric tests. However, they also provide an additional level of intelligence on neuromuscular status by evaluating the force distribution between limbs during double-limb tests, revealing critical information on strength asymmetries and compensatory strategies. The simpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternating Tripod Gait
Alternating may refer to: Mathematics * Alternating algebra, an algebra in which odd-grade elements square to zero * Alternating form, a function formula in algebra * Alternating group, the group of even permutations of a finite set * Alternating knot, a knot or link diagram for which the crossings alternate under, over, under, over, as one travels along each component of the link * Alternating map, a multilinear map that is zero whenever any two of its arguments are equal * Alternating operator, a multilinear map in algebra * Alternating permutation, a type of permutation studied in combinatorics * Alternating series, an infinite series in which the signs of the general terms alternate between positive and negative Electronics * Alternating current, a flow of electric charge that periodically reverses direction Other * Alternating turns, the process by which people in a conversation decide who is to speak next See also * Alternate bass * Alternative (other) Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
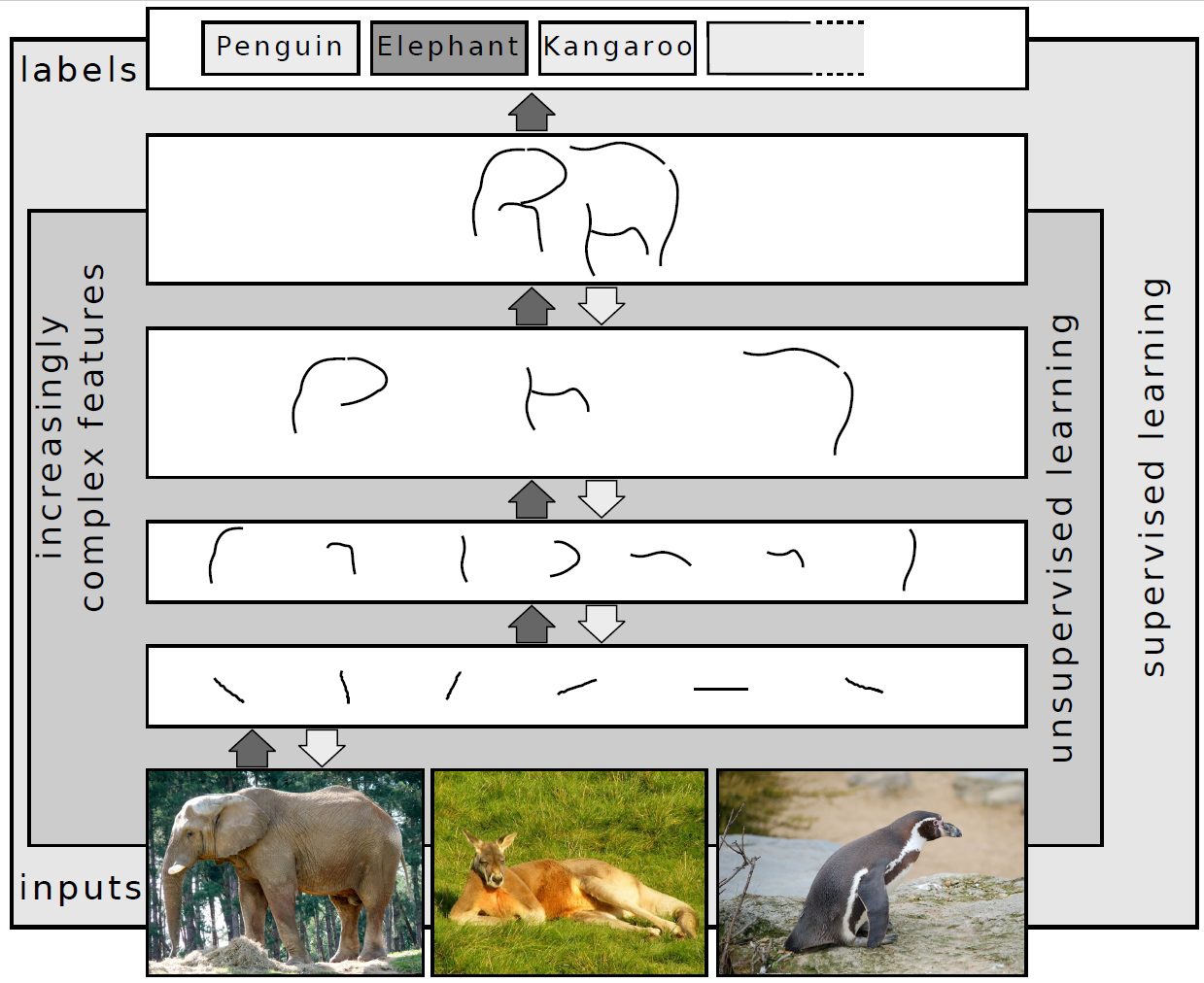
Deep Learning
Deep learning (also known as deep structured learning) is part of a broader family of machine learning methods based on artificial neural networks with representation learning. Learning can be supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised. Deep-learning architectures such as deep neural networks, deep belief networks, deep reinforcement learning, recurrent neural networks, convolutional neural networks and Transformers have been applied to fields including computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing, machine translation, bioinformatics, drug design, medical image analysis, Climatology, climate science, material inspection and board game programs, where they have produced results comparable to and in some cases surpassing human expert performance. Artificial neural networks (ANNs) were inspired by information processing and distributed communication nodes in biological systems. ANNs have various differences from biological brains. Specifically, artificial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pose Estimation
3D pose estimation is a process of predicting the transformation of an object from a user-defined reference pose, given an image or a 3D scan. It arises in computer vision or robotics where the pose or transformation of an object can be used for alignment of a computer-aided design models, identification, grasping, or manipulation of the object. The image data from which the pose of an object is determined can be either a single image, a stereo image pair, or an image sequence where, typically, the camera is moving with a known velocity. The objects which are considered can be rather general, including a living being or body parts, e.g., a head or hands. The methods which are used for determining the pose of an object, however, are usually specific for a class of objects and cannot generally be expected to work well for other types of objects. From an uncalibrated 2D camera It is possible to estimate the 3D rotation and translation of a 3D object from a single 2D photo, if a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |