|
Stops Of Various Quills
''Stops of Various Quills'' is a 1895 book written by William Dean Howells. 55 pages in length, it features 43 poems and illustrations by Howard Pyle. Overview Howells had bonded with Pyle over similar ideas about literary realism and romance in literature and Pyle suggested a professional collaboration in 1891. Several poems by Howells with Pyle's illustration were published in '' Harper's Weekly'' before being collected as part of ''Stops of Various Quills''. Henry Clarence Pitz, illustrator and Howard Pyle biographer, describes this collaborative work as "a labor of love"—where the "great kinship" that existed between author and illustrator is evident in "both text and picture." Howells and Pyle both lost children early in the year 1889; Howells, a daughter named Winifred and Pyle, a son named Sellers. Pitz relates how they "both suffered from interludes of melancholia" as a result—a term found etched in illustrations on the pages of "November" and "Question". Drawing comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Dean Howells
William Dean Howells (; March 1, 1837 – May 11, 1920) was an American realist novelist, literary critic, and playwright, nicknamed "The Dean of American Letters". He was particularly known for his tenure as editor of ''The Atlantic Monthly'', as well as for his own prolific writings, including the Christmas story "Christmas Every Day" and the novels ''The Rise of Silas Lapham'' and '' A Traveler from Altruria''. Biography Early life and family William Dean Howells was born on March 1, 1837, in Martinsville, Ohio (now known as Martins Ferry, Ohio), to William Cooper Howells and Mary Dean Howells, the second of eight children. His father was a newspaper editor and printer who moved frequently around Ohio. In 1840, the family settled in Hamilton, Ohio,Lynn, 36 where his father oversaw a Whig newspaper and followed Swedenborgianism. Their nine years there were the longest period that they stayed in one place. The family had to live frugally, although the young Howells was encou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Poetry Collections
American(s) may refer to: * American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America" ** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America ** American ancestry, people who self-identify their ancestry as "American" ** American English, the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States ** Native Americans in the United States, indigenous peoples of the United States * American, something of, from, or related to the Americas, also known as "America" ** Indigenous peoples of the Americas * American (word), for analysis and history of the meanings in various contexts Organizations * American Airlines, U.S.-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas * American Athletic Conference, an American college athletic conference * American Recordings (record label), a record label previously known as Def American * American University, in Washington, D.C. Sports teams Soccer * Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brandywine School
The Brandywine School was a style of illustration—as well as an artists colony in Wilmington, Delaware and in Chadds Ford, Pennsylvania, near the Brandywine River—both founded by artist Howard Pyle (1853–1911) at the end of the 19th century. The works produced there were widely published in adventure novels, magazines, and romances in the early 20th century. Pyle’s teachings would influence such notable illustrators as N.C. Wyeth, Maxfield Parrish, and Norman Rockwell. Pyle himself would come to be known as the "Father of American Illustration." Many works related to the Brandywine School may be seen at the Brandywine River Museum of Art, in Chadds Ford. History Pyle, one of the foremost illustrators in the United States at the time, began teaching art classes at Drexel University in 1895. However, he was dissatisfied with the confines of formal art education, and beginning in 1898, he began teaching students during the summers at the Turner Mill in Chadds Ford. The mill, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silas Weir Mitchell (physician)
Silas Weir Mitchell (February 15, 1829 – January 4, 1914) was an American physician, scientist, novelist, and poet. He is considered the father of medical neurology, and he discovered causalgia (complex regional pain syndrome) and erythromelalgia, and pioneered the rest cure. Biography Silas Weir Mitchell was born on February 15, 1829, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, to John Kearsley Mitchell and Sarah Henry Mitchell. He studied at Philadelphia's renowned University of Pennsylvania and later earned the degree of MD at the city's Jefferson Medical College in 1850. During the Civil War, he was director of treatment of nervous injuries and maladies at Turners Lane Hospital, Philadelphia, and at the close of the war became a specialist in neurology. In this field Mitchell pioneered the rest cure for diseases now termed "psychiatric", particularly neurasthenia and hysteria, subsequently taken up by the medical world. The treatment consisted primarily in isolation, confinement to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bed Rest
Bed rest, also referred to as the rest-cure, is a medical treatment in which a person lies in bed for most of the time to try to cure an illness. Bed rest refers to voluntarily lying in bed as a treatment and not being confined to bed because of a health impairment which physically prevents leaving bed. The practice is still used although a 1999 systematic review found no benefits for any of the 17 conditions studied and no proven benefit for any conditions at all, beyond that imposed by symptoms. In the United States, nearly 20% of pregnant women have some degree of restricted activity prescribed despite the growing data showing it to be dangerous, causing some experts to call its use "unethical". Medical uses Extended bed rest has been proven to be a potentially harmful treatment needing more careful evaluation. Pregnancy Women who are pregnant and are experiencing early labor, vaginal bleeding, and cervix complications have been prescribed bed rest. This practice in 2013 wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycidas
"Lycidas" () is a poem by John Milton, written in 1637 as a pastoral elegy. It first appeared in a 1638 collection of elegies, ''Justa Edouardo King Naufrago'', dedicated to the memory of Edward King, a friend of Milton at Cambridge who drowned when his ship sank in the Irish Sea off the coast of Wales in August 1637. The poem is 193 lines in length and is irregularly rhymed. Many of the other poems in the compilation are in Greek and Latin, but "Lycidas" is one of the poems written in English. Milton republished the poem in 1645. History of the name Lycidas Herodotus in his Book IX (written in the 5th century BC) mentions an Athenian councilor in Salamis, "a man named Lycidas" ( Λυκίδας), who proposed to his fellow citizens that they submit to a compromise offered by their enemy, Persian King Xerxes I, with whom they were at war. Suspected of collusion with the enemy for suggesting the compromise, Lycidas was stoned to death by "those in the council and those out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Milton
John Milton (9 December 1608 – 8 November 1674) was an English poet and intellectual. His 1667 epic poem '' Paradise Lost'', written in blank verse and including over ten chapters, was written in a time of immense religious flux and political upheaval. It addressed the fall of man, including the temptation of Adam and Eve by the fallen angel Satan and God's expulsion of them from the Garden of Eden. ''Paradise Lost'' is widely considered one of the greatest works of literature ever written, and it elevated Milton's widely-held reputation as one of history's greatest poets. He also served as a civil servant for the Commonwealth of England under its Council of State and later under Oliver Cromwell. Writing in English, Latin, and Italian, Milton achieved global fame and recognition during his lifetime; his celebrated ''Areopagitica'' (1644), written in condemnation of pre-publication censorship, is among history's most influential and impassioned defences of freedom of spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
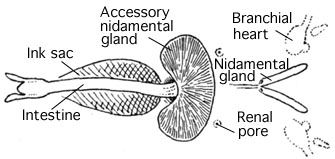
Cephalopod Ink
Cephalopod ink is a dark-coloured or luminous ink released into water by most species of cephalopod, usually as an escape mechanism. All cephalopods, with the exception of the Nautilidae and the Cirrina (deep-sea octopuses), are able to release ink to confuse predators. The ink is released from the ink sacs (located between the gills) and is dispersed more widely when its release is accompanied by a jet of water from the siphon. Its dark color is caused by its main constituent, melanin. Each species of cephalopod produces slightly differently coloured inks; generally, octopuses produce black ink, squid ink is blue-black, and cuttlefish ink is a shade of brown. A number of other aquatic molluscs have similar responses to attack, including the gastropod clade known as sea hares. Types of ink shapes The shapes taken by ink releases are classified as six types: * pseudomorphs; * pseudomorph series; * ink ropes; * clouds/smokescreens; * diffuse puffs; * mantle fills. Inking be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howard Pyle
Howard Pyle (March 5, 1853 – November 9, 1911) was an American illustrator and author, primarily of books for young people. He was a native of Wilmington, Delaware, and he spent the last year of his life in Florence, Italy. In 1894, he began teaching illustration at the Drexel Institute of Art, Science, and Industry (now Drexel University). Among his students there were Violet Oakley, Maxfield Parrish, and Jessie Wilcox Smith. After 1900, he founded his own school of art and illustration named the Howard Pyle School of Illustration Art. Scholar Henry C. Pitz later used the term Brandywine School for the illustration artists and Wyeth family artists of the Brandywine region, several of whom had studied with Pyle. He had a lasting influence on a number of artists who became notable in their own right; N. C. Wyeth, Frank Schoonover, Thornton Oakley, Allen Tupper True, Stanley Arthur, and numerous others studied under him. His 1883 classic publication ''The Merry Adventures of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Clarence Pitz
Henry Clarence Pitz (June 16, 1895 – November 26, 1976) was an Americans, American artist, illustrator, editor, author, and teacher who wrote and/or illustrated over 160 books, and dozens of magazine covers and articles. His most well-known book is ''The Brandywine Tradition'' (1968). Life and career Pitz was born in Philadelphia in 1895. His father was a bookbinder who immigrated from Germany. Pitz graduated from West Philadelphia High School and was awarded a scholarship to the Philadelphia Museum School of Industrial Art. There Pitz studied illustration and became particularly fond of the work of Howard Pyle. One of Pitz's instructors at the Museum School was Thornton Oakley, who had been a student of Pyle. He enlisted in the United States Army Medical Corps in 1917 and became an x-ray technician. He was assigned to Base Camp 56, Allerey, France, assisting Colonel Coates, the unit surgeon. After the war, he returned to Philadelphia. There he began a career of teaching a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harper's Weekly
''Harper's Weekly, A Journal of Civilization'' was an American political magazine based in New York City. Published by Harper & Brothers from 1857 until 1916, it featured foreign and domestic news, fiction, essays on many subjects, and humor, alongside illustrations. It carried extensive coverage of the American Civil War, including many illustrations of events from the war. During its most influential period, it was the forum of the political cartoonist Thomas Nast. History Inception Along with his brothers James, John, and Wesley, Fletcher Harper began the publishing company Harper & Brothers in 1825. Following the successful example of ''The Illustrated London News'', Harper started publishing '' Harper's Magazine'' in 1850. The monthly publication featured established authors such as Charles Dickens and William Makepeace Thackeray, and within several years, demand for the magazine was great enough to sustain a weekly edition.Palmquist & Kailborn 2002, p. 279. In 1857, his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)





.jpg)