|
String Quartet No. 13 (Beethoven)
The String Quartet No. 13 in B major, Op. 130, by Ludwig van Beethoven was completed (in its final form) in November 1826. The number traditionally assigned to it is based on the order of its publication; it is actually Beethoven's 14th quartet in order of composition. It was premiered (in its original form) in March 1826 by the Schuppanzigh Quartet and dedicated to Nikolai Galitzin on its publication in 1827. Movements Beethoven originally wrote the work in six movements, lasting 42–50 minutes, as follows: (Nomenclature: "danza tedesca" means "German dance", "Cavatina" a short and simple song, and "Große Fuge" means "Great Fugue" or "Grand Fugue".) The work is unusual among quartets in having six movements. They follow the pattern of movements seen in the Ninth Symphony and occasionally elsewhere in Beethoven's work (opening, dance movement, slow movement, finale), except that the middle part of the cycle is repeated: opening, dance movement, slow movement, dance movemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late String Quartets (Beethoven)
Ludwig van Beethoven's late string quartets are: :*Opus 127: String Quartet No. 12 (Beethoven), String Quartet No. 12 in E major (1825) :*Opus 130: String Quartet No. 13 (Beethoven), String Quartet No. 13 in B major (1825) :*Opus 131: String Quartet No. 14 (Beethoven), String Quartet No. 14 in C minor (1826) :*Opus 132: String Quartet No. 15 (Beethoven), String Quartet No. 15 in A minor (1825) :*Opus 133: ''Große Fuge'' in B major (1825; originally the finale to Op. 130; it also exists in a piano four-hands transcription, Op. 134) :*Opus 135: String Quartet No. 16 (Beethoven), String Quartet No. 16 in F major (1826) These six works are Beethoven's last major completed compositions. Although dismissed by musicians and audiences of Beethoven's day, they are now widely considered to be among the greatest musical compositions of all time, and have inspired many later composers. Overview Prince Nikolai Borisovich Galitzine, Nikolai Galitzine commissioned the first three quartets (12, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voyager Golden Record
The Voyager Golden Records are two phonograph records that were included aboard both Voyager spacecraft launched in 1977. The records contain sounds and images selected to portray the diversity of life and culture on Earth, and are intended for any intelligent extraterrestrial life form who may find them. The records are a time capsule. Although neither Voyager spacecraft is heading toward any particular star, ''Voyager 1'' will pass within 1.6 light-years' distance of the star Gliese 445, currently in the constellation Camelopardalis, in about 40,000 years. Carl Sagan noted that "The spacecraft will be encountered and the record played only if there are advanced space-faring civilizations in interstellar space, but the launching of this 'bottle' into the cosmic 'ocean' says something very hopeful about life on this planet." Background The ''Voyager 1'' probe is currently the farthest human-made object from Earth. Both ''Voyager 1'' and ''Voyager 2'' have reached interste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moravian Museum
Moravian is the adjective form of the Czech Republic region of Moravia, and refers to people of ancestry from Moravia. Moravian may also refer to: * a member or adherent of the Moravian Church, one of the oldest Protestant denominations * Moravia, the region * Moravians, people from Moravia * Moravian dialects, dialects of Czech spoken in Moravia, sometimes considered a distinct Moravian language * Moravané ("The Moravians"), a political party in the Czech Republic favouring the autonomy or independence of Moravia * Moravian Academy, a private school in Bethlehem, Pennsylvania * Moravian University, a private university in Bethlehem, Pennsylvania * an inhabitant of the Scottish Moray, especially the historic Mormaer of Moray See also * Moravia (other) * Moravian Serbia, one of the Serbian states that emerged from the collapse of the Serbian Empire in the 14th century * Moravian Wallachia, a cultural region in the eastern part of the Czech Republic * Moravian Slovakia, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gestapo
The (), abbreviated Gestapo (; ), was the official secret police of Nazi Germany and in German-occupied Europe. The force was created by Hermann Göring in 1933 by combining the various political police agencies of Prussia into one organisation. On 20 April 1934, oversight of the Gestapo passed to the head of the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS), Heinrich Himmler, who was also appointed Chief of German Police by Hitler in 1936. Instead of being exclusively a Prussian state agency, the Gestapo became a national one as a sub-office of the (SiPo; Security Police). From 27 September 1939, it was administered by the Reich Security Main Office (RSHA). It became known as (Dept) 4 of the RSHA and was considered a sister organisation to the (SD; Security Service). During World War II, the Gestapo played a key role in the Holocaust. After the war ended, the Gestapo was declared a criminal organisation by the International Military Tribunal (IMT) at the Nuremberg trials. History After Adol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occupation Of Czechoslovakia (1938–1945)
The military occupation of Czechoslovakia by Nazi Germany began with the German annexation of the Sudetenland in 1938, continued with the creation of the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia, and by the end of 1944 extended to all parts of Czechoslovakia. Following the ''Anschluss'' of Austria to Nazi Germany in March 1938 and after he had obtained the Munich Agreement in September 1938, Adolf Hitler annexed the ethnic Germans living in Czech regions. The loss of Sudetenland was detrimental to the defense of Czechoslovakia as the extensive Czechoslovak border fortifications were also located in the same area. As a consequence, the incorporation of the Sudetenland into Germany that began on 1 October 1938 left the rest of Czechoslovakia weak. Moreover, a small northeastern part of the borderland region known as Zaolzie was occupied and annexed to Poland ostensibly to "protect" the local ethnic Polish community and as a result of previous territorial claims ( Czech-Polish dispu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czech Jewish
The history of the Jews in the Czech lands, which include the modern Czech Republic as well as Bohemia, Czech Silesia and Moravia, goes back many centuries. There is evidence that Jews have lived in Moravia and Bohemia since as early as the 10th century. As of 2005, there were approximately 4,000 Jews living in the Czech Republic. Jewish Prague Jews are believed to have settled in Prague as early as the 10th century. The 16th century was a golden age for Jews of Prague, Jewry in Prague. One of the famous Jewish scholars of the time was Judah Loew ben Bezalel known as the Maharal, who served as a leading rabbi in Prague for most of his life. He is buried at the Old Jewish Cemetery, Prague, Old Jewish Cemetery in Josefov (Prague), Josefov, and his grave with its tombstone intact, can still be visited. According to a popular legend, it is said that the body of Golem of Prague, Golem (created by the Maharal) lies in the attic of the Old New Synagogue where the genizah of Prague's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Holz (violinist)
Karl Holz (1798 – 9 November 1858) was an Austrian violinist. He played second violin in Ignaz Schuppanzigh's string quartet and served as secretary to Ludwig van Beethoven during the last few years of the composer's life. Early career In Vienna in 1819, the violinist Joseph Böhm assembled a new string quartet, and Holz – a civil servant in the Austrian government by profession – joined as second violin. In 1823, the violinist Ignaz Schuppanzigh returned to the city after several years away. He had formed a string quartet in Vienna in the 1790s; Schuppanzigh was an old friend of Beethoven's and had given the first performance of the composer's String Quartets Nos. 1–6, Op. 18 (Beethoven), first six string quartets Op. 18. Böhm's quartet disbanded, and Holz joined Schuppanzigh's reformed quartet. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M*A*S*H (season 6)
The sixth season of ''M*A*S*H'' aired Tuesdays at 9:00-9:30PM from September 20, 1977 to January 24, 1978 and Mondays at the same time from January 30 to March 27, 1978. Cast Episodes Notes External links List of ''M*A*S*H'' (season 6) episodesat the Internet Movie Database IMDb (an abbreviation of Internet Movie Database) is an online database of information related to films, television series, home videos, video games, and streaming content online – including cast, production crew and personal biographies, ... {{DEFAULTSORT:MASH Episodes (Season 6) 1977 American television seasons 1978 American television seasons MASH 06 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
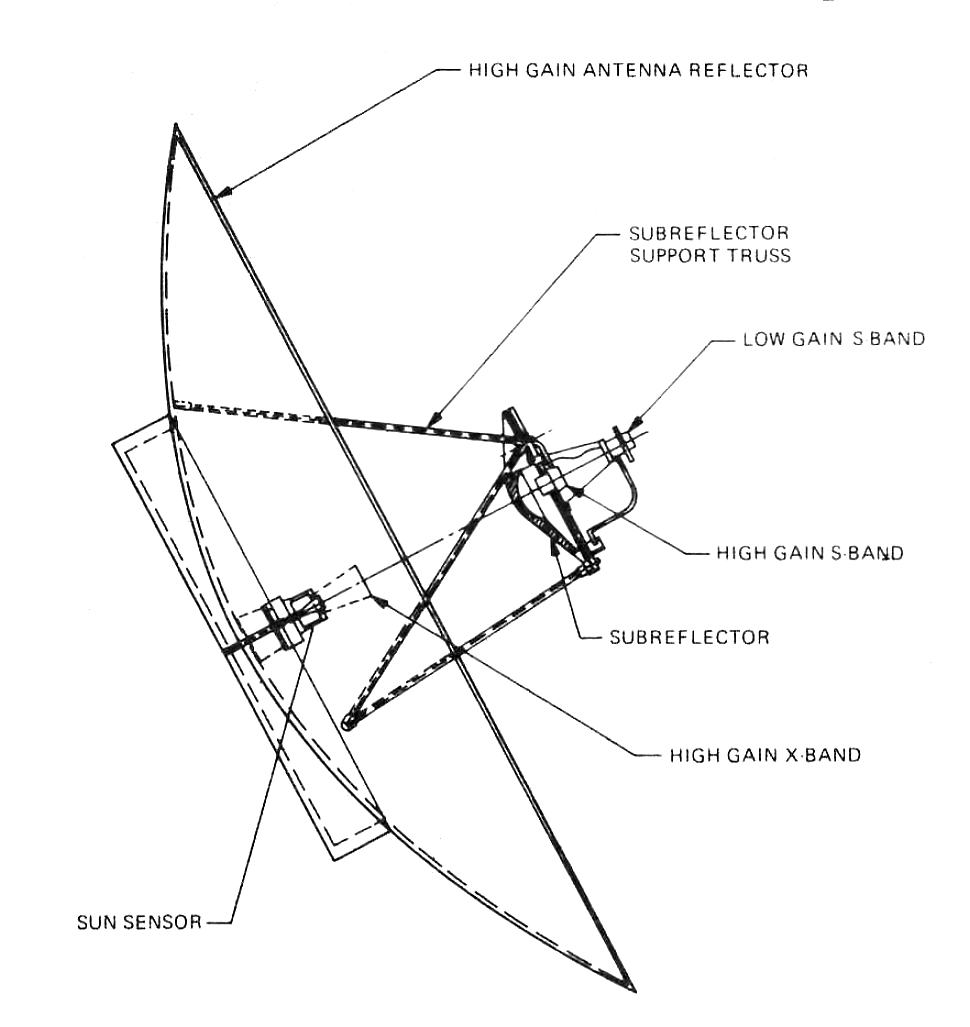
Voyager 2
''Voyager 2'' is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, to study the outer planets and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. As a part of the Voyager program, it was launched 16 days before its twin, ''Voyager 1'', on a trajectory that took longer to reach gas giants Jupiter and Saturn but enabled further encounters with ice giants Uranus and Neptune. ''Voyager 2'' remains the only spacecraft to have visited either of the ice giant planets. ''Voyager 2'' was the fourth of five spacecraft to achieve Solar escape velocity, which allowed it to leave the Solar System. ''Voyager 2'' successfully fulfilled its primary mission of visiting the Jovian system in 1979, the Saturnian system in 1981, Uranian system in 1986, and the Neptunian system in 1989. The spacecraft is now in its extended mission of studying interstellar space. It has been operating for as of ; , it has reached a distance of from Earth. The probe entered interstellar space on November 5, 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voyager 1
''Voyager 1'' is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. Launched 16 days after its twin ''Voyager 2'', ''Voyager 1'' has been operating for as of . It communicates through NASA's Deep Space Network to receive routine commands and to transmit data to Earth. Real-time distance and velocity data is provided by NASA and JPL. At a distance of from Earth , it is the most distant human-made object from Earth. The probe made flybys of Jupiter, Saturn, and Saturn's largest moon, Titan. NASA had a choice of either doing a Pluto or Titan flyby; exploration of the moon took priority because it was known to have a substantial atmosphere. ''Voyager 1'' studied the weather, magnetic fields, and rings of the two gas giants and was the first probe to provide detailed images of their moons. As part of the Voyager program and like its sister craft ''Voyager ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blind Willie Johnson
Blind Willie Johnson (January 25, 1897 – September 18, 1945) was an American gospel blues singer, guitarist and evangelist. His landmark recordings completed between 1927 and 1930—thirty songs in total—display a combination of powerful "chest voice" singing, slide guitar skills, and originality that has influenced generations of musicians. Even though Johnson's records sold well, as a street performer and preacher, he had little wealth in his lifetime. His life was poorly documented, but over time, music historians such as Samuel Charters have uncovered more about Johnson and his five recording sessions. A revival of interest in Johnson's music began in the 1960s, following his inclusion on Harry Smith's '' Anthology of American Folk Music'', and by the efforts of the blues guitarist Reverend Gary Davis. Along with Davis, he has since been considered the dominant player of " holy blues" music, which conveyed religious themes in a blues idiom and often with the genre's sty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dark Was The Night, Cold Was The Ground
"Dark Was the Night, Cold Was the Ground"Because documentation is scarce in early recordings, the title of the song appears differently in many sources. It is often called "Dark Was the Night" or punctuated as "Dark Was the Night (Cold Was the Ground)". is a gospel blues song written and performed by American musician Blind Willie Johnson and recorded in 1927. The song is primarily an instrumental featuring Johnson's self-taught bottleneck slide guitar and picking style accompanied by his vocalizations of humming and moaning. It has the distinction of being one of 27 samples of music included on the Voyager Golden Record, launched into space in 1977 to represent the diversity of life on Earth. The song has been highly praised and covered by numerous musicians and is featured on the soundtracks of several films. Background Born in 1897, Johnson taught himself how to play guitar and dedicated his life to blues and gospel music, playing for people on street corners and in mission ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |