|
St John's Church, Egremont
St John's Church is in Liscard Road, Egremont, Merseyside, England. It is a redundant Anglican parish church, formerly in the diocese of Chester. The church is recorded in the National Heritage List for England as a designated Grade II listed building. History St John's was built in 1832–33, and was designed by Henry Turberville Edwards; it is his only known work. The church was built on land owned by Sir John Tobin, whose son became the first vicar. The church was consecrated on 31 October 1831 by the Rt. Revd. John Bird Sumner, bishop of Chester, and it opened for worship on 19 May 1833. In 1881 it was restored by Cornelius Sherlock; this included removing the galleries, replacing box pews with benches, moving the organ, enclosing the chancel, and adding two new windows. In 1942 the church was damaged by bomb blast, and was repaired in the 1950s with a new roof. It was declared redundant on 1 July 2004, and approval for conversion into residential us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egremont, Merseyside
Egremont is an area of Wallasey, in the Metropolitan Borough of Wirral, Merseyside, England. Historically part of Cheshire and in the north east of the Wirral Peninsula, it is bordered by New Brighton to the north, Liscard to the west and Seacombe to the south. History Egremont was considered part of the Liscard township until the 1820s, when expansion of Liscard was deemed significant enough that it should be split into two townships. One of the earliest buildings in Egremont was the Liscard Manor House, also known as the 'Seabank'. Dating back to the 1790s, it was home to the influential Penkett and Maddock families. The area which grew up around Seabank was eventually to become the Mariners' home founded in 1892 by William Cliff. The name of the area was decided by one Captain Askew who built a house in the area as early as 1835 and named the village 'Egremont' after his Cumberland birthplace. Egremont Ferry was built in 1827 and was the longest pier on Merseyside until i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chancel
In church architecture, the chancel is the space around the altar, including the choir and the sanctuary (sometimes called the presbytery), at the liturgical east end of a traditional Christian church building. It may terminate in an apse. Overview The chancel is generally the area used by the clergy and choir during worship, while the congregation is in the nave. Direct access may be provided by a priest's door, usually on the south side of the church. This is one definition, sometimes called the "strict" one; in practice in churches where the eastern end contains other elements such as an ambulatory and side chapels, these are also often counted as part of the chancel, especially when discussing architecture. In smaller churches, where the altar is backed by the outside east wall and there is no distinct choir, the chancel and sanctuary may be the same area. In churches with a retroquire area behind the altar, this may only be included in the broader definition of chancel. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type building, the strict definition of the term "nave" is restricted to the central aisle. In a broader, more colloquial sense, the nave includes all areas available for the lay worshippers, including the side-aisles and transepts.Cram, Ralph Adams Nave The Catholic Encyclopedia. Vol. 10. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1911. Accessed 13 July 2018 Either way, the nave is distinct from the area reserved for the choir and clergy. Description The nave extends from the entry—which may have a separate vestibule (the narthex)—to the chancel and may be flanked by lower side-aisles separated from the nave by an arcade. If the aisles are high and of a width comparable to the central nave, the structure is sometimes said to have three naves. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reredos
A reredos ( , , ) is a large altarpiece, a screen, or decoration placed behind the altar in a church. It often includes religious images. The term ''reredos'' may also be used for similar structures, if elaborate, in secular architecture, for example very grand carved chimneypieces. It also refers to a simple, low stone wall placed behind a hearth. Description A reredos can be made of stone, wood, metal, ivory, or a combination of materials. The images may be painted, carved, gilded, composed of mosaics, and/or embedded with niches for statues. Sometimes a tapestry or another fabric such as silk or velvet is used. Derivation and history of the term ''Reredos'' is derived through Middle English from the 14th-century Anglo-Norman ''areredos'', which in turn is from''arere'' 'behind' +''dos'' 'back', from Latin ''dorsum''. (Despite its appearance, the first part of the word is not formed by doubling the prefix "re-", but by an archaic spelling of "rear".) In the 14th and 15th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
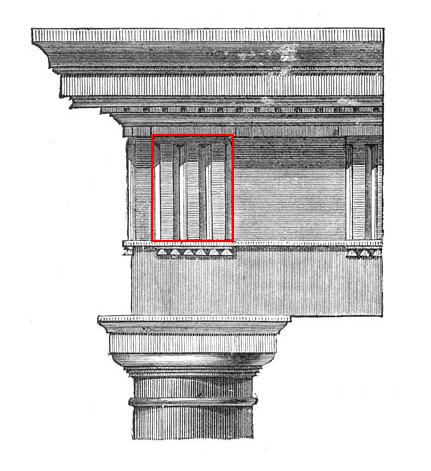
Pilaster
In classical architecture Classical architecture usually denotes architecture which is more or less consciously derived from the principles of Greek and Roman architecture of classical antiquity, or sometimes even more specifically, from the works of the Roman architect V ..., a pilaster is an :Architectural elements, architectural element used to give the appearance of a supporting column and to articulate an extent of wall, with only an ornamental function. It consists of a flat surface raised from the main wall surface, usually treated as though it were a column, with a Capital (architecture), capital at the top, plinth (base) at the bottom, and the various other column elements. In contrast to a pilaster, an engaged column or buttress can support the structure of a wall and roof above. In human anatomy, a pilaster is a ridge that extends vertically across the femur, which is unique to modern humans. Its structural function is unclear. Definition In discussing Leon Battis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parapet
A parapet is a barrier that is an extension of the wall at the edge of a roof, terrace, balcony, walkway or other structure. The word comes ultimately from the Italian ''parapetto'' (''parare'' 'to cover/defend' and ''petto'' 'chest/breast'). Where extending above a roof, a parapet may simply be the portion of an exterior wall that continues above the edge line of the roof surface, or may be a continuation of a vertical feature beneath the roof such as a fire wall or party wall. Parapets were originally used to defend buildings from military attack, but today they are primarily used as guard rails, to conceal rooftop equipment, reduce wind loads on the roof, and to prevent the spread of fires. In the Bible the Hebrews are obligated to build a parapet on the roof of their houses to prevent people falling (Deuteronomy 22:8). Parapet types Parapets may be plain, embattled, perforated or panelled, which are not mutually exclusive terms. *Plain parapets are upward extensions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Architrave
In classical architecture, an architrave (; from it, architrave "chief beam", also called an epistyle; from Greek ἐπίστυλον ''epistylon'' "door frame") is the lintel or beam that rests on the capitals of columns. The term can also apply to all sides, including the vertical members, of a frame with mouldings around a door or window. The word "architrave" has come to be used to refer more generally to a style of mouldings (or other elements) framing a door, window or other rectangular opening, where the horizontal "head" casing extends across the tops of the vertical side casings where the elements join (forming a butt joint, as opposed to a miter joint). Classical architecture In an entablature in classical architecture, it is the lowest part, below the frieze and cornice. The word is derived from the Greek and Latin words ''arche'' and ''trabs'' combined to mean "main beam". The architrave is different in the different Classical orders. In the Tuscan o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pediment
Pediments are gables, usually of a triangular shape. Pediments are placed above the horizontal structure of the lintel, or entablature, if supported by columns. Pediments can contain an overdoor and are usually topped by hood moulds. A pediment is sometimes the top element of a portico. For symmetric designs, it provides a center point and is often used to add grandness to entrances. The tympanum, the triangular area within the pediment, is often decorated with a pedimental sculpture which may be freestanding or a relief sculpture. The tympanum may hold an inscription, or in modern times, a clock face. Pediments are found in ancient Greek architecture as early as 600 BC (e.g. the archaic Temple of Artemis). Variations of the pediment occur in later architectural styles such as Classical, Neoclassical and Baroque. Gable roofs were common in ancient Greek temples with a low pitch (angle of 12.5° to 16°). History The pediment is found in classical Greek temples, Et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frieze
In architecture, the frieze is the wide central section part of an entablature and may be plain in the Ionic or Doric order, or decorated with bas-reliefs. Paterae are also usually used to decorate friezes. Even when neither columns nor pilasters are expressed, on an astylar wall it lies upon the architrave ("main beam") and is capped by the moldings of the cornice. A frieze can be found on many Greek and Roman buildings, the Parthenon Frieze being the most famous, and perhaps the most elaborate. This style is typical for the Persians. In interiors, the frieze of a room is the section of wall above the picture rail and under the crown moldings or cornice. By extension, a frieze is a long stretch of painted, sculpted or even calligraphic decoration in such a position, normally above eye-level. Frieze decorations may depict scenes in a sequence of discrete panels. The material of which the frieze is made of may be plasterwork, carved wood or other decorative medium. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triglyph
Triglyph is an architectural term for the vertically channeled tablets of the Doric frieze in classical architecture, so called because of the angular channels in them. The rectangular recessed spaces between the triglyphs on a Doric frieze are called metopes. The raised spaces between the channels themselves (within a triglyph) are called ''femur'' in Latin or ''meros'' in Greek. In the strict tradition of classical architecture, a set of guttae, the six triangular "pegs" below, always go with a triglyph above (and vice versa), and the pair of features are only found in entablatures of buildings using the Doric order. The absence of the pair effectively converts a building from being in the Doric order to being in the Tuscan order. The triglyph is largely thought to be a tectonic and skeuomorphic representation in stone of the wooden beam ends of the typical primitive hut, as described by Vitruvius and Renaissance writers. The wooden beams were notched in three separate plac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entablature
An entablature (; nativization of Italian , from "in" and "table") is the superstructure of moldings and bands which lies horizontally above columns, resting on their capitals. Entablatures are major elements of classical architecture, and are commonly divided into the architrave (the supporting member immediately above; equivalent to the lintel in post and lintel construction), the frieze (an unmolded strip that may or may not be ornamented), and the cornice (the projecting member below the pediment). The Greek and Roman temples are believed to be based on wooden structures, the design transition from wooden to stone structures being called petrification. Overview The structure of an entablature varies with the orders of architecture. In each order, the proportions of the subdivisions (architrave, frieze, cornice) are defined by the proportions of the column. In Roman and Renaissance interpretations, it is usually approximately a quarter of the height of the column. Varian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluting (architecture)
Fluting in architecture consists of shallow grooves running along a surface. The term typically refers to the grooves (flutes) running vertically on a column shaft or a pilaster, but need not necessarily be restricted to those two applications. If the hollowing out of material meets in a point, the point (sharp ridge) is called an arris. If the raised ridge between two flutes is blunt, the ridge is a . Purpose Fluting promotes a play of light on a column which helps the column appear more perfectly round than a smooth column. As a strong vertical element it also has the visual effect of minimizing any horizontal joints. Greek architects viewed rhythm as an important design element. As such, fluting was often used on buildings and temples to increase the sense of rhythm. It may also be incorporated in columns to make them look thinner, lighter, and more elegant. There is debate as to whether fluting was originally used in imitation of ancient woodworking practices, mimicking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |