|
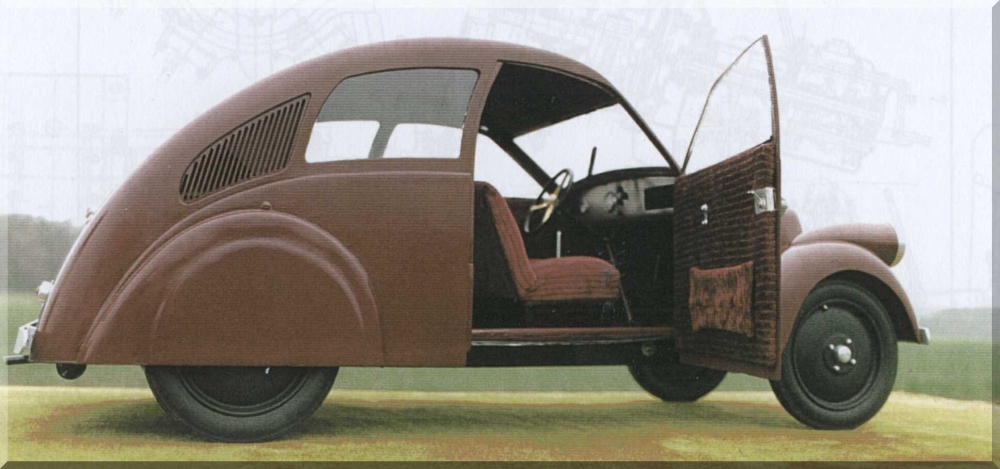
Steyr Automobile
Steyr was an Austrian automotive brand, established in 1915 as a branch of the ''Österreichische Waffenfabriks-Gesellschaft'' (ÖWG) weapon manufacturing company. Renamed ''Steyr-Werke AG'' in 1926 and merged with Austro-Daimler and Puch into Steyr-Daimler-Puch AG, it continued manufacturing Steyr automobiles until 1959. History The ÖWG stock company was founded in 1864 at Steyr in Upper Austria; in 1894 it had already issued a licence from the British Swift Company to manufacture bicycles under the trade-mark name ''Waffenrad''. In order to further to diversify manufacturing, the members of the executive board resolved upon fabricating Steyr automobiles and tractors. They hired 38-year-old designer Hans Ledwinka after he resigned from Nesselsdorfer-Wagenbau. Ledwinka developed Steyr's new six-cylinder car and supervised hiring engineers and mechanics. This, the 12/40 PS, featured the fashionable ''spitzkuhler'' (pointed radiator) of the prewar Mercedes and had very modern f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gearbox
Propulsion transmission is the mode of transmitting and controlling propulsion power of a machine. The term ''transmission'' properly refers to the whole drivetrain, including clutch, gearbox, prop shaft (for rear-wheel drive vehicles), differential, and final drive shafts. In the United States the term is sometimes used in casual speech to refer more specifically to the gearbox alone, and detailed usage differs. The transmission reduces the higher engine speed to the slower wheel speed, increasing torque in the process. Transmissions are also used on pedal bicycles, fixed machines, and where different rotational speeds and torques are adapted. Often, a transmission has multiple gear ratios (or simply "gears") with the ability to switch between them as the speed varies. This switching may be done manually (by the operator) or automatically (by a control unit). Directional (forward and reverse) control may also be provided. Single-ratio transmissions also exist, which simply ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pound Sterling
Sterling (abbreviation: stg; Other spelling styles, such as STG and Stg, are also seen. ISO 4217, ISO code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of #Crown Dependencies and British Overseas Territories, its associated territories. The Pound (currency), pound (pound sign, sign: £) is the main unit of account, unit of sterling, and the word "pound" is also used to refer to the British currency generally, often qualified in international contexts as the British pound or the pound sterling. Sterling is the world's oldest currency that is still in use and that has been in continuous use since its inception. It is currently the fourth most-traded currency in the foreign exchange market, after the United States dollar, the euro, and the Japanese yen. Together with those three currencies and Renminbi, it forms the basket of currencies which special drawing rights#Value definition, calculate the value of International Monetary Fund, IMF special drawing rights. As of mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
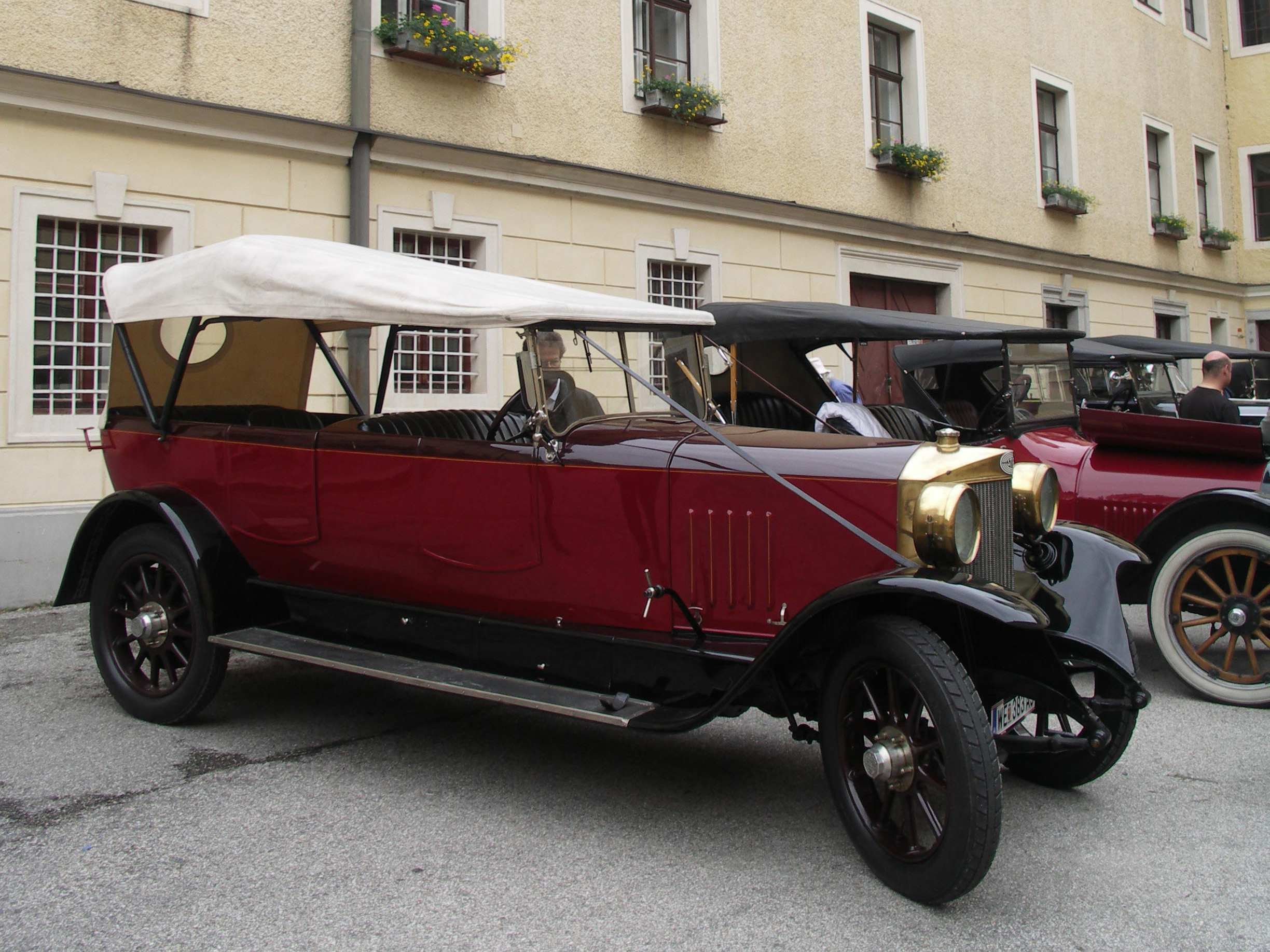
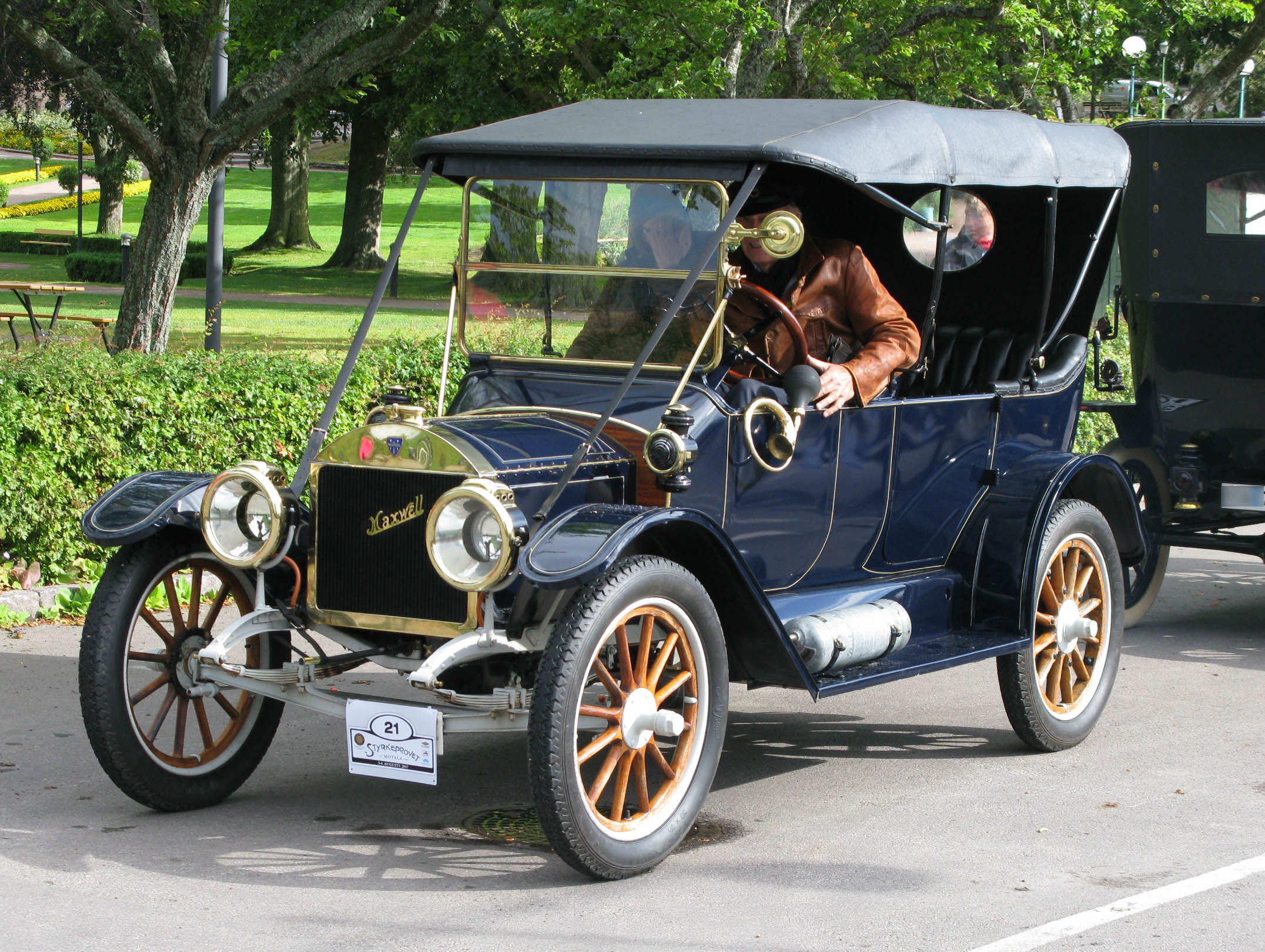
Touring Car
Touring car and tourer are both terms for open cars (i.e. cars without a fixed roof). "Touring car" is a style of open car built in the United States which seats four or more people. The style was popular from the early 1900s to the 1930s. The cars used for touring car racing in various series since the 1960s, are unrelated to these early touring cars, despite sharing the same name. "Tourer" is used in British English for any open car. The term "all-weather tourer" was used to describe convertibles (vehicles that could be fully enclosed). A popular version of the tourer was the torpedo, with the hood/bonnet line at the car's waistline giving the car a straight line from front to back. Touring car (U.S.) Design ''Touring car'' was applied in the U.S. to open cars (cars without a fixed roof, for example convertibles) that seat four or more people and have direct entrance to the tonneau (rear passenger area), although it has also been described as seating five or more people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independent Suspension
Independent suspension is any automobile suspension system that allows each wheel on the same axle to move vertically (i.e. reacting to a bump on the road) independently of the others. This is contrasted with a beam axle or deDion axle system in which the wheels are linked. "Independent" refers to the motion or path of movement of the wheels or suspension. It is common for the left and right sides of the suspension to be connected with anti-roll bars or other such mechanisms. The anti-roll bar ties the left and right suspension spring rates together but does not tie their motion together. Most modern vehicles have independent front suspension (IFS). Many vehicles also have an independent rear suspension (IRS). IRS, as the name implies, has the rear wheels independently sprung. A fully independent suspension has an independent suspension on all wheels. Some early independent systems used swing axles, but modern systems use Chapman Chapman may refer to: Businesses * Chapman E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swing Axle
A swing axle is a simple type of independent (rear wheel) suspension designed and patented by Edmund Rumpler in 1903. This was a revolutionary invention in automotive suspension, allowing driven (powered) wheels to follow uneven road surfaces independently, thus enabling the vehicle's wheels to maintain better road contact and holding; plus each wheel's reduced unsprung weight means their movements have less impact on the vehicle as a whole. The first automotive application was the Rumpler Tropfenwagen, later followed by the Mercedes 130H/150H/170H, the Standard Superior, the Volkswagen Beetle and its derivatives, the Chevrolet Corvair, and the roll-over prone M151 jeep amongst others. Some later automobile rear swing axles have universal joints connecting the driveshafts to the differential, which is attached to the chassis. Swing axles do not have universal joints at the wheels — the wheels are always perpendicular to the driveshafts; the design is therefore not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaf Spring
A leaf spring is a simple form of spring commonly used for the suspension in wheeled vehicles. Originally called a ''laminated'' or ''carriage spring'', and sometimes referred to as a semi-elliptical spring, elliptical spring, or cart spring, it is one of the oldest forms of vehicle suspension. A leaf spring is one or more narrow, arc-shaped, thin plates which are attached to the axle and chassis in a way that allows the leaf spring to flex vertically in response to irregularities in the road surface. Lateral leaf springs are the most commonly used arrangement, running the length of the vehicle and mounted perpendicular to the wheel axle, but numerous examples of transverse leaf springs exist as well. Leaf springs can serve multiple suspension functions: location, springing, and to some extent damping as well, through interleaf friction. However, this friction is not well controlled, resulting in stiction and irregular suspension motions. For this reason, some manufacturers ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volkswagen Beetle
The Volkswagen Beetle—officially the Volkswagen Type 1, informally in German (meaning "beetle"), in parts of the English-speaking world the Bug, and known by many other nicknames in other languages—is a two-door, rear-engine economy car, intended for five occupants (later, Beetles were restricted to four people in some countries), that was manufactured and marketed by German automaker Volkswagen (VW) from 1938 until 2003. The need for a ''people's car'' ( in German), its concept and its functional objectives were formulated by the leader of Nazi Germany, Adolf Hitler, who wanted a cheap, simple car to be mass-produced for his country's new road network ( Reichsautobahn). Members of the National Socialist party, with an additional dues surcharge, were promised the first production, but the Spanish Civil War shifted most production resources to military vehicles to support the Nationalists under Francisco Franco. Lead engineer Ferdinand Porsche and his team took until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volkswagen
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a global brand post-World War II by the British Army Officer Ivan Hirst, it is known for the iconic Beetle and serves as the flagship brand of the Volkswagen Group, the largest automotive manufacturer by worldwide sales in 2016 and 2017. The group's biggest market is in China, which delivers 40 percent of its sales and profits. Its name is derived from the German-language terms and , translating to "people's car" when combined. History 1932–1940: People's Car project Volkswagen was established in 1937 by the German Labour Front (''Deutsche Arbeitsfront'') in Berlin. In the early 1930s, cars were a luxury – most Germans could afford nothing more elaborate than a motorcycle and only one German out of 50 owned a car. Seeking a potential new market, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tatra (car)
Tatra is a Czech vehicle manufacturer from Kopřivnice. It is owned by the ''Tatra Trucks'' company, and it is the third oldest company in the world producing cars with an unbroken history. The company was founded in 1850 as ''Ignatz Schustala & Cie'', in 1890 renamed in German ''Nesselsdorfer Wagenbau-Fabriksgesellschaft'' when it became a wagon and carriage manufacturer. In 1897, Tatra produced the first motor car in central Europe, the Präsident automobile. In 1918, it changed its name to ''Kopřivnická vozovka a.s.'', and in 1919 it changed from the Nesselsdorfer marque to the ''Tatra'' badge, named after the nearby Tatra Mountains on the Czechoslovak- Polish border (now on the Polish- Slovak border). During World War II Tatra was instrumental in the production of trucks and tank engines for the German war effort. Production of passenger cars ceased in 1999, but the company still produces a range of primarily all-wheel-drive trucks, from 4×4 to 18×18. The brand is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
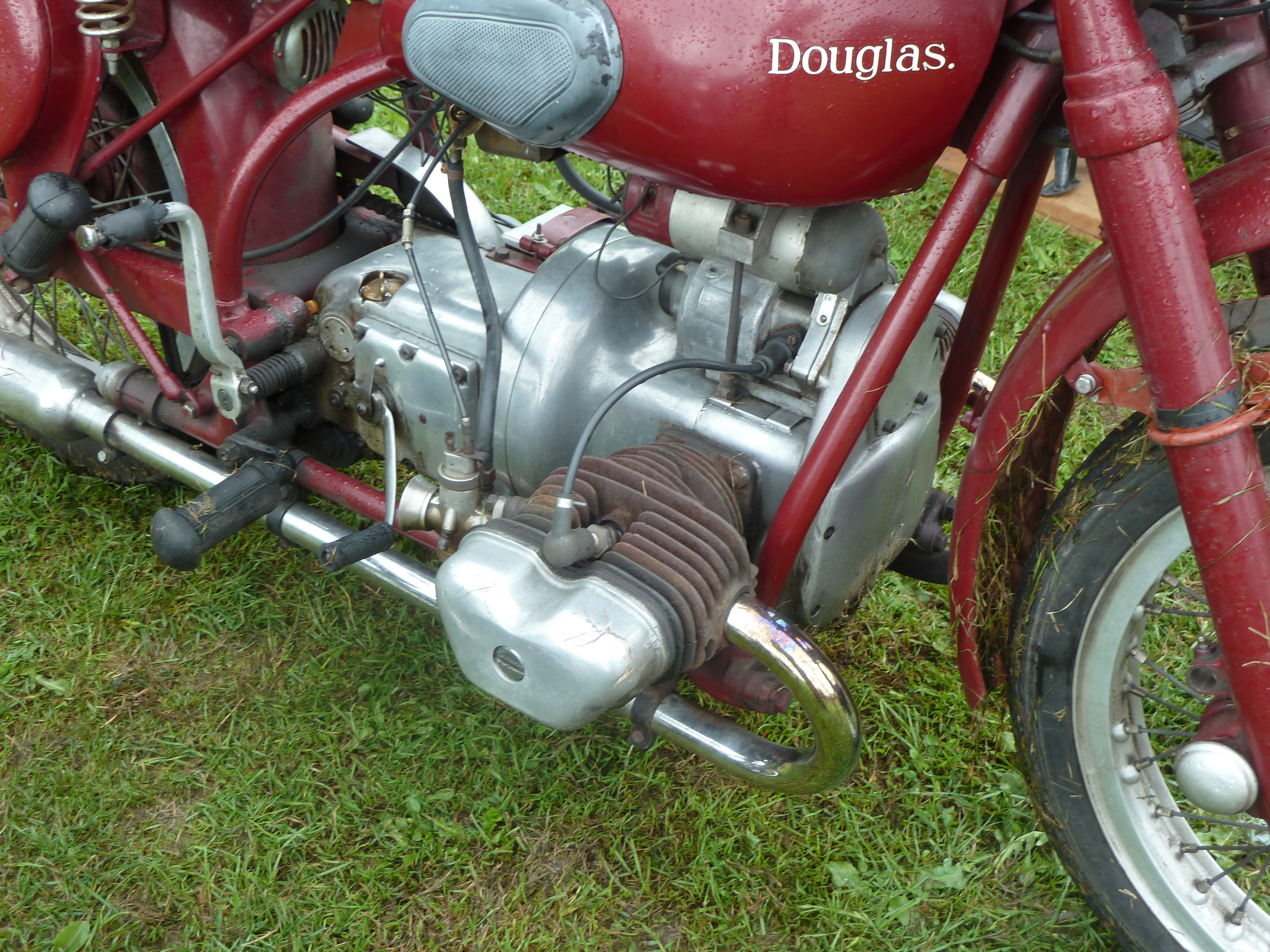
Flat-2
A flat-twin engine is a two-cylinder internal combustion engine with the cylinders on opposite sides of the crankshaft. The most common type of flat-twin engine is the boxer-twin engine, where both pistons move inwards and outwards at the same time. The flat-twin design was patented by Karl Benz in 1896 and the first production flat-twin engine was used in the ''Lanchester 8 hp Phaeton'' car released in 1900. The flat-twin engine was used in several other cars since, however a more common usage is in motorcycles; early models oriented the cylinders in line with the frame, however later models switched to the cylinders being perpendicular to the frame to provide even cooling across both cylinders. Flat-twin engines were also used in several aircraft up until the 1930s and in various stationary applications from the 1930s to the 1960s. The Australian lawnmower manufacturer Victa also produced a flat-twin engine push mower from August 1975 to 1980 dubbed as the ‘Twin 500’ and � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
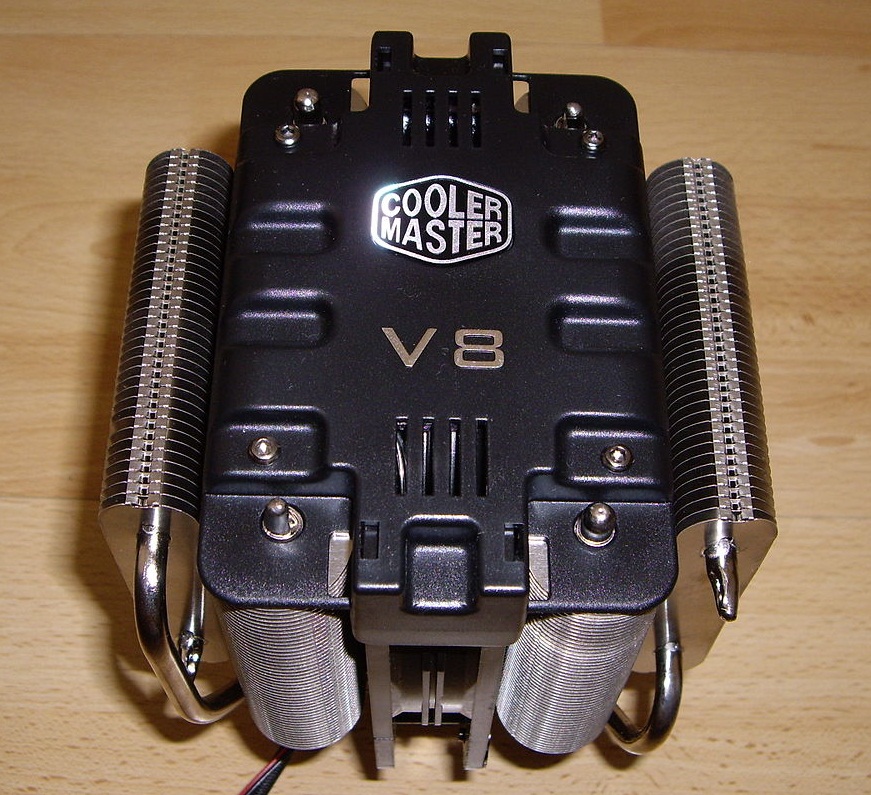
Air Cooling
Air cooling is a method of dissipating heat. It works by expanding the surface area or increasing the flow of air over the object to be cooled, or both. An example of the former is to add cooling fins to the surface of the object, either by making them integral or by attaching them tightly to the object's surface (to ensure efficient heat transfer). In the case of the latter, it is done by using a fan blowing air into or onto the object one wants to cool. The addition of fins to a heat sink increases its total surface area, resulting in greater cooling effectiveness. There are two types of cooling pads that can used for air cooling: one is the honeycomb design and another one is excelsior. In all cases, the air has to be cooler than the object or surface from which it is expected to remove heat. This is due to the second law of thermodynamics, which states that heat will only move spontaneously from a hot reservoir (the heat sink) to a cold reservoir (the air). Derating at hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)