|
St Michael's Church, Kirkham
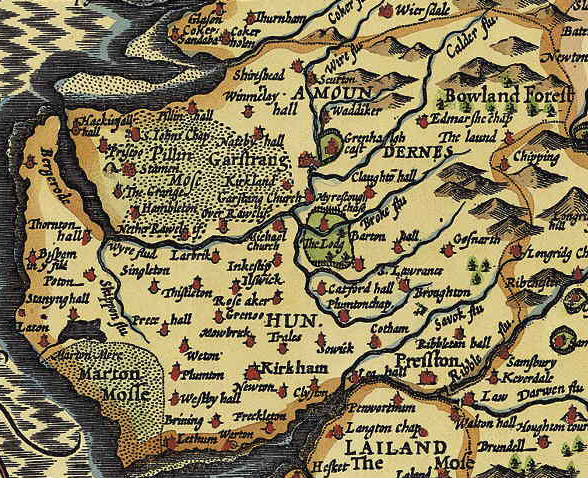
St Michael's Church is in the town of Kirkham, Lancashire, England. The church is recorded in the National Heritage List for England as a designated Grade II* listed building. It is an active Anglican parish church in the diocese of Blackburn, the archdeaconry of Lancaster and the deanery of Kirkham. History The earliest evidence of a church on the site is in 684 AD. Kirkham was one of the oldest foundations in Lancashire and one of only three listed in the Doomsday Book as existing in Amounderness. This hundred was part of the vast possessions of Roger earl of Poictou and the church was held by the Priory Church of St. Mary, Lancaster. William of York (died 1154) issued a charter to return the church to Shrewsbury Abbey. In a later charter, dated 5 December 1280, King Edward I conveyed the advowson of Kirkham to the abbot and convent of Vale Royal Abbey which held the church until the dissolution in the reign King Henry VIII. It was then given to the dean and chapter of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirkham, Lancashire
Kirkham (originally Kirkam-in-Amounderness) is a town and civil parish in the Borough of Fylde in Lancashire, England, midway between Blackpool and Preston ( west of Preston) and adjacent to the smaller town of Wesham. It owes its existence to Carr Hill upon which it was built and which was the location of a Roman fort. At the census of 2011, it had a population 7,194. History In his 1878 ''History of the Fylde of Lancashire'', John Porter described Kirkham as ".. probably the earliest inhabited locality in the Fylde district."Porter, J. MRCS, LSA (1878''History of the Fylde of Lancashire'' Fleetwood and Blackpool, W. Porter and Sons Publisher, Chapter XII – The Parish of Kirkham. Remains found at Carleton in the 1970s of an elk with two harpoons embedded suggest that the Fylde was inhabited as long ago as 8,000 BC.Singleton, F. J. (1980), ''Kirkham – A Short History'', Kirkham & District Local History Society. The town is pre-Roman in its origin with a name originatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of Blackburn
The Diocese of Blackburn is a Church of England diocese, covering much of Lancashire, created on 12 November 1926 from part of the Diocese of Manchester. The diocese includes the towns of Blackburn, Blackpool and Burnley, the cities of Lancaster and Preston, as well as a large part of the Ribble Valley. The cathedral is Blackburn Cathedral. The See is currently vacant following the retirement of Julian Henderson. The diocesan retreat and conference centre is located at Whalley Abbey in the Ribble Valley, alongside the ruins of the 14th-century Cistercian monastery, dissolved in 1537. The abbey was in private possession until 1923 and has been in the possession of the Diocese of Blackburn since 1926. Bishops Alongside the diocesan Bishop of Blackburn, the diocese has two suffragan bishops: Jill Duff, Bishop suffragan of Lancaster, consecrated in 2018; and Philip North, Bishop suffragan of Burnley, appointed in 2015. *Since 1994, Michael Vickers, retired area Bishop of Colc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry VIII Of England
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disagreement with Pope Clement VII about such an annulment led Henry to initiate the English Reformation, separating the Church of England from papal authority. He appointed himself Supreme Head of the Church of England and dissolved convents and monasteries, for which he was excommunicated by the pope. Henry is also known as "the father of the Royal Navy" as he invested heavily in the navy and increased its size from a few to more than 50 ships, and established the Navy Board. Domestically, Henry is known for his radical changes to the English Constitution, ushering in the theory of the divine right of kings in opposition to papal supremacy. He also greatly expanded royal power during his reign. He frequently used charges of treason and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vale Royal Abbey
Vale Royal Abbey is a former medieval abbey and later country house in Whitegate England. The precise location and boundaries of the abbey are difficult to determine in today's landscape. The original building was founded c. 1270 by the Lord Edward, later Edward I for Cistercian monks. Edward had supposedly taken a vow during a rough sea crossing in the 1260s. Civil wars and political upheaval delayed the build until 1272, the year he inherited the throne. The original site at Darnhall was unsatisfactory, so was moved a few miles north to the Delamere Forest. Edward intended the structure to be on a grand scale—had it been completed it would have been the largest Cistercian monastery in the country—but his ambitions were frustrated by recurring financial difficulties. Early during construction, England became involved in war with Wales. As the treasury was thus in need of resources, Vale Royal lost all of its grants, skilled masons and builders. When work resumed in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward I Of England
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies of Aquitaine and Gascony as a vassal of the French king. Before his accession to the throne, he was commonly referred to as the Lord Edward. The eldest son of Henry III, Edward was involved from an early age in the political intrigues of his father's reign, which included a rebellion by the English barons. In 1259, he briefly sided with a baronial reform movement, supporting the Provisions of Oxford. After reconciliation with his father, however, he remained loyal throughout the subsequent armed conflict, known as the Second Barons' War. After the Battle of Lewes, Edward was held hostage by the rebellious barons, but escaped after a few months and defeated the baronial leader Simon de Montfort at the Battle of Evesham in 1265. Within two years the rebellion was extin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrewsbury Abbey
The Abbey Church of Saint Peter and Saint Paul, Shrewsbury (commonly known as Shrewsbury Abbey) is an ancient foundation in Shrewsbury, the county town of Shropshire, England. The Abbey was founded in 1083 as a Benedictine monastery by the Norman Earl of Shrewsbury, Roger de Montgomery. It grew to be one of the most important and influential abbeys in England, and an important centre of pilgrimage. Although much of the Abbey was destroyed in the 16th century, the nave survived as a parish church, and today serves as the mother church for the Parish of Holy Cross. The Abbey is a Grade I listed building and is a member of the Greater Churches Group. It is located to the east of Shrewsbury town centre, near the English Bridge, and is surrounded by a triangular area which is today referred to as Abbey Foregate. History Foundation Before the Norman conquest a small Saxon chapel dedicated to St Peter stood outside the east gate of Shrewsbury; it had been built by Siward, son o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Of York
William of York (late 11th century – 8 June 1154) was an English priest and twice Archbishop of York, before and after a rival, Henry Murdac. He was thought to be related to King Stephen of England, who helped to secure his election to the province after several candidates had failed to gain papal confirmation. William faced opposition from the Cistercians, who after the election of the Cistercian Pope Eugene III, had William deposed in favour of a Cistercian, Murdac. From 1147 until 1153, William worked to be restored to York, which he achieved after the deaths of Murdac and Eugene III. He did not hold the province long, dying shortly after his return, allegedly from poison in the chalice he used to celebrate Mass.Emma J. Wells, "Making Sense of Things", ''History Today'', Vol. 69, No. 5 (May 2019), p. 40 Miracles were reported at his tomb from 1177. He was canonised in 1226. Early life Born William fitzHerbert in York, William was the son of Herbert of Winchester, or Herbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancaster, Lancashire
Lancaster (, ) is a city and the county town of Lancashire, England, standing on the River Lune. Its population of 52,234 compares with one of 138,375 in the wider City of Lancaster local government district. The House of Lancaster was a branch of the English royal family. The Duchy of Lancaster still holds large estates on behalf of Charles III, who is also Duke of Lancaster. Its long history is marked by Lancaster Castle, Lancaster Priory Church, Lancaster Cathedral and the Ashton Memorial. It is the seat of Lancaster University and has a campus of the University of Cumbria. The Port of Lancaster played a big role in the city's growth, but for many years the outport of Glasson Dock has become the main shipping facility. History The name of the city first appeared in the Domesday Book of 1086, as ''Loncastre'', where "Lon" refers to the River Lune and "castre" (from the Old English ''cæster'' and Latin ''castrum'' for "fort") to the Roman fort that stood on the site. Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancaster Priory
Lancaster Priory, formally the Priory Church of St Mary, is the Church of England parish church of the city of Lancaster, Lancashire, England. It is located near Lancaster Castle and since 1953 has been designated a Grade I listed building. It is in the deanery of Lancaster, the archdeaconry of Lancaster and the Diocese of Blackburn. Its benefice is combined with that of St John and St Anne. History Pre-construction A Roman fort existed on the site from the 1st century, and some form of church may possibly have been established around the year 200.Fleury, p.4 A Saxon church is thought to have stood on the site from the sixth century. In 1912 excavations revealed a wall beneath the present chancel area which may be from Roman times, and a small Saxon doorway has been exposed in the west wall of the present nave. It also believed that a monastery had been established here prior to the Norman conquest of England. Construction to 17th century In 1094 Roger de Poitou establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred (county Subdivision)
A hundred is an administrative division that is geographically part of a larger region. It was formerly used in England, Wales, some parts of the United States, Denmark, Southern Schleswig, Sweden, Finland, Norway, the Bishopric of Ösel–Wiek, Curonia, the Ukrainian state of the Cossack Hetmanate and in Cumberland County, New South Wales, Cumberland County in the British Colony of New South Wales. It is still used in other places, including in Australia (in South Australia and the Northern Territory). Other terms for the hundred in English and other languages include ''#wapentake, wapentake'', ''herred'' (Danish and Bokmål, Bokmål Norwegian), ''herad'' (Nynorsk, Nynorsk Norwegian), ''hérað'' (Icelandic), ''härad'' or ''hundare'' (Swedish), ''Harde'' (German), ''hiird'' (North Frisian language, North Frisian), ''satakunta'' or ''kihlakunta'' (Finnish), ''kihelkond'' (Estonian), ''kiligunda'' (Livonian), ''cantref'' (Welsh) and ''sotnia'' (Slavic). In Ireland, a similar subdi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amounderness
The Amounderness Hundred () is one of the six subdivisions of the historic county of Lancashire in North West England, but the name is older than the system of hundreds first recorded in the 13th century and might best be described as the name of a Norse wapentake. In the Domesday Book, it was used for some territories north of the River Ribble included together with parts of Yorkshire. The area eventually became part of Lancashire, sitting geographically between the Rivers Lune and Ribble, in the strip of coast between the Irish Sea and Bowland Forest. Etymology and history In the 19th century, the name was considered to have been first recorded in 705, as Hacmunderness. The Domesday Book in 1086 spells it Agemundrenessa. There are two suggested etymologies for Amounderness. The traditional 19th century reading was that the name derived from ''ac'' (oak) and ''mund'' (protection), "a ness or promontory sheltered by oaks". This was given currency by Porter.Porter, J, ''A His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)