|
Stenonychosaurus
''Stenonychosaurus'' (meaning "narrow claw lizard") is a genus of troodontid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Dinosaur Park Formation of Alberta, Canada, as well as possibly the Two Medicine Formation. The type and only species, ''S. inequalis'', was named by Charles Mortram Sternberg in 1932, based on a foot, fragments of a hand, and some caudal vertebrae from the Late Cretaceous of Alberta. ''S. inequalis'' was reassigned in 1987 by Phil Currie to the genus ''Troodon'', which was reverted by the recognition of ''Stenonychosaurus'' as a separate genus from the possibly dubious ''Troodon'' in 2017 by Evans ''et al.'' and also later in the same year by Van der Reest and Currie. History of discovery The first specimens currently assigned to ''Troodon'' that were not teeth were both found by Sternberg in 1928, in the Dinosaur Park Formation of Alberta. The first was named ''Stenonychosaurus inequalis'' by Sternberg in 1932, based on a foot, fragments of a hand, and some tail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosauroid
''Stenonychosaurus'' (meaning "narrow claw lizard") is a genus of troodontid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Dinosaur Park Formation of Alberta, Canada, as well as possibly the Two Medicine Formation. The type and only species, ''S. inequalis'', was named by Charles Mortram Sternberg in 1932, based on a foot, fragments of a hand, and some caudal vertebrae from the Late Cretaceous of Alberta. ''S. inequalis'' was reassigned in 1987 by Phil Currie to the genus ''Troodon'', which was reverted by the recognition of ''Stenonychosaurus'' as a separate genus from the possibly dubious ''Troodon'' in 2017 by Evans ''et al.'' and also later in the same year by Van der Reest and Currie. History of discovery The first specimens currently assigned to ''Troodon'' that were not teeth were both found by Sternberg in 1928, in the Dinosaur Park Formation of Alberta. The first was named ''Stenonychosaurus inequalis'' by Sternberg in 1932, based on a foot, fragments of a hand, and some tail verte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
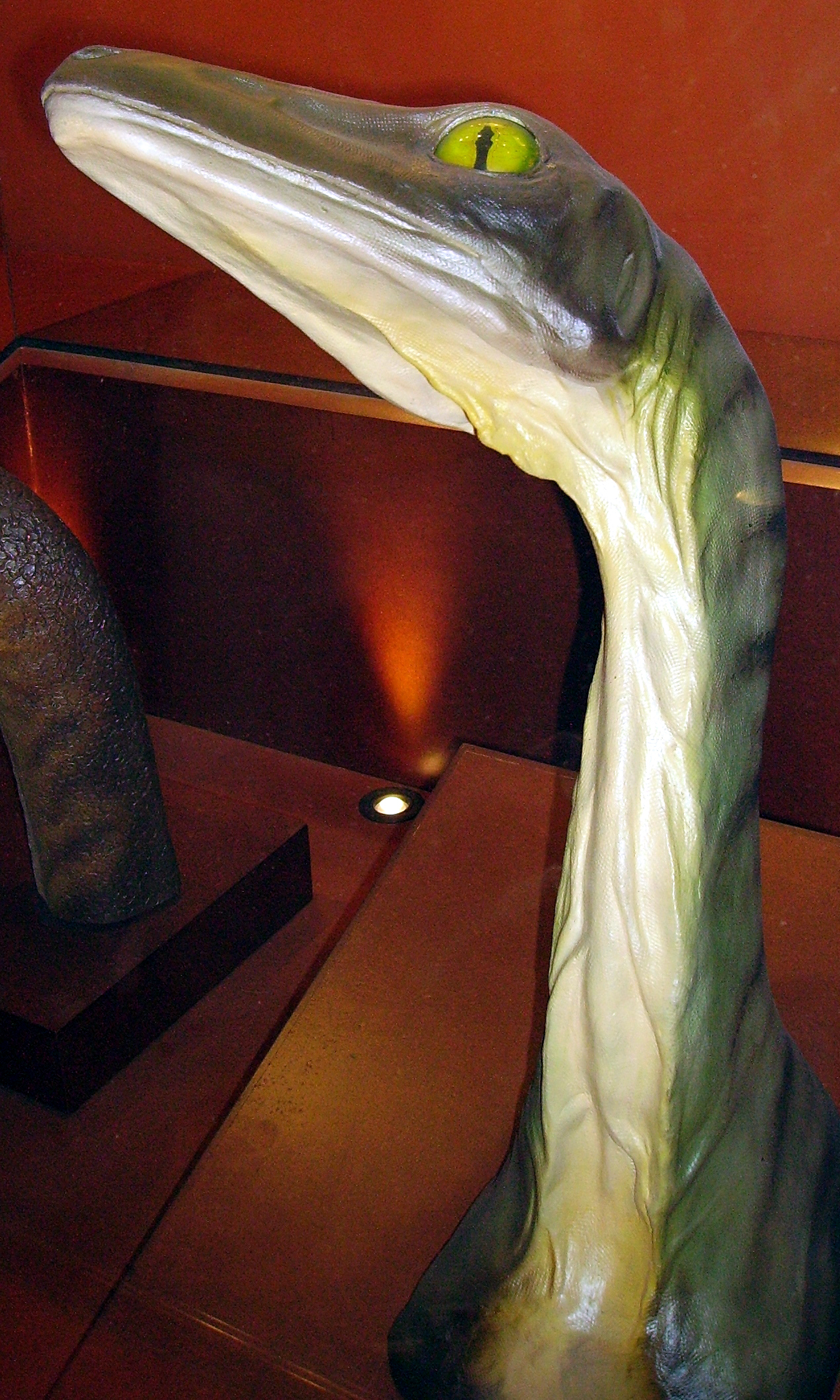
Stenonychosaurus Head Neck NHM
''Stenonychosaurus'' (meaning "narrow claw lizard") is a genus of troodontid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Dinosaur Park Formation of Alberta, Canada, as well as possibly the Two Medicine Formation. The type and only species, ''S. inequalis'', was named by Charles Mortram Sternberg in 1932, based on a foot, fragments of a hand, and some caudal vertebrae from the Late Cretaceous of Alberta. ''S. inequalis'' was reassigned in 1987 by Phil Currie to the genus ''Troodon'', which was reverted by the recognition of ''Stenonychosaurus'' as a separate genus from the possibly dubious ''Troodon'' in 2017 by Evans ''et al.'' and also later in the same year by Van der Reest and Currie. History of discovery The first specimens currently assigned to ''Troodon'' that were not teeth were both found by Sternberg in 1928, in the Dinosaur Park Formation of Alberta. The first was named ''Stenonychosaurus inequalis'' by Sternberg in 1932, based on a foot, fragments of a hand, and some tail verte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troodon
''Troodon'' ( ; ''Troödon'' in older sources) is a wastebasket taxon and a dubious genus of relatively small, bird-like dinosaurs known definitively from the Campanian age of the Late Cretaceous period (about 77 mya). It includes at least one species, ''Troodon formosus'', known from Montana. Discovered in October 1855, ''T. formosus'' was among the first dinosaurs found in North America, although it was thought to be a lizard until 1877. Several well-known troodontid specimens from the Dinosaur Park Formation in Alberta were once believed to be members of this genus. However, recent analyses in 2017 have found the genus to be undiagnostic and referred some of these specimens to the genus '' Stenonychosaurus'' (long believed to be synonymous with ''Troodon'') and others to the genus '' Latenivenatrix''. The genus name is Ancient Greek for "wounding tooth", referring to the teeth, which were different from those of most other theropods known at the time of their discovery. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latenivenatrix
''Latenivenatrix'' (meaning "hiding huntress") is a genus of troodontid known from one species, ''L. mcmasterae''. Along with the contemporary ''Stenonychosaurus'', it is known from the non-tooth fossils formerly assigned to the genus ''Troodon''. Although described as separate, it has been considered a junior synonym of ''Stenonychosaurus''. Discovery and specimens The type specimen or holotype of ''Latenivenatrix'', CMN 12340, was originally described in 1969 by Dale Alan Russell and referred by him to the genus ''Stenonychosaurus''. In 1987 it was referred to ''Troodon''. It had been collected in 1968 by Irene Vanderloh in the Dinosaur Park Formation strata from Alberta, southern Canada. The specimen has preserved some skull bones ( frontals, parietals, postorbital, basioccipital and basisphenoid), four vertebrae and four ribs, some chevrons and gastralia, fairly complete forelimb and incomplete hindlimbs. Moreover, three additional specimens coming from the same locality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyodontosaurus
''Polyodontosaurus'' (meaning "many-toothed lizard") is a potentially dubious genus of troodontid dinosaur named in 1932 by Charles W. Gilmore for a left dentary from the Dinosaur Park Formation. Gilmore, C. W. (1932). A new fossil lizard from the Belly River Formation of Alberta. ''Transactions of the Royal Society of Canada'', section 4, series 3 16:117-119 It had been considered a synonym of ''Stenonychosaurus'' or ''Troodon'' for a significant time, before being declared a '' nomen dubium''. The only known species is the type, ''P. grandis''. History of discovery The holotype and only known specimen of ''Polyodontosaurus'' was collected in 1928 by Charles Mortram Sternberg, and includes only a left dentary, lacking any teeth. Sternberg presented the dentary to Charles Gilmore, who identified it as a lizard. Gilmore thus named the binomial ''Polyodontosaurus grandis'' for the new taxon in 1932. Sternberg revisited the material in 1951 and determined that it represented a carn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur Park Formation
The Dinosaur Park Formation is the uppermost member of the Belly River Group (also known as the Judith River Group), a major geologic unit in southern Alberta. It was deposited during the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous, between about 76.5 and 74.4 million years ago. It was deposited in alluvial plain, alluvial and coastal plain environments, and it is bounded by the nonmarine Oldman Formation below it and the marine (ocean), marine Bearpaw Formation above it.Eberth, D.A. 2005. The geology. In: Currie, P.J., and Koppelhus, E.B. (eds), Dinosaur Provincial Park: A Spectacular Ancient Ecosystem Revealed. Indiana University Press: Bloomington and Indianapolis, p.54-82. . The Dinosaur Park Formation contains dense concentrations of dinosaur skeletons, both articulated and disarticulated, which are often found with preserved remains of soft tissues. Remains of other animals such as fish, turtles, and crocodilians, as well as plant remains, are also abundant. The formation h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troodontidae
Troodontidae is a clade of bird-like theropod dinosaurs. During most of the 20th century, troodontid fossils were few and incomplete and they have therefore been allied, at various times, with many dinosaurian lineages. More recent fossil discoveries of complete and articulated specimens (including specimens which preserve feathers, eggs, embryos, and complete juveniles), have helped to increase understanding about this group. Anatomical studies, particularly studies of the most primitive troodontids, like ''Sinovenator'', demonstrate striking anatomical similarities with ''Archaeopteryx'' and primitive dromaeosaurids, and demonstrate that they are relatives comprising a clade called Paraves. Description Troodontids are a group of small, bird-like, gracile maniraptorans. All troodontids have unique features of the skull, such as large numbers of closely spaced teeth in the lower jaw. Troodontids have sickle-claws and raptorial hands, and some of the highest non-avian encephali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saurornithoides
''Saurornithoides'' ( ) is a genus of troodontid maniraptoran dinosaur, which lived during the Late Cretaceous period. These creatures were predators, which could run fast on their hind legs and had excellent sight and hearing. The name is derived from the Greek stems ''saur~'' (lizard), ''ornith~'' (bird) and ''eides'' (form), referring to its bird-like skull. Description ''Saurornithoides'' is a member of the troodontids, a group of small, bird-like, gracile maniraptorans. All troodontids have many unique features of the skull, such as closely spaced teeth in the lower jaw, and large numbers of teeth. Troodontids have sickle-claws and raptorial hands, and some of the highest non-avian encephalization quotients, meaning they were behaviourally advanced and had keen senses. ''Saurornithoides'' was a rather small troodontid. Though a possible adult, the type specimen has a midline skull length of 189 millimetres, compared to 272 millimetres for ''Zanabazar junior'', itself ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saurornithoididae
Troodontidae is a clade of bird-like theropod dinosaurs. During most of the 20th century, troodontid fossils were few and incomplete and they have therefore been allied, at various times, with many dinosaurian lineages. More recent fossil discoveries of complete and articulated specimens (including specimens which preserve feathers, eggs, embryos, and complete juveniles), have helped to increase understanding about this group. Anatomical studies, particularly studies of the most primitive troodontids, like ''Sinovenator'', demonstrate striking anatomical similarities with '' Archaeopteryx'' and primitive dromaeosaurids, and demonstrate that they are relatives comprising a clade called Paraves. Description Troodontids are a group of small, bird-like, gracile maniraptorans. All troodontids have unique features of the skull, such as large numbers of closely spaced teeth in the lower jaw. Troodontids have sickle-claws and raptorial hands, and some of the highest non- avian enc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phil Currie
Philip John Currie (born March 13, 1949) is a Canadian palaeontologist and museum curator who helped found the Royal Tyrrell Museum of Palaeontology in Drumheller, Alberta and is now a professor at the University of Alberta in Edmonton. In the 1980s, he became the director of the Canada-China Dinosaur Project, the first cooperative palaeontological partnering between China and the West since the Central Asiatic Expeditions in the 1920s, and helped describe some of the first feathered dinosaurs. He is one of the primary editors of the influential ''Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs'', and his areas of expertise include theropods (especially Tyrannosauridae), the origin of birds, and dinosaurian migration patterns and herding behavior. He was one of the models for palaeontologist Alan Grant in the film ''Jurassic Park''. Biography Currie received his Bachelor of Science degree from the University of Toronto in 1972, a Master of Science degree from McGill University in 1975, and a Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humanoid
A humanoid (; from English ''human'' and '' -oid'' "resembling") is a non-human entity with human form or characteristics. The earliest recorded use of the term, in 1870, referred to indigenous peoples in areas colonized by Europeans. By the 20th century, the term came to describe fossils which were morphologically similar, but not identical, to those of the human skeleton. Although this usage was common in the sciences for much of the 20th century, it is now considered rare. More generally, the term can refer to anything with distinctly human characteristics or adaptations, such as possessing opposable anterior forelimb-appendages (i.e. thumbs), visible spectrum- binocular vision (i.e. having two eyes), or biomechanic plantigrade- bipedalism (i.e. the ability to walk on heels and metatarsals in an upright position). Science fiction media frequently present sentient extraterrestrial lifeforms as humanoid as a byproduct of convergent evolution. In theoretical convergent ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two Medicine Formation
The Two Medicine Formation is a geological formation, or rock body, in northwestern Montana and southern Alberta that was deposited between and (million years ago), during Campanian (Late Cretaceous) time. It crops out to the east of the Rocky Mountain Overthrust Belt, and the western portion (about thick) of this formation is folded and faulted while the eastern part, which thins out into the Sweetgrass Arch, is mostly undeformed plains. Below the formation are the nearshore (beach and tidal zone) deposits of the Virgelle Sandstone, and above it is the marine Bearpaw Shale. Throughout the Campanian, the Two Medicine Formation was deposited between the western shoreline of the Late Cretaceous Interior Seaway and the eastward advancing margin of the Cordilleran Overthrust Belt. The Two Medicine Formation is mostly sandstone, deposited by rivers and deltas. History of research In 1913, a US Geological Survey crew headed by Eugene Stebinger and a US National Museum crew head ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |