|
Stelliferous
This is the timeline of the stelliferous era but also partly charts the primordial era, and charts more of the degenerate era of the heat death scenario. The scale is 10 \times \log_\ where \ is the time since the Big Bang expressed in years. Example: one million years is \ = 1000000;\ \ 10 \times \log_\ = 10\times 6 = 60. Timeline ImageSize = width:720 height:2000 PlotArea = left:40 right:235 bottom:75 top:75 Colors = id:period1 value:rgb(1,1,0.7) # light yellow id:period2 value:rgb(0.7,0.7,1) # light blue id:events value:rgb(1,0.7,1) # light purple id:era2 value:lightorange id:era1 Value:yellowgreen DateFormat = yyyy Period = from:56 till:200 TimeAxis = format:yyyy orientation:vertical ScaleMajor = unit:year increment:10 start:60 ScaleMinor = unit:year increment:1 start:56 AlignBars = justify BarData = bar:Era bar:Dummy2 bar:Dummy3 bar:Periods bar:Dummy4 bar:Events TextData = fontsize:M pos:(250,75) text:" Photon epoch" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Timeline Of The Big Bang
The chronology of the universe describes the history and future of the universe according to Big Bang cosmology. Research published in 2015 estimates the earliest stages of the universe's existence as taking place 13.8 billion years ago, with an uncertainty of around 21 million years at the 68% confidence level. The Planck Collaboration in 2015 published the estimate of 13.799 ± 0.021 billion years ago (68% confidence interval). See PDF: page 32, Table 4, Age/Gyr, last column. Outline Chronology in five stages For the purposes of this summary, it is convenient to divide the chronology of the universe since it originated, into five parts. It is generally considered meaningless or unclear whether time existed before this chronology: The very early universe The first picosecond (10−12) of cosmic time. It includes the Planck epoch, during which currently established laws of physics may not apply; the emergence in stages of the four known fundamental interactions o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg) |
Future Of An Expanding Universe
Observations suggest that the expansion of the universe will continue forever. The prevailing theory is that the universe will cool as it expands, eventually becoming too cold to sustain life. For this reason, this future scenario once popularly called " Heat Death" is now known as the "Big Chill" or "Big Freeze". If dark energy—represented by the cosmological constant, a ''constant'' energy density filling space homogeneously, or scalar fields, such as quintessence or moduli, ''dynamic'' quantities whose energy density can vary in time and space—accelerates the expansion of the universe, then the space between clusters of galaxies will grow at an increasing rate. Redshift will stretch ancient, incoming photons (even gamma rays) to undetectably long wavelengths and low energies. Stars are expected to form normally for 1012 to 1014 (1–100 trillion) years, but eventually the supply of gas needed for star formation will be exhausted. As existing stars run out of fuel and cea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Graphical Timeline From Big Bang To Heat Death
This is the timeline of the Universe from Big Bang to Heat Death scenario. The different eras of the universe are shown. The heat death will occur in around 1.7×10106 years, if protons decay. Timeline ImageSize = width:840 height:2000 PlotArea = left:40 right:235 bottom:75 top:75 Colors = id:period1 value:rgb(1,1,0.7) # light yellow id:period2 value:rgb(0.7,0.7,1) # light blue id:events value:rgb(1,0.7,1) # light purple id:era1 Value:yellowgreen id:era2 value:lightorange id:time1 Value:coral id:time2 Value:lavender DateFormat = yyyy Period = from:-171 till:300 TimeAxis = format:yyyy orientation:vertical # order:reverse does not work ScaleMajor = unit:year increment:10 start:-170 ScaleMinor = unit:year increment:1 start:-171 AlignBars = justify BarData = bar:Clock bar:Dummy1 bar:Era bar:Dummy2 bar:Dummy3 bar:Periods bar:Dummy4 bar:Events TextData = fontsize:M pos:(365,75) text:"Planck epoch" # pos:(210,50) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Graphical Timeline Of The Universe
This more than 20-billion-year timeline of our universe shows the best estimates of major events from the universe's beginning to anticipated future events. Zero on the scale is the present day. A large step on the scale is one billion years; a small step, one hundred million years. The past is denoted by a minus sign: e.g., the oldest rock on Earth was formed about four billion years ago and this is marked at -4e+09 years, where 4e+09 represents 4 times 10 to the power of 9. The "Big Bang" event most likely happened 13.8 billion years ago; see age of the universe. Timeline ImageSize = width:773 height:2000 PlotArea = left:60 right:60 bottom:45 top:45 AlignBars = early Colors = id:period1 value:rgb(1,1,0.7) # light yellow id:period2 value:rgb(0.7,0.7,1) # light blue id:events value:rgb(1,0.7,1) # light purple id:time1 Value:yellowgreen id:time2 value:lightorange id:elapse1 Value:coral id:elapse2 Value:lavender id:grayKindOf Value:gray(0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Graphical Timeline Of The Big Bang
This timeline of the Big Bang shows a sequence of events as currently theorized by scientists. It is a logarithmic scale that shows 10 \cdot \log_ ''second'' instead of ''second''. For example, one microsecond is 10 \cdot \log_ 0.000 001 = 10 \cdot (-6) = -60. To convert −30 read on the scale to second calculate 10^ = 10^ = 0.001 second = one millisecond. On a logarithmic time scale a step lasts ten times longer than the previous step. ImageSize = width:720 height:1000 PlotArea = left:40 right:256 bottom:75 top:75 Colors = id:period1 value:rgb(1,1,0.7) # light yellow id:period2 value:rgb(0.7,0.7,1) # light blue id:events value:rgb(1,0.7,1) # light purple id:era1 Value:yellowgreen id:era2 value:lightorange id:time1 Value:coral id:time2 Value:lavender DateFormat = yyyy Period = from:-430 till:155 TimeAxis = format:yyyy orientation:vertical # order:reverse does not work ScaleMajor = unit:year increment:10 start:-430 # second ScaleMi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
1 E19 S And More
An order of magnitude of time is usually a decimal prefix or decimal order-of-magnitude quantity together with a base unit of time, like a microsecond or a million years. In some cases, the order of magnitude may be implied (usually 1), like a "second" or "year". In other cases, the quantity name implies the base unit, like "century". In most cases, the base unit is seconds or years. Prefixes are not usually used with a base unit of years. Therefore, it is said "a million years" instead of "a mega year". Clock time and calendar time have duodecimal or sexagesimal orders of magnitude rather than decimal, e.g., a year is 12 months, and a minute is 60 seconds. The smallest meaningful increment of time is the Planck time―the time light takes to traverse the Planck distance, many decimal orders of magnitude smaller than a second. The largest realized amount of time, based on known scientific data, is the age of the universe, about 13.8 billion years—the tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Isaac Asimov
Isaac Asimov ( ; 1920 – April 6, 1992) was an American writer and professor of biochemistry at Boston University. During his lifetime, Asimov was considered one of the "Big Three" science fiction writers, along with Robert A. Heinlein and Arthur C. Clarke. A prolific writer, he wrote or edited more than 500 books. He also wrote an estimated 90,000 letters and postcards. Best known for his hard science fiction, Asimov also wrote mystery fiction, mysteries and fantasy, as well as much nonfiction. Asimov's most famous work is the ''Foundation series, Foundation'' series, the first three books of which won the one-time Hugo Award for "Best All-Time Series" in 1966. His other major series are the ''Galactic Empire series, Galactic Empire'' series and the ''Robot series, Robot'' series. The ''Galactic Empire'' novels are set in the much earlier history of the same fictional universe as the ''Foundation'' series. Later, with ''Foundation and Earth'' (1986), he linked this distant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
The Last Question
"The Last Question" is a science fiction short story by American writer Isaac Asimov. It first appeared in the November 1956 issue of Science Fiction Quarterly and was anthologized in the collections Nine Tomorrows (1959), The Best of Isaac Asimov (1973), Robot Dreams (1986), The Best Science Fiction of Isaac Asimov (1986), the retrospective Opus 100 (1969), and in Isaac Asimov: The Complete Stories, Vol. 1 (1990). While he also considered it one of his best works, “The Last Question” was Asimov's favorite short story of his own authorship, and is one of a loosely connected series of stories concerning a fictional computer called Multivac. Through successive generations, humanity questions Multivac on the subject of entropy. The story overlaps science fiction, theology, and philosophy. History In conceiving Multivac, Asimov was extrapolating the trend towards centralization that characterized computation technology planning in the 1950s to an ultimate centrally-ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Black Dwarf
A black dwarf is a theoretical stellar remnant, specifically a white dwarf that has cooled sufficiently to no longer emit significant heat or light. Because the time required for a white dwarf to reach this state is calculated to be longer than the current age of the universe (13.8 billion years), no black dwarfs are expected to exist in the universe so far. The temperature of the coolest white dwarfs is one observational limit on the universe's age. The name "black dwarf" has also been applied to hypothetical late-stage cooled brown dwarfs – substellar objects with insufficient mass (less than approximately 0.07 ) to maintain hydrogen-burning nuclear fusion. Formation A white dwarf is what remains of a main-sequence star of low or medium mass (below approximately 9 to 10 solar masses ()) after it has either expelled or fused all the elements for which it has sufficient temperature to fuse. What is left is then a dense sphere of electron-degenerate matter that co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
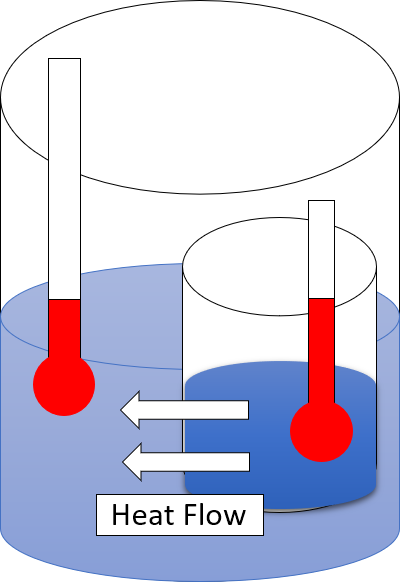 |
Second Law Of Thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law based on universal experience concerning heat and energy interconversions. One simple statement of the law is that heat always moves from hotter objects to colder objects (or "downhill"), unless energy in some form is supplied to reverse the direction of heat flow. Another definition is: "Not all heat energy can be converted into work in a cyclic process."Young, H. D; Freedman, R. A. (2004). ''University Physics'', 11th edition. Pearson. p. 764. The second law of thermodynamics in other versions establishes the concept of entropy as a physical property of a thermodynamic system. It can be used to predict whether processes are forbidden despite obeying the requirement of conservation of energy as expressed in the first law of thermodynamics and provides necessary criteria for spontaneous processes. The second law may be formulated by the observation that the entropy of isolated systems left to spontaneous evolution cannot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Ultimate Fate Of The Universe
The ultimate fate of the universe is a topic in physical cosmology, whose theoretical restrictions allow possible scenarios for the evolution and ultimate fate of the universe to be described and evaluated. Based on available observational evidence, deciding the fate and evolution of the universe has become a valid cosmological question, being beyond the mostly untestable constraints of mythological or theological beliefs. Several possible futures have been predicted by different scientific hypotheses, including that the universe might have existed for a finite and infinite duration, or towards explaining the manner and circumstances of its beginning. Observations made by Edwin Hubble during the 1930s–1950s found that galaxies appeared to be moving away from each other, leading to the currently accepted Big Bang theory. This suggests that the universe began very dense about 13.787 billion years ago, and it has expanded and (on average) become less dense ever since. Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |