|
St Mary Magdalene, Richmond
St Mary Magdalene, Richmond, in the Anglican Diocese of Southwark, is a Grade II* listed parish church on Paradise Road, Richmond, London. The church, dedicated to Jesus' companion Mary Magdalene, was built in the early 16th century but has been greatly altered so that, apart from the tower, the visible parts of the church date from the 18th, 19th and early 20th centuries. Since 1996 St Mary Magdalene's has been part of the Richmond Team Ministry, which also includes the churches of St John the Divine and St Matthias. It has a strong musical tradition and offers choral services each Sunday. History The initial chapel was built in around 1220. The church was entirely reconstructed during the reign of Henry VII who, after rebuilding the royal palace of Sheen, renamed Sheen as Richmond in 1501. The two bottom sections of the tower that survive from this period were re-faced in flint in 1904. In the early 17th century, a south aisle was added to the nave. The north aisl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britain by the 3rd century and to the 6th-century Gregorian mission to Kent led by Augustine of Canterbury. The English church renounced papal authority in 1534 when Henry VIII failed to secure a papal annulment of his marriage to Catherine of Aragon. The English Reformation accelerated under Edward VI's regents, before a brief restoration of papal authority under Queen Mary I and King Philip. The Act of Supremacy 1558 renewed the breach, and the Elizabethan Settlement charted a course enabling the English church to describe itself as both Reformed and Catholic. In the earlier phase of the English Reformation there were both Roman Catholic martyrs and radical Protestant martyrs. The later phases saw the Penal Laws punish Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Matthias Church, Richmond
St Matthias Church is a Grade II listed Anglican church in Richmond, London. It was built in the Victorian Gothic style in 1857, and is described by Bridget Cherry and Nikolaus Pevsner as "the grandest church in Richmond". The architect was George Gilbert Scott. The church is dedicated to Saint Matthias who was, according to the Acts of the Apostles, chosen by the apostles to replace Judas Iscariot following the latter's betrayal of Jesus and his subsequent death. The church building is located at the top of Richmond Hill at the intersection of Friars Stile Road, Kings Road, and Church Road. At , the spire of the church is a familiar landmark for miles around. The church was renovated in the 1970s by the architects Hutchison, Locke & Monk. St Matthias' Church is part of the Richmond Team Ministry, which also includes the churches of St John the Divine and St Mary Magdalene. Gallery Rose window Richmond.jpg, The rose window St Matthias Church Richmond Greater London close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richmond Cemetery
Richmond Cemetery is a cemetery on Lower Grove Road in Richmond in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames, England. The cemetery opened in 1786 on a plot of land granted by an Act of Parliament the previous year. The cemetery has been expanded several times and now occupies a 15-acre (6-hectare) site which, prior to the expansion of London, was a rural area of Surrey. It is bounded to the east by Richmond Park and to the north by East Sheen Cemetery, with which it is now contiguous and whose chapel is used for services by both cemeteries. Richmond cemetery originally contained two chapels—one Anglican and one Nonconformist—both built in the Gothic revival style, but both are now privately owned and the Nonconformist chapel today falls outside the cemetery walls after a redrawing of its boundaries. Many prominent people are buried in the cemetery, as are 39 soldiers who died at the South African Hospital in Richmond Park during the First World War and many ex-servicemen fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Elizabeth Braddon
Mary Elizabeth Braddon (4 October 1835 – 4 February 1915) was an English popular novelist of the Victorian era. She is best known for her 1862 sensation novel ''Lady Audley's Secret'', which has also been dramatised and filmed several times. Biography Born in Soho, London, Mary Elizabeth Braddon was privately educated. Her mother Fanny separated from her father Henry because of his infidelities in 1840, when Mary was five. When Mary was ten years old, her brother Edward Braddon left for India and later Australia, where he became Premier of Tasmania. Mary worked as an actress for three years, when she was befriended by Clara and Adelaide Biddle. They were only playing minor roles, but Braddon was able to support herself and her mother. Adelaide noted that Braddon's interest in acting waned as she took up writing novels. Mary met John Maxwell (1824–1895), a publisher of periodicals, in April 1861 and moved in with him in 1861.Victor E. Neuburg, ''The Popular Press Companion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
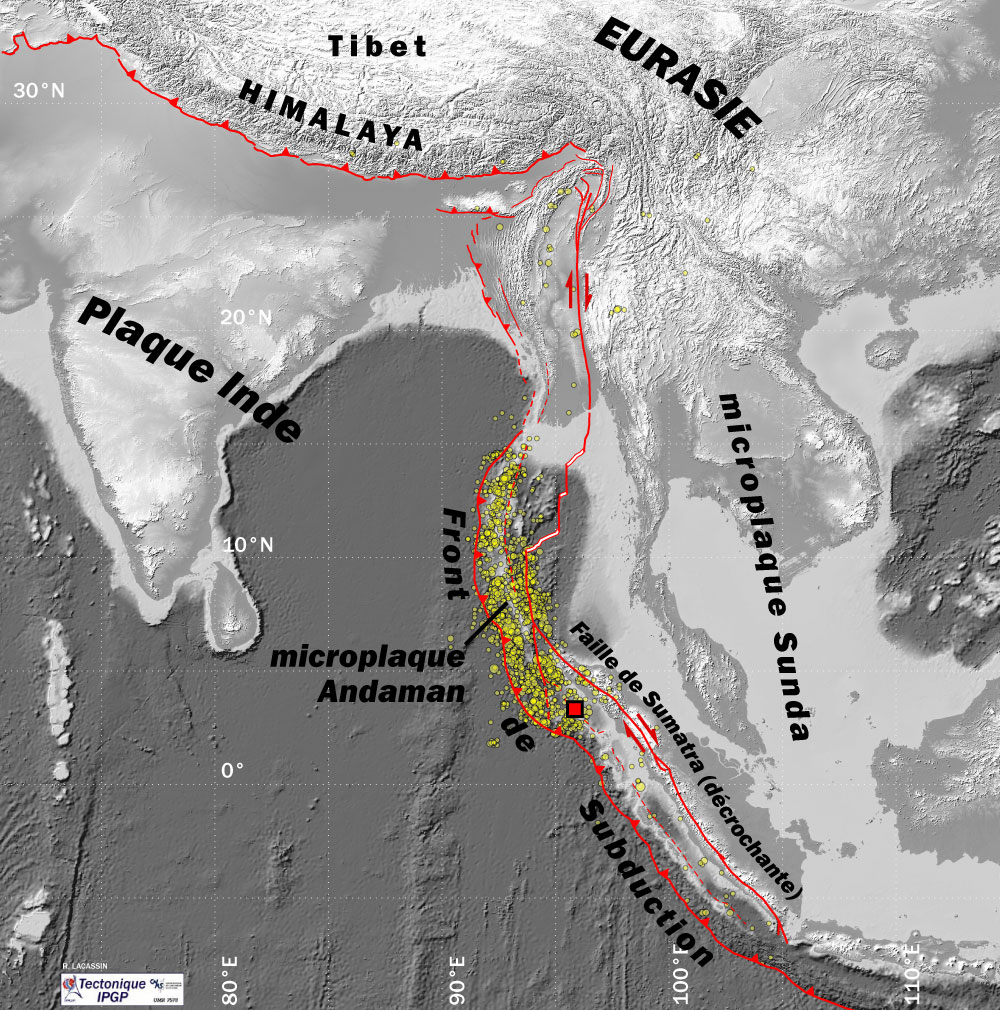
2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake And Tsunami
An earthquake and a tsunami, known as the Boxing Day Tsunami and, by the scientific community, the Sumatra–Andaman earthquake, occurred at 07:58:53 local time (UTC+7) on 26 December 2004, with an epicentre off the west coast of northern Sumatra, Indonesia. It was an undersea megathrust earthquake that registered a magnitude of 9.1–9.3 , reaching a Mercalli intensity up to IX in certain areas. The earthquake was caused by a rupture along the fault between the Burma Plate and the Indian Plate. A series of massive tsunami waves grew up to high once heading inland, after being created by the underwater seismic activity offshore. Communities along the surrounding coasts of the Indian Ocean were devastated, and the tsunamis killed an estimated 227,898 people in 14 countries, making it one of the deadliest natural disasters in recorded history. The direct results caused major disruptions to living conditions and commerce in coastal provinces of surrounded countries, including Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Attenborough
Richard Samuel Attenborough, Baron Attenborough, (; 29 August 192324 August 2014) was an English actor, filmmaker, and entrepreneur. He was the president of the Royal Academy of Dramatic Art (RADA) and the British Academy of Film and Television Arts (BAFTA), as well as the life president of Chelsea FC. He joined the Royal Air Force during the Second World War and served in the film unit, going on several bombing raids over Europe and filming the action from the rear gunner's position. He was the older brother of broadcaster Sir David Attenborough and motor executive John Attenborough. He was married to actress Sheila Sim from 1945 until his death. As an actor, he is best remembered for his film roles in '' Brighton Rock'' (1948), ''I'm All Right Jack'' (1959), '' The Great Escape'' (1963), ''The Sand Pebbles'' (1966), ''Doctor Dolittle'' (1967), '' 10 Rillington Place'' (1971), '' Jurassic Park'' (1993), and ''Miracle on 34th Street'' (1994). In 1952 he appeared on the West En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Mary Magdalene's, Richmond, Richard Attenborough Memorial
ST, St, or St. may refer to: Arts and entertainment * Stanza, in poetry * Suicidal Tendencies, an American heavy metal/hardcore punk band * Star Trek, a science-fiction media franchise * Summa Theologica, a compendium of Catholic philosophy and theology by St. Thomas Aquinas * St or St., abbreviation of "State", especially in the name of a college or university Businesses and organizations Transportation * Germania (airline) (IATA airline designator ST) * Maharashtra State Road Transport Corporation, abbreviated as State Transport * Sound Transit, Central Puget Sound Regional Transit Authority, Washington state, US * Springfield Terminal Railway (Vermont) (railroad reporting mark ST) * Suffolk County Transit, or Suffolk Transit, the bus system serving Suffolk County, New York Other businesses and organizations * Statstjänstemannaförbundet, or Swedish Union of Civil Servants, a trade union * The Secret Team, an alleged covert alliance between the CIA and American industr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Revival Architecture
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly serious and learned admirers of the neo-Gothic styles sought to revive medieval Gothic architecture, intending to complement or even supersede the neoclassical styles prevalent at the time. Gothic Revival draws upon features of medieval examples, including decorative patterns, finials, lancet windows, and hood moulds. By the middle of the 19th century, Gothic had become the preeminent architectural style in the Western world, only to fall out of fashion in the 1880s and early 1890s. The Gothic Revival movement's roots are intertwined with philosophical movements associated with Catholicism and a re-awakening of high church or Anglo-Catholic belief concerned by the growth of religious nonconformism. Ultimately, the "Anglo-Catholicism" t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestry
A vestry was a committee for the local secular and ecclesiastical government for a parish in England, Wales and some English colonies which originally met in the vestry or sacristy of the parish church, and consequently became known colloquially as the "vestry". Overview For many centuries, in the absence of any other authority (which there would be in an incorporated city or town), the vestries were the sole ''de facto'' local government in most of the country, and presided over local, communal fundraising and expenditure until the mid or late 19th century using local established Church chairmanship. They were concerned for the spiritual but also the temporal as well as physical welfare of parishioners and its parish amenities, collecting local rates or taxes and taking responsibility for numerous functions such as the care of the poor, the maintaining of roads, and law enforcement, etc. More punitive matters were dealt with by the manorial court and hundred court, and latter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chancel
In church architecture, the chancel is the space around the altar, including the choir and the sanctuary (sometimes called the presbytery), at the liturgical east end of a traditional Christian church building. It may terminate in an apse. Overview The chancel is generally the area used by the clergy and choir during worship, while the congregation is in the nave. Direct access may be provided by a priest's door, usually on the south side of the church. This is one definition, sometimes called the "strict" one; in practice in churches where the eastern end contains other elements such as an ambulatory and side chapels, these are also often counted as part of the chancel, especially when discussing architecture. In smaller churches, where the altar is backed by the outside east wall and there is no distinct choir, the chancel and sanctuary may be the same area. In churches with a retroquire area behind the altar, this may only be included in the broader definition of chancel. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Box Pew
A box pew is a type of church pew that is encased in panelling and was prevalent in England and other Protestant countries from the 16th to early 19th centuries. History in England Before the rise of Protestantism, seating was not customary in churches and only accorded to the lord of the manor, civic dignitaries and finally churchwardens. After 1569 stools and seating were installed in Protestant churches primarily because the congregation were expected to listen to sermons, and various types of seating were introduced including the box pew. There are records of box pews being installed in Ludlow parish church before 1577. Box pews provided privacy and allowed the family to sit together. In the 17th century they could include windows, curtains, tables and even fireplaces, and were treated as personal property that could be willed to legatees. Sometimes the panelling was so high it was difficult to see out, and the privacy was used as a cover for non-devotional activity. William Hog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type building, the strict definition of the term "nave" is restricted to the central aisle. In a broader, more colloquial sense, the nave includes all areas available for the lay worshippers, including the side-aisles and transepts.Cram, Ralph Adams Nave The Catholic Encyclopedia. Vol. 10. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1911. Accessed 13 July 2018 Either way, the nave is distinct from the area reserved for the choir and clergy. Description The nave extends from the entry—which may have a separate vestibule (the narthex)—to the chancel and may be flanked by lower side-aisles separated from the nave by an arcade. If the aisles are high and of a width comparable to the central nave, the structure is sometimes said to have three naves. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)