|
Stoke, Kent
Stoke is a civil parish on the Hoo Peninsula in Kent, England, to the south of Allhallows, on the north of the Medway Estuary. According to the 2001 census it had a population of 1,063, reducing marginally to 1,060 at the 2011 census. The two small villages of Lower Stoke and Stoke (sometimes referred to as Upper Stoke) stand on low-lying fertile farmland that is at most 17 m above highwater. The farmland descends to the Stoke Saltings – a maze of intricate channels and small islands beloved by wading birds. The church of Saints Peter and Paul is in Stoke; it was an appendage to the Manor of Great Hoo. The building contains some Norman and Early English work dating from 1175. It has no spire.Brian Matthews, the History of Strood Rural District, 1971, Strood Rural District Council In an Anglo-Saxon charter Stoke is referred to as "Andescohesham". It was passed with other lands by Eadberht, son of King Wihtred of Kent to the See of Rochester for "the good of his soul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medway
Medway is a unitary authority district and conurbation in Kent, South East England. It had a population of 278,016 in 2019. The unitary authority was formed in 1998 when Rochester-upon-Medway amalgamated with the Borough of Gillingham to form Medway Towns. It is now a unitary authority area run by Medway Council, independent of Kent County Council but still part of the ceremonial county of Kent. Medway is one of the boroughs included in the Thames Gateway development scheme. It is also the home of Universities at Medway, a tri-partite collaboration of the University of Greenwich, the University of Kent and Canterbury Christ Church University on a single campus in Chatham, together with the University for the Creative Arts, which has a campus in Rochester. Geography Because of its strategic location by the major crossing of the River Medway, it has made a wide and significant contribution to Kent, and to England, dating back thousands of years, as evident in the siting of Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isle Of Grain
Isle of Grain (Old English ''Greon'', meaning gravel) is a village and the easternmost point of the Hoo Peninsula within the district of Medway in Kent, south-east England. No longer an island and now forming part of the peninsula, the area is almost all marshland and is a major habitat for diverse wetland birds. The village constitutes a civil parish, which at the 2011 census had a population of 1,648, a net decrease of 83 people in 10 years. History Extract from the ''Topographical Dictionary of Great Britain and Ireland'' by John Gorton, 1833: "GRAINE, ISLE OF, co. Kent'' "A parish in the Hundred of Hoo, lathe of Aylesford, opposite to Sheppey at the mouth of the Thames; it is about three miles and a half long, and two and a half broad and is formed by Yantlet Creek running from the Medway to the Thames. The Creek was filled up, and had a road across it for 40 years until 1823, when the Lord Mayor ordered it to be again reopened, so as to give about eight feet naviga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nore
The Nore is a long bank of sand and silt running along the south-centre of the final narrowing of the Thames Estuary, England. Its south-west is the very narrow Nore Sand. Just short of the Nore's easternmost point where it fades into the channels it has a notable point once marked by a lightship on the line where the estuary of the Thames nominally becomes the North Sea. A lit buoy today stands on this often map-marked divisor: between Havengore Creek in east Essex and Warden Point on the Isle of Sheppey in Kent. Until 1964 it marked the seaward limit of the Port of London Authority. As the sandbank was a major hazard for shipping coming in and out of London, in 1732 it received the world's first lightship. This became a major landmark, and was used as an assembly point for shipping. Today it is marked by Sea Reach No. 1 Buoy. The Nore is an anchorage, or open roadstead, used by the Royal Navy's North Sea Fleet, and to its local Command. It was the site of a notorious mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SS Richard Montgomery
SS ''Richard Montgomery'' was an American Liberty cargo ship built during World War II. She was named after Richard Montgomery, an Irish officer who fought in the American Revolutionary War. The ship was wrecked on the Nore sandbank in the Thames Estuary, near Sheerness, Kent, England, in August 1944, while carrying a cargo of munitions. About of explosives remaining on board presents a hazard but the likelihood of explosion is claimed to be remote. Construction ''Richard Montgomery'' was laid down on 15 March 1943 under a Maritime Commission (MARCOM) contract, MC hull 1199, by the St. Johns River Shipbuilding Company, Jacksonville, Florida. She was sponsored by Mrs. Rockwell, the wife of the director of MARCOM, Production Division, and was launched on 15 June 1943. She was the seventh of the 82 liberty ships built by the yard. Service history She was allocated to Agwilines Inc. on 29 July 1943. In August 1944, on what was to be her final voyage, the ship left Hog Island, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Stoke
Stoke is a civil parish on the Hoo Peninsula in Kent, England, to the south of Allhallows, on the north of the Medway Estuary. According to the 2001 census it had a population of 1,063, reducing marginally to 1,060 at the 2011 census. The two small villages of Lower Stoke and Stoke (sometimes referred to as Upper Stoke) stand on low-lying fertile farmland that is at most 17 m above highwater. The farmland descends to the Stoke Saltings – a maze of intricate channels and small islands beloved by wading birds. The church of Saints Peter and Paul is in Stoke; it was an appendage to the Manor of Great Hoo. The building contains some Norman and Early English work dating from 1175. It has no spire.Brian Matthews, the History of Strood Rural District, 1971, Strood Rural District Council In an Anglo-Saxon charter Stoke is referred to as "Andescohesham". It was passed with other lands by Eadberht, son of King Wihtred of Kent to the See of Rochester for "the good of his sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
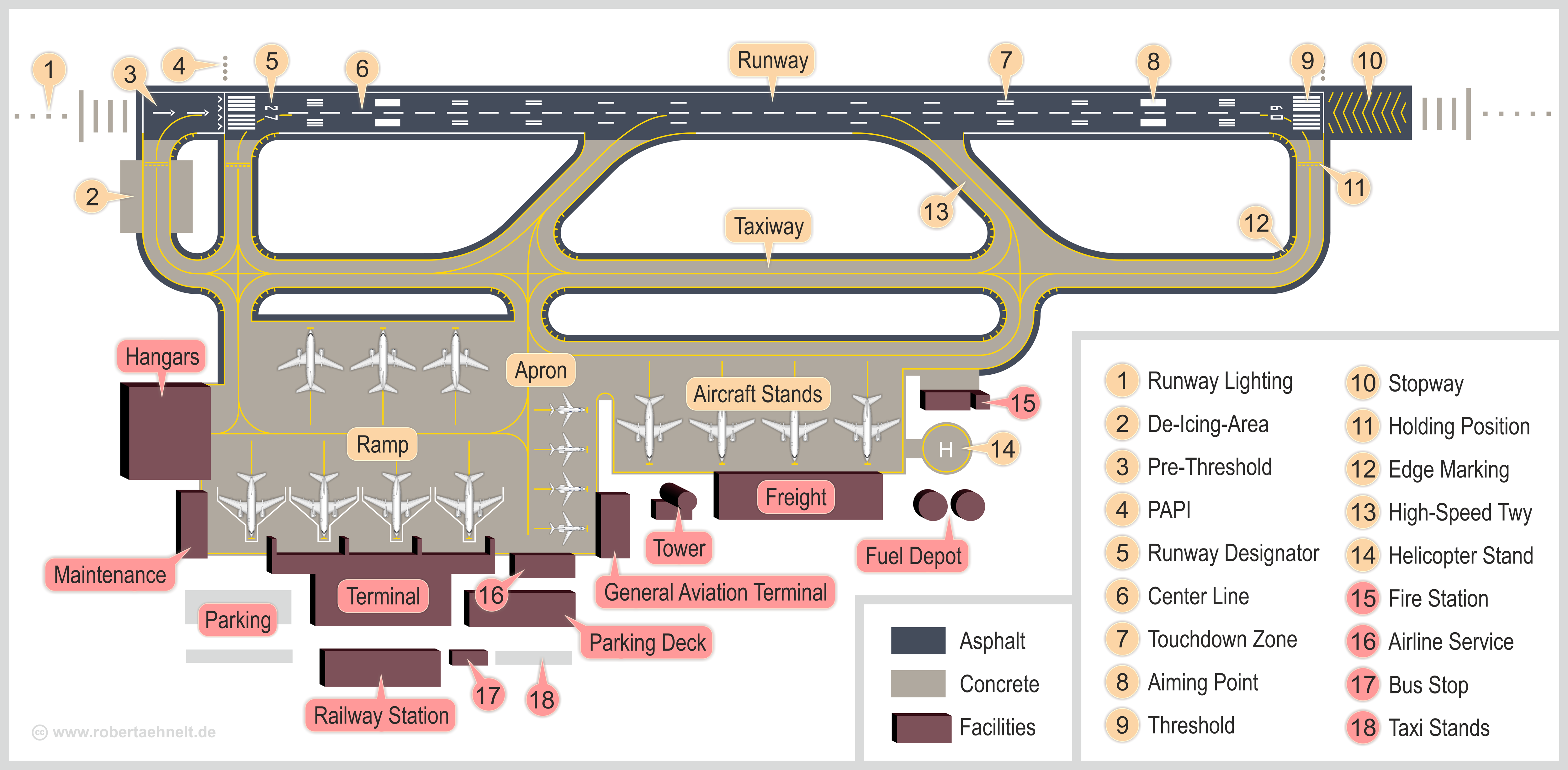
Airport
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface such as a runway for a plane to take off and to land or a helipad, and often includes adjacent utility buildings such as control towers, hangars and terminals, to maintain and monitor aircraft. Larger airports may have airport aprons, taxiway bridges, air traffic control centres, passenger facilities such as restaurants and lounges, and emergency services. In some countries, the US in particular, airports also typically have one or more fixed-base operators, serving general aviation. Operating airports is extremely complicated, with a complex system of aircraft support services, passenger services, and aircraft control services contained within the operation. Thus airports can be major employers, as well as important hubs for tourism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-speed Rail
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail system that runs significantly faster than traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated tracks. While there is no single standard that applies worldwide, lines built to handle speeds above or upgraded lines in excess of are widely considered to be high-speed. The first high-speed rail system, the Tōkaidō Shinkansen, began operations in Japan in 1964 and was widely known as the bullet train. High-speed trains mostly operate on standard gauge tracks of continuously welded rail on grade-separated rights of way with large radii. However, certain regions with wider legacy railways, including Russia and Uzbekistan, have sought to develop a high speed railway network in Russian gauge. There are no narrow gauge high-speed trains; the fastest is the Cape gauge Spirit of Queensland at . Many countries have developed, or are currently building, high-speed rail infrastructure to connect major citie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thames Hub Integrated Infrastructure Vision
The Thames Hub is a proposal for a new approach to integrated infrastructure development that combines rail, intermodal freight logistics, aviation, tidal renewable energy and its transmission, flood protection and regional development in the Thames Estuary and connects this infrastructure to a trade and utilities spine that runs the length of the UK. It was developed by architects Foster + Partners, infrastructure consultants Halcrow and economists Volterra and launched by Lord Foster at the Institution of Civil Engineers in London on 2 November 2011. A more developed proposal for a platform-based Thames Hub Airport, located on the Isle of Grain in the Thames Estuary in Kent, was submitted to the Airports Commission in July 2013 by Foster+Partners. Background Infrastructure challenges The Thames Hub concept was developed to address a number of infrastructure challenges facing the UK. These include: * The economic divide between the North and South of the count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |