|
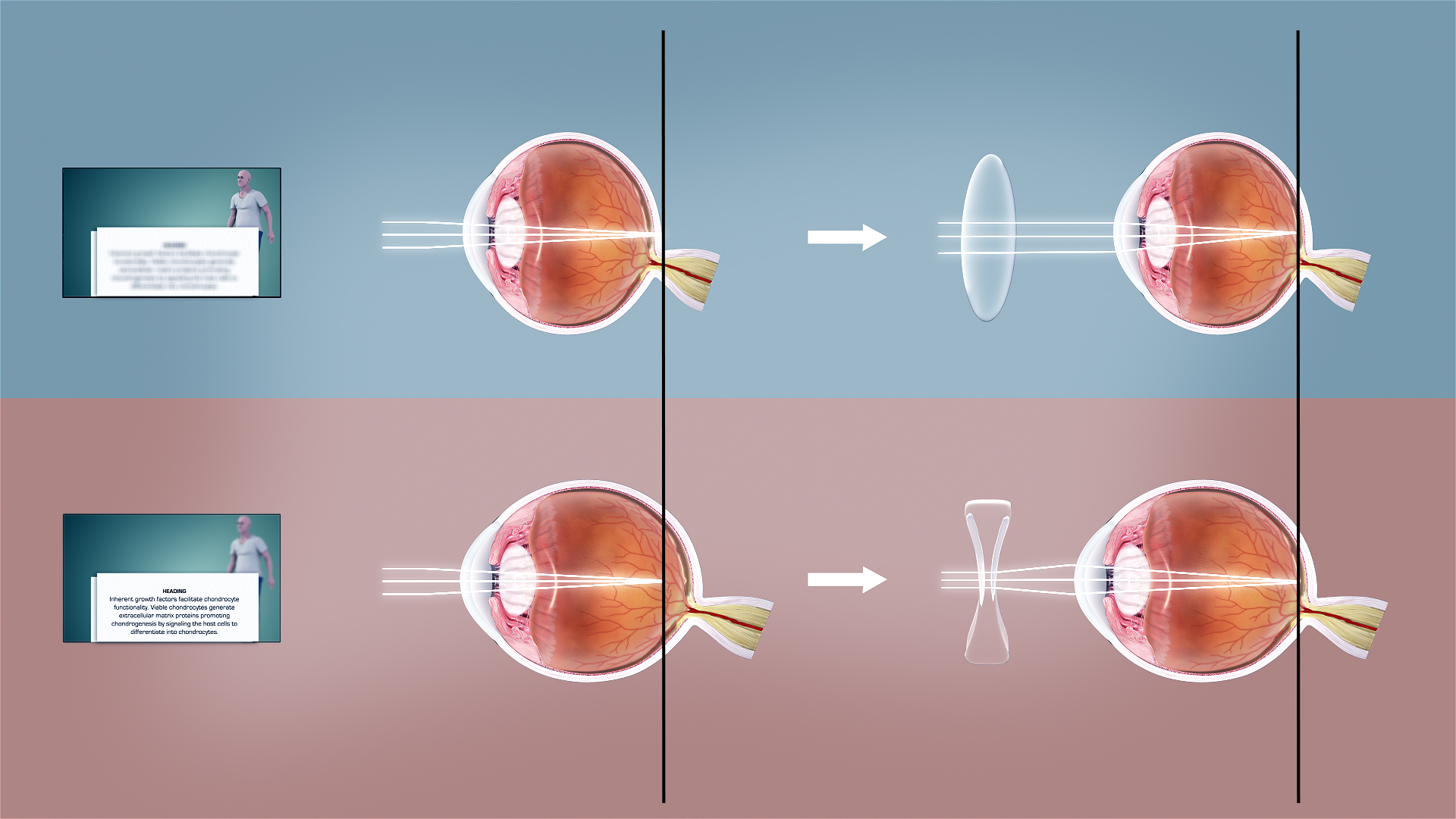
Stokes Lens
Stokes lens also known as variable power cross cylinder lens is a lens used to diagnose a type of refractive error known as astigmatism. Lens design The Stokes lens also known as variable power cross cylinder lens, in its standard version, is a lens combination consisted of equal but opposite (one plano-convex and other plano-concave) power cylindrical lenses attached together in a way so that the lenses be rotated in opposite directions. When the axes are parallel, the two powers cancel each other out to achieve the resulting power zero; When the axes are vertical, a sphero-cylindrical lens with maximum power is obtained. Uses Stokes lens is a lens used to diagnose and measure astigmatism. Adaptations American ophthalmologist Edward Jackson revised the Stokes lens concept and made a cross cylinder lens to refine power and axis of astigmatism. This lens combination is known as Jackson cross cylinder. Based on the Stokes lens, James P. Foley and Charles E. Campbell made a var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astigmatism
Astigmatism is a type of refractive error due to rotational asymmetry in the eye's refractive power. This results in distorted or blurred vision at any distance. Other symptoms can include eyestrain, headaches, and trouble driving at night. Astigmatism often occurs at birth and can change or develop later in life. If it occurs in early life and is left untreated, it may result in amblyopia. The cause of astigmatism is unclear; however, it is believed to be partly related to genetic factors. The underlying mechanism involves an irregular curvature of the cornea and protective reaction changes in the lens of the eye, called lens astigmatism, that has the same mechanism as spasm of accomodation. Diagnosis is by an eye examination called autorefractor keratometry (objective, allows to see lens and cornea components of astigmatism) and subjective refraction, but subjective methods are almost always inaccurate, if lens astigmatism is not fully removed first with a week of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Error
Refractive error, also known as refraction error, is a problem with focusing light accurately on the retina due to the shape of the eye and or cornea. The most common types of refractive error are near-sightedness, far-sightedness, astigmatism, and presbyopia. Near-sightedness results in far away objects being blurry, far-sightedness and presbyopia result in close objects being blurry, and astigmatism causes objects to appear stretched out or blurry. Other symptoms may include double vision, headaches, and eye strain. Near-sightedness is due to the length of the eyeball being too long, far-sightedness the eyeball too short, astigmatism the cornea being the wrong shape, and presbyopia aging of the lens of the eye such that it cannot change shape sufficiently. Some refractive errors occur more often among those whose parents are affected. Diagnosis is by eye examination. Refractive errors are corrected with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or surgery. Eyeglasses are the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astigmatism
Astigmatism is a type of refractive error due to rotational asymmetry in the eye's refractive power. This results in distorted or blurred vision at any distance. Other symptoms can include eyestrain, headaches, and trouble driving at night. Astigmatism often occurs at birth and can change or develop later in life. If it occurs in early life and is left untreated, it may result in amblyopia. The cause of astigmatism is unclear; however, it is believed to be partly related to genetic factors. The underlying mechanism involves an irregular curvature of the cornea and protective reaction changes in the lens of the eye, called lens astigmatism, that has the same mechanism as spasm of accomodation. Diagnosis is by an eye examination called autorefractor keratometry (objective, allows to see lens and cornea components of astigmatism) and subjective refraction, but subjective methods are almost always inaccurate, if lens astigmatism is not fully removed first with a week of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylindrical Lens
A cylindrical lens is a lens which focuses light into a line instead of a point, as a spherical lens would. The curved face or faces of a cylindrical lens are sections of a cylinder, and focus the image passing through it into a line parallel to intersection of the surface of the lens and a plane tangent to it along the cylinder's axis. The lens converges or diverges the image in the direction perpendicular to this line, and leaves it unaltered in the direction parallel to its cylinder's axis (in the tangent plane). A toric lens combines the effect of a cylindrical lens with that of an ordinary spherical lens. Uses Uses in optometry * Cylindrical lenses are prescribed to correct astigmatism. * Cross cylinder, which is a combination of two cylindrical lenses with equal strength and opposite power, is used in subjective refraction to diagnose astigmatism, and assess the strength and axis of the astigmatic power etc. * Maddox rods, made up of cylindrical lenses arranged in parallel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Jackson (ophthalmologist)
Edward Jackson (March 30, 1856 - October 29, 1942) was an American ophthalmologist better known for popularizing retinoscopy in the United States. He also described detecting astigmatism and its correct axis using a cross-cylinder. The modified Stokes lens he made was later known as Jackson's cross-cylinder. Biography Edward Jackson was born March 30, 1856, in West Goshen Township, Chester County, Pennsylvania, the son of Holiday and Emily Jackson. He completed his Bachelor of Science in Civil Engineering from Union College, New York in 1874, and in 1878 received his medical degree from the University of Pennsylvania. Jackson married Jenny L. Price in 1878. After she died in 1896, he settled in Denver in 1898, where he married Emily Churchman. Jackson died of heart block on October 29, 1942, at the age of 86. Career Jackson, who served as Professor of Ophthalmology at the Penn Medicine Rittenhouse (previously Philadelphia Polyclinic) and surgeon at Wills Eye Hospital later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jackson Cross Cylinder
The Jackson cross cylinder (JCC) is an instrument used by ophthalmologists, orthoptists and optometrists in their routine eye examination, particularly in determination of corrective lens power in patients with astigmatism. It is also used for testing near point of the eye. Instrument Jackson cross cylinder is a single low power lens, which is a combination of a plus cylinder and a minus cylinder of equal power with axis perpendicular to each other, with a handle placed between the two axes at 45 degrees. Therefore JCC is a spherocylindrical lens in which the power of the cylinder is double the power of the sphere and of opposite sign e.g. +0.5DS/-1.0DC or +0.25DS/-0.5DC. JCC are available in different powers including +/-1.00, most commonly used are of +/- 0.25 and +/- 0.50. There are dots or lines to indicate axis of minus and plus powers. Indications The Jackson cross cylinder is used to determine corrective lens power and its axis in patients with astigmatism. It is also u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Biddell Airy
Sir George Biddell Airy (; 27 July 18012 January 1892) was an English mathematician and astronomer, and the seventh Astronomer Royal from 1835 to 1881. His many achievements include work on planetary orbits, measuring the mean density of the Earth, a method of solution of two-dimensional problems in solid mechanics and, in his role as Astronomer Royal, establishing Greenwich as the location of the prime meridian. Biography Airy was born at Alnwick, one of a long line of Airys who traced their descent back to a family of the same name residing at Kentmere, in Westmorland, in the 14th century. The branch to which he belonged, having suffered in the English Civil War, moved to Lincolnshire and became farmers. Airy was educated first at elementary schools in Hereford, and afterwards at Colchester Royal Grammar School. An introverted child, Airy gained popularity with his schoolmates through his great skill in the construction of peashooters. From the age of 13, Airy stayed fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir George Stokes, 1st Baronet
Sir George Gabriel Stokes, 1st Baronet, (; 13 August 1819 – 1 February 1903) was an Irish English physicist and mathematician. Born in County Sligo, Ireland, Stokes spent all of his career at the University of Cambridge, where he was the Lucasian Professor of Mathematics from 1849 until his death in 1903. As a physicist, Stokes made seminal contributions to fluid mechanics, including the Navier–Stokes equations; and to physical optics, with notable works on polarization and fluorescence. As a mathematician, he popularised "Stokes' theorem" in vector calculus and contributed to the theory of asymptotic expansions. Stokes, along with Felix Hoppe-Seyler, first demonstrated the oxygen transport function of hemoglobin and showed color changes produced by aeration of hemoglobin solutions. Stokes was made a baronet by the British monarch in 1889. In 1893 he received the Royal Society's Copley Medal, then the most prestigious scientific prize in the world, "for his research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagnostic Ophthalmology
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " cause and effect". In systems engineering and computer science, it is typically used to determine the causes of symptoms, mitigations, and solutions. Computer science and networking * Bayesian networks * Complex event processing * Diagnosis (artificial intelligence) * Event correlation * Fault management * Fault tree analysis * Grey problem * RPR Problem Diagnosis * Remote diagnostics * Root cause analysis * Troubleshooting * Unified Diagnostic Services Mathematics and logic * Bayesian probability * Block Hackam's dictum * Occam's razor * Regression diagnostics * Sutton's law copy right remover block Medicine * Medical diagnosis * Molecular diagnostics Methods * CDR Computerized Assessment System * Computer-assisted diagnosis * Differential diagnosis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optometry
Optometry is a specialized health care profession that involves examining the eyes and related structures for defects or abnormalities. Optometrists are health care professionals who typically provide comprehensive primary eye care. In the United States and Canada, optometrists are those that hold a Doctor of Optometry degree. They are trained and licensed to practice medicine for eye related conditions, in addition to providing refractive (optical) eye care. In the United Kingdom, optometrists may also practice medicine (and provide refractive care) for eye related conditions. The Doctor of Optometry title can also be used in the UK for those that hold the postgraduate O.D. degree. Within their scope of practice, optometrists are considered physicians and bill medical insurance(s) (example: Medicare) accordingly. Moreover, many participate in academic research for eye related conditions and disease. Optometrists are the only health care professionals with a first professional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)