|
Strabismus Surgery
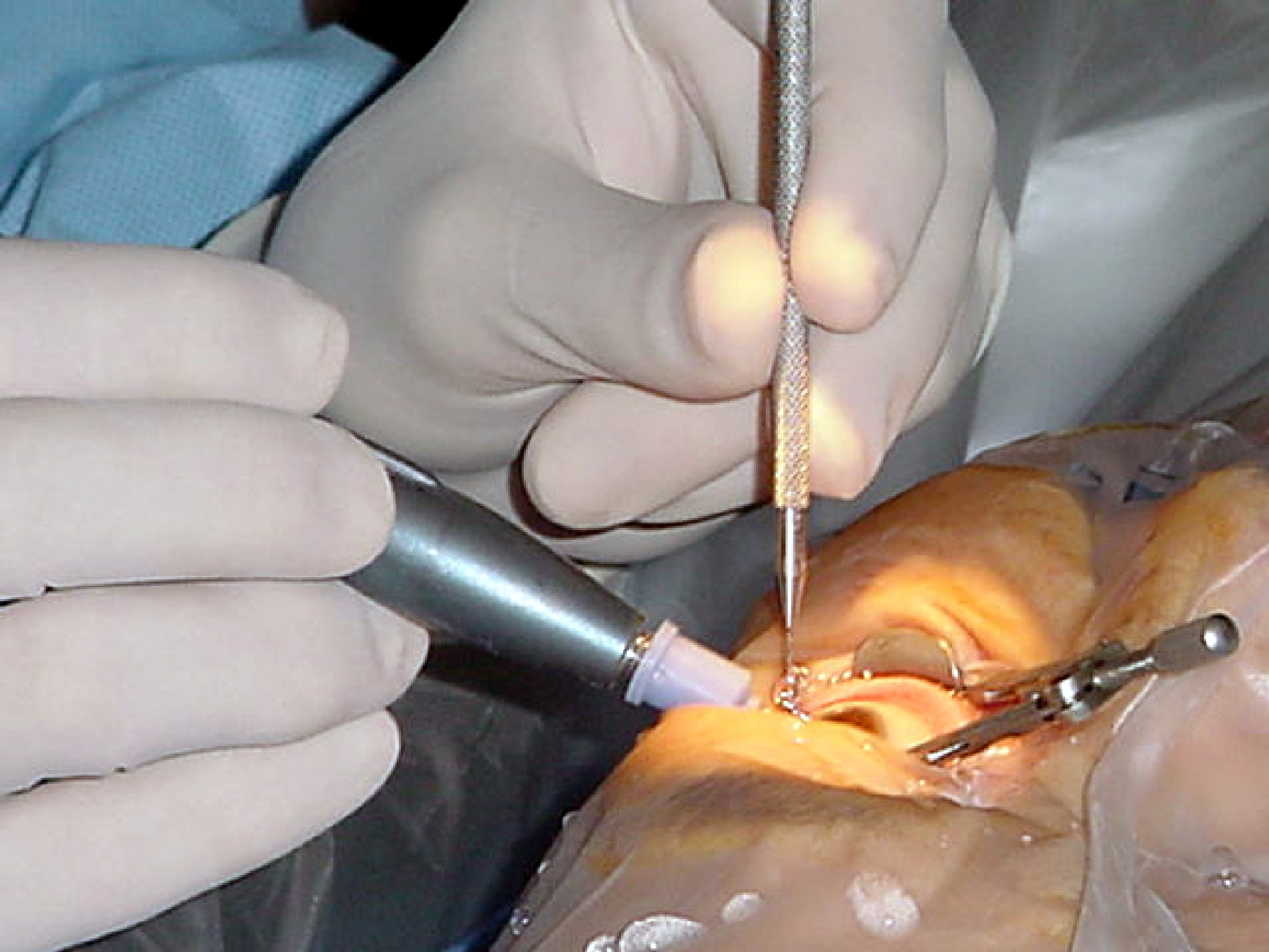
Strabismus surgery (also: ''extraocular muscle surgery'', ''eye muscle surgery'', or ''eye alignment surgery'') is surgery on the extraocular muscles to correct strabismus, the misalignment of the eyes. Strabismus surgery is a one-day procedure that is usually performed under general anesthesia most commonly by either a neuro- or pediatric ophthalmologist. The patient spends only a few hours in the hospital with minimal preoperative preparation. After surgery, the patient should expect soreness and redness but is generally free to return home. History The earliest successful strabismus surgery intervention is known to have been performed on 26 October 1839 by Johann Friedrich Dieffenbach on a 7-year-old esotropic child; a few earlier attempts had been performed in 1818 by William Gibson of Baltimore, a general surgeon and professor at the University of Maryland. The idea of treating strabismus by cutting some of the extraocular muscle fibers was published in American newspapers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pathological condition such as a disease or injury, to help improve bodily function, appearance, or to repair unwanted ruptured areas. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure, operation, or simply "surgery". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments or surgical nurse. The person or subject on which the surgery is performed can be a person or an animal. A surgeon is a person who practices surgery and a surgeon's assistant is a person who practices surgical assistance. A surgical team is made up of the surgeon, the surgeon's assistant, an anaesthetist, a circulating nurse and a surgical technologist. Surgery usually spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantile Esotropia
Infantile esotropia is an ocular condition of early onset in which one or either eye turns inward. It is a specific sub-type of esotropia and has been a subject of much debate amongst ophthalmologists with regard to its naming, diagnostic features, and treatment. Presentation Historically the term 'congenital strabismus' was used to describe constant esotropias with onset between birth and six months of age. However, this term was felt to be an inadequate classification as it covered a variety of esotropias with different causes, features and prognoses. In 1988, American ophthalmologist Gunter K. Von Noorden discussed what he described as 'Essential Infantile Esotropia'. He described the condition as: "early acquired, not... congenital ..., although congenital factors may favor its development between the ages of 3 and 6 months". He identified this squint sub-type as having the following features: # Onset between birth and six months of age. # Large size (greater than 30 diop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EyeWiki
This is a list of medical wikis, collaboratively-editable websites that focus on medical information. Many of the most popular medical wikis take the form of encyclopedias, with a separate article for each medical term. Some of these websites, such as WikiDoc and Radiopaedia, are editable by anyone, while others, such as Ganfyd, restrict editing access to professionals. The majority of them have content available only in English. The largest and most popular general encyclopedia, Wikipedia, also hosts a significant amount of health and medical information. Open licensed Clinfowiki Clinfowiki is devoted to topics in biomedical informatics and is maintained by the Department of Medical Informatics & Clinical Epidemiology at Oregon Health and Science University. Dean F. Sittig launched the site on 27 June 2005, and Vishnu Mohan was its editor. Radiopaedia Radiopaedia is a wiki-based international collaborative radiology educational resource with reference articles, radiology im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereopsis Recovery
Stereopsis recovery, also recovery from stereoblindness, is the phenomenon of a stereoblind person gaining partial or full ability of stereo vision (stereopsis). Recovering stereo vision as far as possible has long been established as an approach to the therapeutic treatment of stereoblind patients. Treatment aims to recover stereo vision in very young children, as well as in patients who had acquired but lost their ability for stereopsis due to a medical condition. In contrast, this aim has normally not been present in the treatment of those who missed out on learning stereopsis during their first few years of life. In fact, the acquisition of binocular and stereo vision was long thought to be impossible unless the person acquired this skill during a critical period in infancy and early childhood. This hypothesis normally went unquestioned and has formed the basis for the therapeutic approaches to binocular disorders for decades. It has been put in doubt in recent years. In partic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthoptist
Orthoptics is a profession allied to the eye care profession. Orthoptists are the experts in diagnosing and treating defects in eye movements and problems with how the eyes work together, called binocular vision. These can be caused by issues with the muscles around the eyes or defects in the nerves enabling the brain to communicate with the eyes. Orthoptists are responsible for the diagnosis and non-surgical management of strabismus (cross-eyed), amblyopia (lazy eye) and eye movement disorders.International Orthoptic Association document "professional role" The word ''orthoptics'' comes from the Greek words ὀρθός ''orthos'', "straight" and ὀπτικός ''optikοs'', "relating to sight" and much of the practice of orthoptists concerns disorders of binocular vision and defects of eye movement. Orthoptists are trained professionals who specialize in orthoptic treatment, such as eye patches, eye exercises, prisms or glasses. They commonly work with paediatric patients and also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Surgery
Eye surgery, also known as ophthalmic or ocular surgery, is surgery performed on the eye or its adnexa, by an ophthalmologist or sometimes, an optometrist. Eye surgery is synonymous with ophthalmology. The eye is a very fragile organ, and requires extreme care before, during, and after a surgical procedure to minimize or prevent further damage. An expert eye surgeon is responsible for selecting the appropriate surgical procedure for the patient, and for taking the necessary safety precautions. Mentions of eye surgery can be found in several ancient texts dating back as early as 1800 BC, with cataract treatment starting in the fifth century BC. Today it continues to be a widely practiced type of surgery, with various techniques having been developed for treating eye problems. Preparation and precautions Since the eye is heavily supplied by nerves, anesthesia is essential. Local anesthesia is most commonly used. Topical anesthesia using lidocaine topical gel is often used fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oculocardiac Reflex
The oculocardiac reflex, also known as Aschner phenomenon, Aschner reflex, or Aschner–Dagnini reflex, is a decrease in pulse rate associated with traction applied to extraocular muscles and/or compression of the eyeball. The reflex is mediated by nerve connections between the ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal cranial nerve via the ciliary ganglion, and the vagus nerve of the parasympathetic nervous system. Nerve fibres from the maxillary and mandibular divisions of the trigeminal nerve have also been documented. These afferents synapse with the visceral motor nucleus of the vagus nerve, located in the reticular formation of the brain stem. The efferent portion is carried by the vagus nerve from the cardiovascular center of the medulla to the heart, of which increased stimulation leads to decreased output of the sinoatrial node. This reflex is especially sensitive in neonates and children, particularly during strabismus correction surgery. Oculocardiac reflex can be profound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitomycin C
Mitomycin C is a mitomycin that is used as a chemotherapeutic agent by virtue of its antitumour activity. Medical uses It is given intravenously to treat upper gastro-intestinal cancers (e.g. esophageal carcinoma), anal cancers, and breast cancers, as well as by bladder instillation for superficial bladder tumours. Mitomycin C has also been used topically rather than intravenously in several areas. The first is cancers, particularly bladder cancers and intraperitoneal tumours. It is now well known that a single instillation of this agent within 6 hours of bladder tumor resection can prevent recurrence. The second is in eye surgery where mitomycin C 0.02% is applied topically to prevent scarring during glaucoma filtering surgery and to prevent haze after PRK or LASIK; mitomycin C has also been shown to reduce fibrosis in strabismus surgery. The third is in esophageal and tracheal stenosis where application of mitomycin C onto the mucosa immediately following dilatation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is a pathological wound healing in which connective tissue replaces normal parenchymal tissue to the extent that it goes unchecked, leading to considerable tissue remodelling and the formation of permanent scar tissue. Repeated injuries, chronic inflammation and repair are susceptible to fibrosis where an accidental excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix components, such as the collagen is produced by fibroblasts, leading to the formation of a permanent fibrotic scar. In response to injury, this is called scarring, and if fibrosis arises from a single cell line, this is called a fibroma. Physiologically, fibrosis acts to deposit connective tissue, which can interfere with or totally inhibit the normal architecture and function of the underlying organ or tissue. Fibrosis can be used to describe the pathological state of excess deposition of fibrous tissue, as well as the process of connective tissue deposition in healing. Define ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplopia
Diplopia is the simultaneous perception of two images of a single object that may be displaced horizontally or vertically in relation to each other. Also called double vision, it is a loss of visual focus under regular conditions, and is often voluntary. However, when occurring involuntarily, it results in impaired function of the extraocular muscles, where both eyes are still functional, but they cannot turn to target the desired object. Problems with these muscles may be due to mechanical problems, disorders of the neuromuscular junction, disorders of the cranial nerves ( III, IV, and VI) that innervate the muscles, and occasionally disorders involving the supranuclear oculomotor pathways or ingestion of toxins. Diplopia can be one of the first signs of a systemic disease, particularly to a muscular or neurological process, and it may disrupt a person's balance, movement, or reading abilities. Causes Diplopia has a diverse range of ophthalmologic, infectious, autoimmune, neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binocular Vision
In biology, binocular vision is a type of vision in which an animal has two eyes capable of facing the same direction to perceive a single three-dimensional image of its surroundings. Binocular vision does not typically refer to vision where an animal has eyes on opposite sides of its head and shares no field of view between them, like in some animals. Neurological researcher Manfred Fahle has stated six specific advantages of having two eyes rather than just one: #It gives a creature a "spare eye" in case one is damaged. #It gives a wider field of view. For example, humans have a maximum horizontal field of view of approximately 190 degrees with two eyes, approximately 120 degrees of which makes up the binocular field of view (seen by both eyes) flanked by two uniocular fields (seen by only one eye) of approximately 40 degrees. #It can give stereopsis in which binocular disparity (or parallax) provided by the two eyes' different positions on the head gives precise depth per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extraocular Muscle
The extraocular muscles (extrinsic ocular muscles), are the seven extrinsic muscles of the human eye. Six of the extraocular muscles, the four recti muscles, and the superior and inferior oblique muscles, control movement of the eye and the other muscle, the levator palpebrae superioris, controls eyelid elevation. The actions of the six muscles responsible for eye movement depend on the position of the eye at the time of muscle contraction. Structure Since only a small part of the eye called the fovea provides sharp vision, the eye must move to follow a target. Eye movements must be precise and fast. This is seen in scenarios like reading, where the reader must shift gaze constantly. Although under voluntary control, most eye movement is accomplished without conscious effort. Precisely how the integration between voluntary and involuntary control of the eye occurs is a subject of continuing research."eye, human."Encyclopædia Britannica from Encyclopædia Britannica 2006 Ultim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)