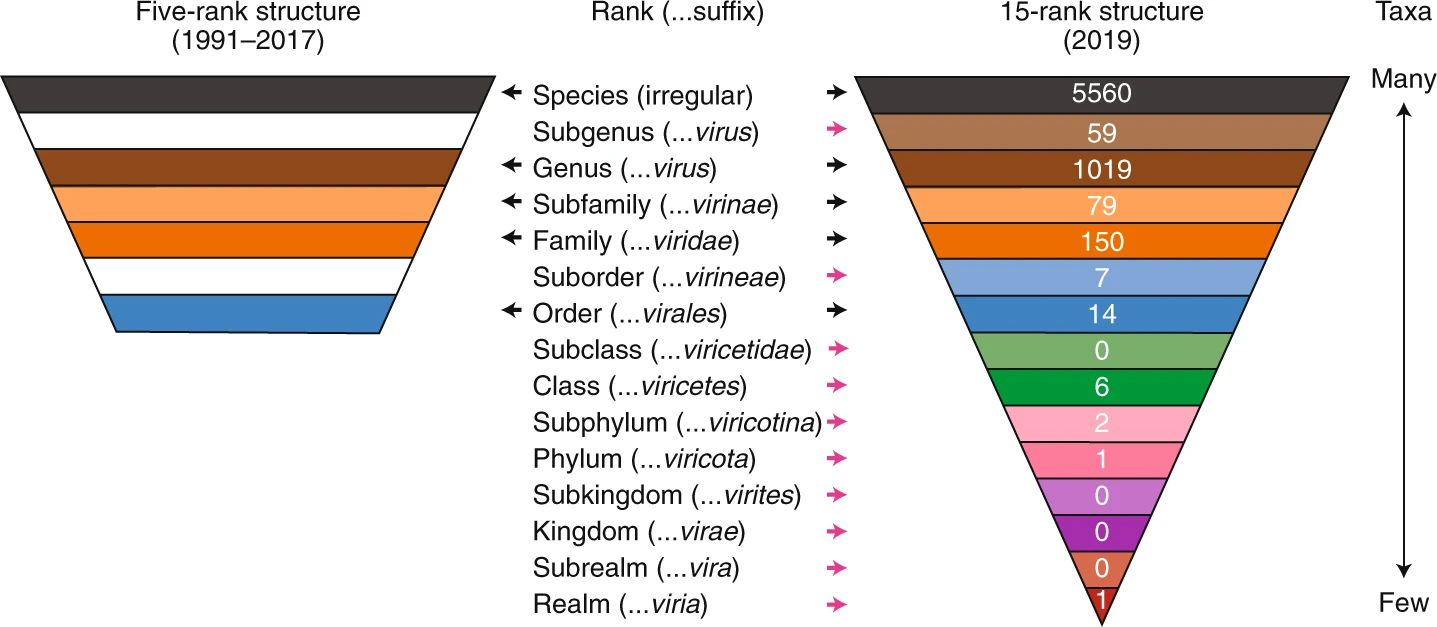
|
Stelpaviricetes
''Stelpaviricetes'' is a class of non-enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses which infect plants and animals. Characteristic of the group is a VPg protein attached to the 5'-end of the genome and a conserved 3C- like protease from the PA clan of proteases for processing the translated polyprotein Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called prot .... The name of the group is a syllabic abbreviation of member orders "''stel''lavirales, ''pa''tatavirales" with the suffix ''-viricetes'' denoting a virus class. Orders The following orders are recognized: * '' Patatavirales'' * '' Stellavirales'' References {{Baltimore classification Viruses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive-strand RNA Virus
Positive-strand RNA viruses (+ssRNA viruses) are a group of related viruses that have positive-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid. The positive-sense genome can act as messenger RNA (mRNA) and can be directly translated into viral proteins by the host cell's ribosomes. Positive-strand RNA viruses encode an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) which is used during replication of the genome to synthesize a negative-sense antigenome that is then used as a template to create a new positive-sense viral genome. Positive-strand RNA viruses are divided between the phyla ''Kitrinoviricota'', ''Lenarviricota'', and ''Pisuviricota'' (specifically classes ''Pisoniviricetes'' and '' Stelpavirictes'') all of which are in the kingdom '' Orthornavirae'' and realm '' Riboviria''. They are monophyletic and descended from a common RNA virus ancestor. In the Baltimore classification system, +ssRNA viruses belong to Group IV. Positive-sense RNA viruses include pathogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Envelope
A viral envelope is the outermost layer of many types of viruses. It protects the genetic material in their life cycle when traveling between host cells. Not all viruses have envelopes. Numerous human pathogenic viruses in circulation are encased in lipid bilayers, and they infect their target cells by causing the viral envelope and cell membrane to fuse. Although there are effective vaccines against some of these viruses, there is no preventative or curative medicine for the majority of them. In most cases, the known vaccines operate by inducing antibodies that prevent the pathogen from entering cells. This happens in the case of enveloped viruses when the antibodies bind to the viral envelope proteins. The membrane fusion event that triggers viral entrance is caused by the viral fusion protein. Many enveloped viruses only have one protein visible on the surface of the particle, which is required for both mediating adhesion to the cell surface and for the subsequent membrane fusi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude the fungi and some algae, as well as the prokaryotes (the archaea and bacteria). By one definition, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (Latin name for "green plants") which is sister of the Glaucophyta, and consists of the green algae and Embryophyta (land plants). The latter includes the flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms, ferns and their allies, hornworts, liverworts, and mosses. Most plants are multicellular organisms. Green plants obtain most of their energy from sunlight via photosynthesis by primary chloroplasts that are derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria. Their chloroplasts contain chlorophylls a and b, which gives them their green color. Some plants are parasitic or mycotrophic and have lost the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directionality (molecular Biology)
Directionality, in molecular biology and biochemistry, is the end-to-end chemical orientation of a single strand of nucleic acid. In a single strand of DNA or RNA, the chemical convention of naming carbon atoms in the nucleotide pentose-sugar-ring means that there will be a 5′ end (usually pronounced "five-prime end"), which frequently contains a phosphate group attached to the 5′ carbon of the ribose ring, and a 3′ end (usually pronounced "three-prime end"), which typically is unmodified from the ribose -OH substituent. In a DNA double helix, the strands run in opposite directions to permit base pairing between them, which is essential for replication or transcription of the encoded information. Nucleic acids can only be synthesized in vivo in the 5′-to-3′ direction, as the polymerases that assemble various types of new strands generally rely on the energy produced by breaking nucleoside triphosphate bonds to attach new nucleoside monophosphates to the 3′- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picornain 3C
Picornain 3C () is a protease found in picornaviruses, which cleaves peptide bonds of non-terminal sequences. Picornain 3C’s endopeptidase activity is primarily responsible for the catalytic process of selectively cleaving Gln-Gly bonds in the polyprotein of poliovirus and with substitution of Glu for Gln, and Ser or Thr for Gly in other picornaviruses. Picornain 3C are cysteine proteases related by amino acid sequence to trypsin-like serine proteases. Picornain 3C is encoded by enteroviruses, rhinoviruses, aphtoviruses and cardioviruses. These genera of picoviruses cause a wide range of infections in humans and mammals. Picornavirus belongs to the family ''Picornaviridae''. Picornavirus virions are nonenveloped and the +ssRNA nonsegmented genome is encapsulated in an icosahedral protein structure made from four capsid proteins encoded by the virus. Picornavirus viral replication typically takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. Picornavirus +ssRNA genome then gets translated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3C-like Protease
The 3C-like protease (3CLpro) or main protease (Mpro), formally known as C30 endopeptidase or 3-chymotrypsin-like protease, is the main protease found in coronaviruses. It cleaves the coronavirus polyprotein at eleven conserved sites. It is a cysteine protease and a member of the PA clan of proteases. It has a cysteine-histidine catalytic dyad at its active site and cleaves a Gln–(Ser/Ala/Gly) peptide bond. The Enzyme Commission refers to this family as SARS coronavirus main proteinase (Mpro; ). The 3CL protease corresponds to coronavirus nonstructural protein 5 (nsp5). The "3C" in the common name refers to the 3C protease (3Cpro) which is a homologous protease found in picornaviruses. Function The 3C-like protease is able to catalytically cleave a peptide bond between a glutamine at position P1 and a small amino acid (serine, alanine, or glycine) at position P1'. The SARS coronavirus 3CLpro can for instance self-cleave the following peptides: The protease is impor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PA Clan Of Proteases
The PA clan ( Proteases of mixed nucleophile, superfamily A) is the largest group of proteases with common ancestry as identified by structural homology. Members have a chymotrypsin-like fold and similar proteolysis mechanisms but can have identity of <10%. The clan contains both and (different ). PA clan proteases can be found in , |
Polyproteins
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes including apoptosis, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or misfolded proteins in cells. Consequently, abnormality in the regulation of proteolysis can cause disease. Proteolysis can also be used as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, and it may also be used in industry, for example in food process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syllabic Abbreviation
An abbreviation (from Latin ''brevis'', meaning ''short'') is a shortened form of a word or phrase, by any method. It may consist of a group of letters or words taken from the full version of the word or phrase; for example, the word ''abbreviation'' can itself be represented by the abbreviation ''abbr.'', ''abbrv.'', or ''abbrev.''; ''NPO'', for nil (or nothing) per (by) os (mouth) is an abbreviated medical instruction. It may also consist of initials only, a mixture of initials and words, or words or letters representing words in another language (for example, e.g., i.e. or RSVP). Some types of abbreviations are acronyms (some pronounceable, some initialisms) or grammatical contractions or crasis. An abbreviation is a shortening by any of these or other methods. Different types of abbreviation Acronyms, initialisms, contractions and crasis share some semantic and phonetic functions, and all four are connected by the term "abbreviation" in loose parlance. A initialism is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus Classification
Virus classification is the process of naming viruses and placing them into a taxonomic system similar to the classification systems used for cellular organisms. Viruses are classified by phenotypic characteristics, such as morphology, nucleic acid type, mode of replication, host organisms, and the type of disease they cause. The formal taxonomic classification of viruses is the responsibility of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) system, although the Baltimore classification system can be used to place viruses into one of seven groups based on their manner of mRNA synthesis. Specific naming conventions and further classification guidelines are set out by the ICTV. A catalogue of all the world's known viruses has been proposed and, in 2013, some preliminary efforts were underway. Definitions Species definition Species form the basis for any biological classification system. Before 1982, it was thought that viruses could not be made to fit Ernst Mayr's r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patatavirales
''Potyviridae'' is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses that encompasses more than 30% of known plant viruses, many of which are of great agricultural significance. The family has 12 genera and 235 species, three of which are unassigned to a genus. Structure Potyvirid virions are nonenveloped, flexuous filamentous, rod-shaped particles. The diameter is around 12–15 nm, with a length of 200–300 nm. Genome Genomes are linear and usually nonsegmented, around 8–12kb in length, consisting of positive-sense RNA, which is surrounded by a protein coat made up of a single viral encoded protein called a capsid. All induce the formation of virus inclusion bodies called cylindrical inclusions (‘pinwheels’) in their hosts. These consist of a single protein (about 70 kDa) made in their hosts from a single viral genome product. Member viruses encode large polypeptides that are cleaved into mature proteins. In 5'–3' order these proteins are * P1 (a serine p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |