|
Stanford Torus
The Stanford torus is a proposed NASA design for a space habitat capable of housing 10,000 to 140,000 permanent residents. The Stanford torus was proposed during the 1975 NASA Summer Study, conducted at Stanford University, with the purpose of exploring and speculating on designs for future space colonies (Gerard O'Neill later proposed his Island One or Bernal sphere as an alternative to the torus). "Stanford torus" refers only to this particular version of the design, as the concept of a ring-shaped rotating space station was previously proposed by Wernher von Braun and Herman Potočnik. It consists of a torus, or doughnut-shaped ring, that is 1.8 km in diameter (for the proposed 10,000 person habitat described in the 1975 Summer Study) and rotates once per minute to provide between 0.9g and 1.0g of artificial gravity on the inside of the outer ring via centrifugal force. Sunlight is provided to the interior of the torus by a system of mirrors, including a large no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford Torus External View By Don Davis AC76-0525
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is considered among the most prestigious universities in the world. Stanford was founded in 1885 by Leland and Jane Stanford in memory of their only child, Leland Stanford Jr., who had died of typhoid fever at age 15 the previous year. Leland Stanford was a U.S. senator and former governor of California who made his fortune as a railroad tycoon. The school admitted its first students on October 1, 1891, as a coeducational and non-denominational institution. Stanford University struggled financially after the death of Leland Stanford in 1893 and again after much of the campus was damaged by the 1906 San Francisco earthquake. Following World War II, provost of Stanford Frederick Terman inspired and supported faculty and graduates' entrepreneuriali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to support scientific re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O'Neill Cylinder
An O'Neill cylinder (also called an O'Neill colony) is a space settlement concept proposed by American physicist Gerard K. O'Neill in his 1976 book '' The High Frontier: Human Colonies in Space''. O'Neill proposed the colonization of space for the 21st century, using materials extracted from the Moon and later from asteroids. An O'Neill cylinder would consist of two counter-rotating cylinders. The cylinders would rotate in opposite directions to cancel any gyroscopic effects that would otherwise make it difficult to keep them aimed toward the Sun. Each would be in diameter and long, connected at each end by a rod via a bearing system. Their rotation would provide artificial gravity. Background While teaching undergraduate physics at Princeton University, O'Neill set his students the task of designing large structures in outer space, with the intent of showing that living in space could be desirable. Several of the designs were able to provide volumes large enough to be sui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
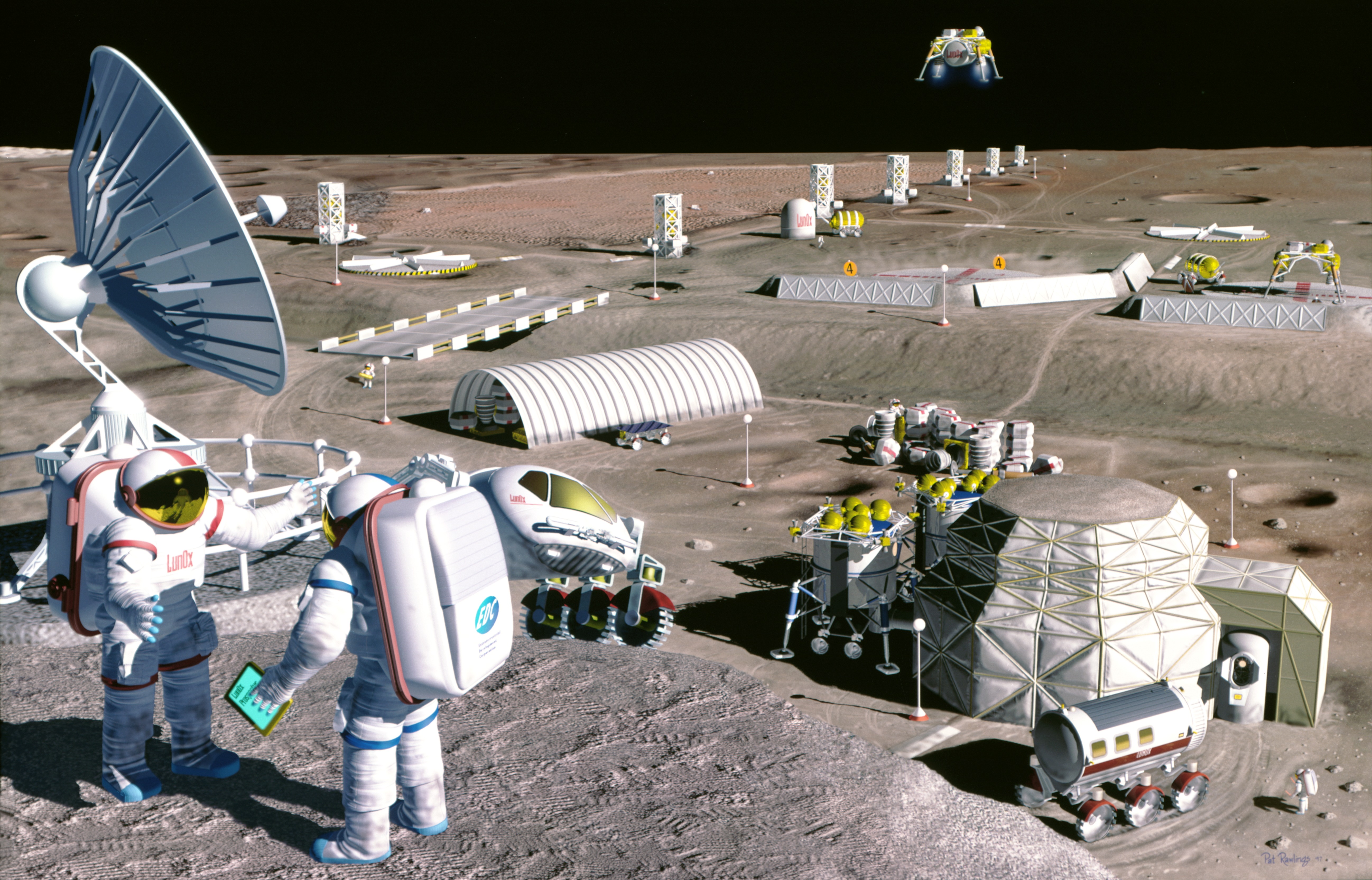
Colonization Of The Moon
Colonization of the Moon or Lunar settlement is a process, or concept employed by some proposals, for claiming robotic or human exploitation and settlement on the Moon. Laying claim to the Moon has been declared illegal through international space law and no state has made such claims, despite having a range of probes and artificial remains on the Moon. While a range of proposals for missions of lunar colonization, exploitation or permanent exploration have been raised, current projects for establishing permanent crewed presence on the Moon are not for colonizing the Moon, but rather focus on building moonbases for exploration and to a lesser extent for exploitation of lunar resources. The commercialization of the Moon is a contentious issue for national and international lunar regulation and laws (such as the Moon treaty). History Colonization of the Moon has been imagined as early as the first half of the 17th century by John Wilkins in ''A Discourse Concerning a New Pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Habitat
A space habitat (also called a space settlement, space colony, spacestead, space city, orbital habitat, orbital settlement, orbital colony, orbital stead or orbital city) is a more advanced form of living quarters than a space station or habitation module, in that it is intended as a permanent settlement or green habitat rather than as a simple way-station or other specialized facility. No space habitat has been constructed yet, but many design concepts, with varying degrees of realism, have come both from engineers and from science-fiction authors. The term ''space habitat'' sometimes includes more broadly habitats built on or in a body other than Earth—such as the Moon, Mars or an asteroid. This article concentrates on self-contained structures envisaged for micro-g environments. Definition A space habitat, or more precisely a space settlement, is any large-scale habitation facility in space, or more particularly in outer space or an orbit. A space habitat is typically de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Soil
Lunar soil is the fine fraction of the regolith found on the surface of the Moon. Its properties can differ significantly from those of terrestrial soil. The physical properties of lunar soil are primarily the result of mechanical disintegration of basaltic and anorthositic rock, caused by continual meteoric impacts and bombardment by solar and interstellar charged atomic particles over billions of years. The process is largely one of mechanical weathering in which the particles are ground to progressively finer size over time. This situation contrasts fundamentally to terrestrial dirt formation, mediated by the presence of molecular oxygen (O2), humidity, atmospheric wind, and a robust array of contributing biological processes. ''Lunar soil'' typically refers to only the finer fraction of lunar regolith, which is composed of grains 1 cm in diameter or less, but is often used interchangeably. Lunar dust generally connotes even finer materials than ''lunar soil''. There is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolution Per Minute
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines. Standards ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionless unit equal to 1, which it refers to as a revolution, but does not define the revolution as a unit. It defines a unit of rotational frequency equal to s−1. The superseded standard ISO 80000-3:2006 did however state with reference to the unit name 'one', symbol '1', that "The special name revolution, symbol r, for this unit is widely used in specifications on rotating machines." The International System of Units (SI) does not recognize rpm as a unit, and defines the unit of frequency, Hz, as equal to s−1. :\begin 1~&\text &&=& 60~&\text \\ \frac~&\text &&=& 1~&\text \end A corresponding but distinct quantity for describing rotation is angular velocity, for which the SI unit is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asteroid Mining
Asteroid mining is the hypothetical exploitation of materials from asteroids and other minor planets, including near-Earth objects. Notable asteroid mining challenges include the high cost of spaceflight, unreliable identification of asteroids which are suitable for mining, and the challenges of extracting usable material in a space environment. Asteroid sample return research missions (see completed missions ''Hayabusa'' and '' Hayabusa2'' and in-progress ''OSIRIS-REx'') illustrate the challenges of collecting ore from space using current technology. As of 2021, less than 1 gram of asteroid material has been successfully returned to Earth from space. In progress missions promise to increase this amount to approximately 60 grams (two ounces). Asteroid research missions are complex endeavors and return a tiny amount of material (less than 1 milligram ''Hayabusa'', 100 milligrams ''Hayabusa2'', 60 grams planned ''OSIRIS-REx'') relative to the size and expense of these projects ($3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagrangian Point
In celestial mechanics, the Lagrange points (; also Lagrangian points or libration points) are points of equilibrium for small-mass objects under the influence of two massive orbiting bodies. Mathematically, this involves the solution of the restricted three-body problem in which two bodies are far more massive than the third. Normally, the two massive bodies exert an unbalanced gravitational force at a point, altering the orbit of whatever is at that point. At the Lagrange points, the gravitational forces of the two large bodies and the centrifugal force balance each other. This can make Lagrange points an excellent location for satellites, as few orbit corrections are needed to maintain the desired orbit. Small objects placed in orbit at Lagrange points are in equilibrium in at least two directions relative to the center of mass of the large bodies. For any combination of two orbital bodies there are five Lagrange points, L1 to L5, all in the orbital plane of the two lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Catcher
A mass catcher is a theoretical device envisioned to decelerate a mass of material, usually in the context of outer space transport. A large object placed in space with a conical shape would stop other objects hurtling towards the center of the back of it. These other objects would not bounce back into space because small debris from previous impacts with the mass catcher would form a coating similar to regolith, which would absorb the impact and decelerate the object to the velocity of the mass catcher. Interstellar transport of bulk materials would be a potential source of demand for the construction of a mass catcher (e.g. lunar or asteroidal mined ore originally accelerated into a trajectory intercepting the mass catcher by a mass driver). This device was proposed in 1978 by Thomas A. Heppenheimer. See also * Mass driver A mass driver or electromagnetic catapult is a proposed method of non-rocket spacelaunch which would use a linear motor to accelerate and catapult paylo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Driver
A mass driver or electromagnetic catapult is a proposed method of non-rocket spacelaunch which would use a linear motor to Acceleration, accelerate and catapult Payload (air and space craft), payloads up to high speeds. Existing and contemplated mass drivers use coils of wire energized by electricity to make electromagnets, though a rotary mass driver has also been proposed. Sequential firing of a row of electromagnets accelerates the payload along a path. After leaving the path, the payload continues to move due to momentum. Although any device used to propel a Ballistics, ballistic payload is technically a mass driver, in this context a mass driver is essentially a coilgun that magnetically accelerates a package consisting of a magnetizable holder containing a payload. Once the payload has been accelerated, the two separate, and the holder is slowed and recycled for another payload. Mass drivers can be used to propel spacecraft in three different ways: A large, ground-based mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |