|
St John's Church, Wroxall
St. John's Church, Wroxall is a parish church in the Church of England located in Wroxall, Isle of Wight. History The church dates from 1875 to 1877 by the architect T. R. Saunders.The Buildings of England, Hampshire and the Isle of Wight. Nikolaus Pevsner Sir Nikolaus Bernhard Leon Pevsner (30 January 1902 – 18 August 1983) was a German-British art historian and architectural historian best known for his monumental 46-volume series of county-by-county guides, ''The Buildings of England'' (1 ... The tower was added in 1911. Its consecration service was performed by the Archdeacon of Winchester on 21 December 1877. The church consisted of a chancel, nave, organ chamber, south porch and a small western belfry housing one bell, and provided seating for 130. The stone excavated during the construction of the nearby Ventnor railway tunnel provided the building material. This kept down costs but it has since proved to be of poor quality and the building is in constant n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John The Evangelist
John the Evangelist ( grc-gre, Ἰωάννης, Iōánnēs; Aramaic: ܝܘܚܢܢ; Ge'ez: ዮሐንስ; ar, يوحنا الإنجيلي, la, Ioannes, he, יוחנן cop, ⲓⲱⲁⲛⲛⲏⲥ or ⲓⲱ̅ⲁ) is the name traditionally given to the author of the Gospel of John. Christians have traditionally identified him with John the Apostle, John of Patmos, and John the Presbyter, although this has been disputed by most modern scholars. Identity The Gospel of John refers to an otherwise unnamed "disciple whom Jesus loved", who "bore witness to and wrote" the Gospel's message.Theissen, Gerd and Annette Merz. The historical Jesus: a comprehensive guide. Fortress Press. 1998. translated from German (1996 edition). Chapter 2. Christian sources about Jesus. The author of the Gospel of John seemed interested in maintaining the internal anonymity of the author's identity, although interpreting the Gospel in the light of the Synoptic Gospels and considering that the author names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britain by the 3rd century and to the 6th-century Gregorian mission to Kent led by Augustine of Canterbury. The English church renounced papal authority in 1534 when Henry VIII failed to secure a papal annulment of his marriage to Catherine of Aragon. The English Reformation accelerated under Edward VI's regents, before a brief restoration of papal authority under Queen Mary I and King Philip. The Act of Supremacy 1558 renewed the breach, and the Elizabethan Settlement charted a course enabling the English church to describe itself as both Reformed and Catholic. In the earlier phase of the English Reformation there were both Roman Catholic martyrs and radical Protestant martyrs. The later phases saw the Penal Laws punish Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wroxall, Isle Of Wight
Wroxall is a village and civil parish in the central south of the Isle of Wight. It is close to Appuldurcombe House. The parish church is St. John's Church, Wroxall. Bus services operated by Southern Vectis link the village with the towns of Newport, Ryde, Sandown, Shanklin and Ventnor Ventnor () is a seaside resort and civil parish established in the Victorian era on the southeast coast of the Isle of Wight, England, from Newport. It is situated south of St Boniface Down, and built on steep slopes leading down to the sea. ..., as well as intermediate villages. References Villages on the Isle of Wight Civil parishes in the Isle of Wight {{IsleofWight-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
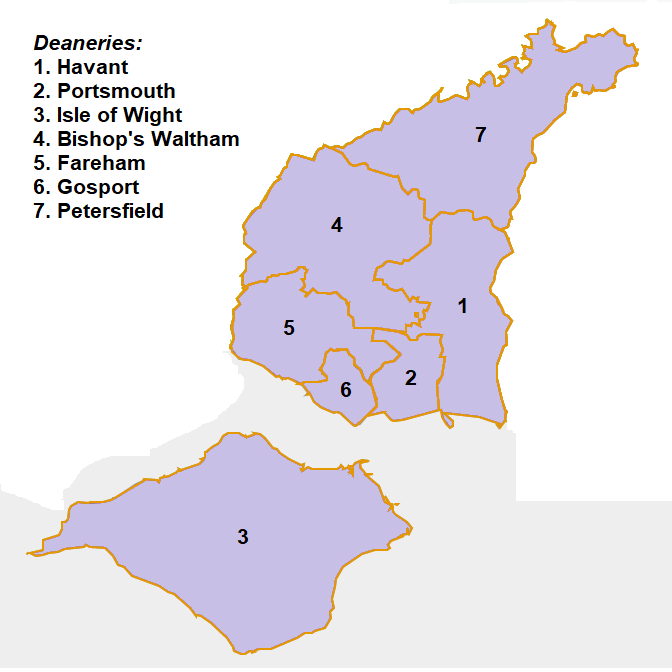
Anglican Diocese Of Portsmouth
The Diocese of Portsmouth is an administrative division of the Church of England Province of Canterbury in England. The diocese covers south-east Hampshire and the Isle of Wight. The see is based in the City of Portsmouth in Hampshire, where the seat is located at the Cathedral Church of St Thomas of Canterbury. Origin The Diocese of Portsmouth was created on 1 May 1927 under George V from the Diocese of Winchester. It consists of the three archdeaconries of: *Portsdown (comprising the deaneries of Portsmouth and Havant); * The Meon (comprising the deaneries of Fareham, Gosport, Petersfield and Bishop's Waltham); *The Isle of Wight (comprising the deanery of the Isle of Wight). Bishops The Bishop of Portsmouth leads the diocese as one of two diocesan bishops in the Church of England not assisted by a suffragan bishop, the other being the Bishop of Hereford. Alternative episcopal oversight (for parishes in the diocese which do not accept the ordination of women as priests ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Canterbury
The Province of Canterbury, or less formally the Southern Province, is one of two ecclesiastical provinces which constitute the Church of England. The other is the Province of York (which consists of 12 dioceses). Overview The Province consists of 30 dioceses, covering roughly two-thirds of England, parts of Wales, all of the Channel Islands and continental Europe, Morocco, Turkey, Mongolia and the territory of the former Soviet Union (under the jurisdiction of the Diocese of Gibraltar in Europe). The Province previously also covered all of Wales but lost most of its jurisdiction in 1920, when the then four dioceses of the Church in Wales were disestablished and separated from Canterbury to form a distinct ecclesiastical province of the Anglican Communion. The Province of Canterbury retained jurisdiction over eighteen areas of Wales that were defined as part of "border parishes", parishes whose ecclesiastical boundaries straddled the temporal boundary between England and Wale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parish Church
A parish church (or parochial church) in Christianity is the church which acts as the religious centre of a parish. In many parts of the world, especially in rural areas, the parish church may play a significant role in community activities, often allowing its premises to be used for non-religious community events. The church building reflects this status, and there is considerable variety in the size and style of parish churches. Many villages in Europe have churches that date back to the Middle Ages, but all periods of architecture are represented. Roman Catholic Church Each diocese (administrative unit, headed by a Bishop) is divided into parishes. Normally, a parish comprises all Catholics living within its geographically defined area. Within a diocese, there can also be overlapping parishes for Catholics belonging to a particular rite, language, nationality, or community. Each parish has its own central church called the parish church, where religious services take pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolaus Pevsner
Sir Nikolaus Bernhard Leon Pevsner (30 January 1902 – 18 August 1983) was a German-British art historian and architectural historian best known for his monumental 46-volume series of county-by-county guides, ''The Buildings of England'' (1951–74). Life Nikolaus Pevsner was born in Leipzig, Saxony, the son of Anna and her husband Hugo Pevsner, a Russian-Jewish fur merchant. He attended St. Thomas School, Leipzig, and went on to study at several universities, Munich, Berlin, and Frankfurt am Main, before being awarded a doctorate by Leipzig in 1924 for a thesis on the Baroque architecture of Leipzig. In 1923, he married Carola ("Lola") Kurlbaum, the daughter of distinguished Leipzig lawyer Alfred Kurlbaum. He worked as an assistant keeper at the Dresden Gallery between 1924 and 1928. He converted from Judaism to Lutheranism early in his life. During this period he became interested in establishing the supremacy of German modernist architecture after becoming aware of Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archdeacon Of Winchester
The Archdeacon of Winchester is a senior ecclesiastical officer within the Diocese of Winchester. History Originally created as the archdeaconry of Basingstoke on 26 July 1927 within the Diocese of Winchester and from the old Archdeacon of Bournemouth, Archdeaconry of Winchester, the office replaced that of Archdeacon of Surrey, which had been newly transferred to the Diocese of Guildford. The Basingstoke archdeaconry was renamed to Winchester in 2000, the ancient Archdeaconry of Winchester having been renamed to Archdeacon of Bournemouth, Bournemouth. As archdeacon, he is responsible for the disciplinary supervision of the clergy within the archdeaconry, which (on its creation) consisted of six rural deaneries in the northern part of the diocese: Aldershot, Alton, Andover, Basingstoke, Kingsclere and Silchester. Since a pastoral reorganisation in 2000, the diocese now consists of the new archdeaconry of Winchester (the north) and the Archdeacon of Bournemouth, archdeaconry of Bou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)