|
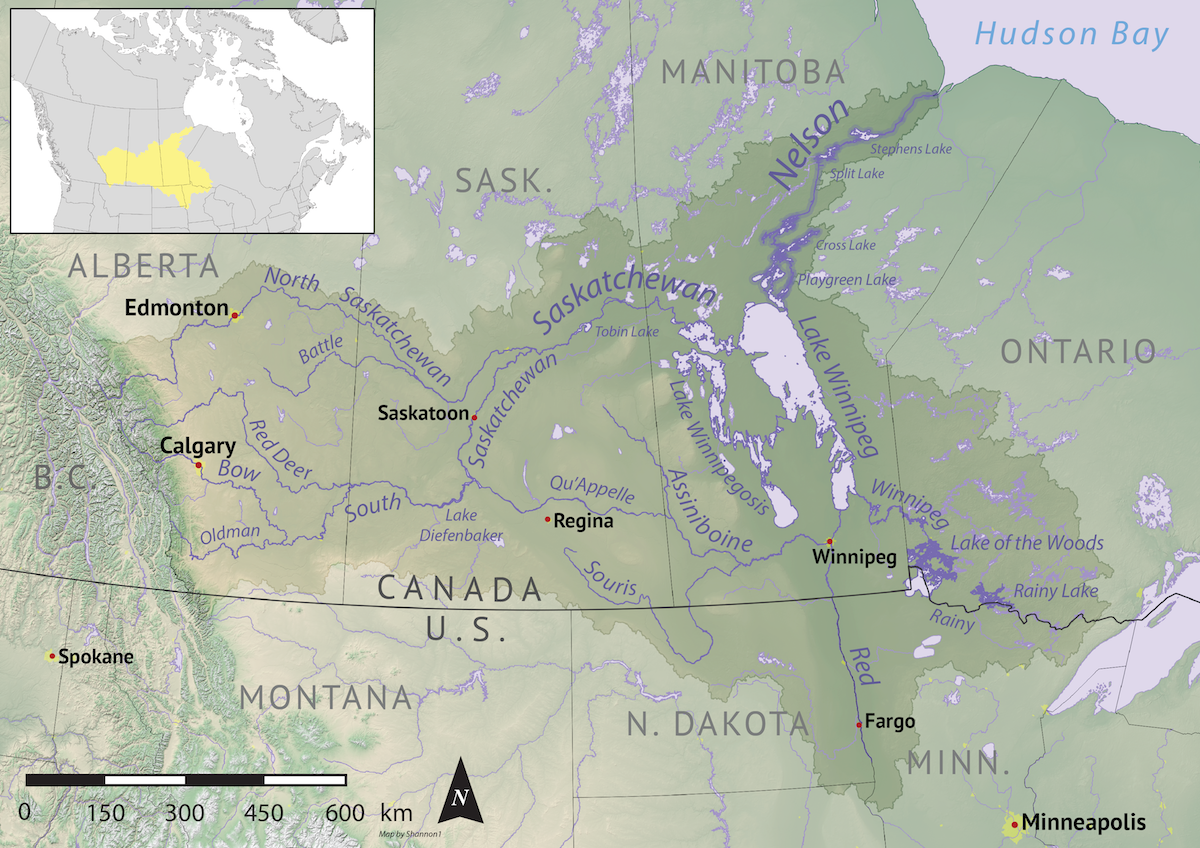
St. Laurent, Manitoba
St. Laurent (French: ''Saint-Laurent'') is a community on the eastern shore of Lake Manitoba. It lies within the boundaries of the Rural Municipality of St. Laurent, from Winnipeg. A historically-Métis settlement, St. Laurent is one of the few remaining places in which the Michif French language is still spoken. History Prior to the arrival of European colonists, the area between Lake Manitoba and Lake Winnipeg was contested among the Ojibwa, Cree, and Sioux peoples for much of the 18th century, with the Ojibwa ultimately achieving dominance. In the 1730s, La Vérendrye was the first European who systematically explored the territory. By the early 19th century, the interlake region of Manitoba was inhabited by Ojibwa Saulteaux, but it is unclear if any of the groups lived in the immediate vicinity of St. Laurent when it was founded. St. Laurent was established as Fond du Lac in 1824 by Métis leaving Pembina, North Dakota. Pembina, located in Rupert's Land, had been re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics Canada
Statistics Canada (StatCan; french: Statistique Canada), formed in 1971, is the agency of the Government of Canada commissioned with producing statistics to help better understand Canada, its population, resources, economy, society, and culture. It is headquartered in Ottawa.Statistics Canada, 150 Tunney's Pasture Driveway Ottawa, Ontario K1A 0T6; Statistique Canada 150, promenade du pré Tunney Ottawa, Ontario K1A 0T6 The agency is led by the chief statistician of Canada, currently Anil Arora, who assumed the role on September 19, 2016. StatCan is responsible to Parliament through the Minister of Innovation, Science and Industry, currently François-Philippe Champagne. Statistics Canada acts as the national statistical agency for Canada, and Statistics Canada produces statistics for all the provinces as well as the federal government. In addition to conducting about 350 active surveys on virtually all aspects of Canadian life, the ''Statistics Act'' mandates that Statisti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rural Municipality Of St
In general, a rural area or a countryside is a geographic area that is located outside towns and cities. Typical rural areas have a low population density and small settlements. Agricultural areas and areas with forestry typically are described as rural. Different countries have varying definitions of ''rural'' for statistical and administrative purposes. In rural areas, because of their unique economic and social dynamics, and relationship to land-based industry such as agriculture, forestry and resource extraction, the economics are very different from cities and can be subject to boom and bust cycles and vulnerability to extreme weather or natural disasters, such as droughts. These dynamics alongside larger economic forces encouraging to urbanization have led to significant demographic declines, called rural flight, where economic incentives encourage younger populations to go to cities for education and access to jobs, leaving older, less educated and less wealthy popul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of 1818
The Convention respecting fisheries, boundary and the restoration of slaves, also known as the London Convention, Anglo-American Convention of 1818, Convention of 1818, or simply the Treaty of 1818, is an international treaty signed in 1818 between the United States and the United Kingdom. This treaty resolved standing boundary issues between the two nations. The treaty allowed for joint occupation and settlement of the Oregon Country, known to the British and in Canadian history as the Columbia District of the Hudson's Bay Company, and including the southern portion of its sister district New Caledonia. The two nations agreed to a boundary line involving the 49th parallel north, in part because a straight-line boundary would be easier to survey than the pre-existing boundaries based on watersheds. The treaty marked both the United Kingdom's last permanent major loss of territory in what is now the Continental United States and the United States' first permanent significant ces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land (french: Terre de Rupert), or Prince Rupert's Land (french: Terre du Prince Rupert, link=no), was a territory in British North America which comprised the Hudson Bay drainage basin; this was further extended from Rupert's Land to the Pacific coast in December 1821. It was established to be a commercial monopoly by the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), based at York Factory. The territory operated for 200 years from 1670 to 1870. Its namesake was Prince Rupert of the Rhine, who was a nephew of Charles I and the first governor of HBC. The areas formerly belonging to Rupert's Land lie mostly within what is today Canada, and included the whole of Manitoba, most of Saskatchewan, southern Alberta, southern Nunavut, and northern parts of Ontario and Quebec. Additionally, it also extended into areas that would eventually become part of Minnesota, North Dakota, and Montana. The southern border west of Lake of the Woods to the Rocky Mountains was the drainage divide betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pembina, North Dakota
Pembina () is a city in Pembina County, North Dakota, United States. The population was 512 at the 2020 census. Pembina is located south of the Canada–US border. Interstate 29 passes on the west side of Pembina, leading north to the Canada–US border at Emerson, Manitoba and south to the cities of Grand Forks and Fargo. The Pembina-Emerson Border Crossing is the busiest between Blaine, Washington and Detroit, Michigan and the fifth busiest along the Canada-United States border. It is one of three 24-hour Port of entry, ports of entry in North Dakota, the others being Portal, North Dakota, Portal and Dunseith, North Dakota, Dunseith. The Noyes–Emerson East Border Crossing, Noyes–Emerson Border Crossing, located to the east on the Minnesota side of the Red River of the North, Red River, also processed cross border traffic until its closure in 2006. The area of Pembina was long inhabited by various indigenous peoples. At the time of 16th century French exploration a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saulteaux
The Saulteaux (pronounced , or in imitation of the French pronunciation , also written Salteaux, Saulteau and other variants), otherwise known as the Plains Ojibwe, are a First Nations band government in Ontario, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta and British Columbia, Canada. They are a branch of the Ojibwe who pushed west. They formed a mixed culture of woodlands and plains Indigenous customs and traditions. Ethnic classification The Saulteaux are a branch of the Ojibwe Nations within Canada. They are sometimes called the Anihšināpē (Anishinaabe). ''Saulteaux'' is a French term meaning "people of the rapids," referring to their former location in the area of Sault Ste. Marie. They are primarily hunters and fishers, and when still the primary dwellers of their sovereign land, they had extensive trading relations with the French, British and later Americans at that post. Location The Saulteaux historically were settled around Lake Superior and Lake Winnipeg, principal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interlake
Interlake was a provincial electoral division in the Canadian province of Manitoba. It was created by redistribution in 1979, and has formally existed since the 1981 provincial election. Previously, much of the Interlake region was included in the constituency of St. George. As its name implies, Interlake was located between Lake Winnipeg and Lake Manitoba, in the mid-northern section of the province. Interlake was bordered to the east by Lake Winnipeg, to the south by Lakeside and Gimli, to the north by Swan River, and to the west by Lake Manitoba. Communities in the riding include Arborg, Riverton, Ashern, Fraserwood. The Black and Deer Islands are also located in the riding. Prior to the 2019 Manitoba general election, Interlake was abolished and its area was redistributed to the new riding of Interlake-Gimli. In 1996, the riding's population was 18,653. In 1999, the average family income was $32,570, and the unemployment rate was 10.60%. Twenty-two per c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Gaultier De Varennes, Sieur De La Vérendrye
Pierre Gaultier de Varennes, sieur de La Vérendrye (17 November 1685 – 5 December 1749) was a French Canadian military officer, fur trader, and explorer. In the 1730s, he and his four sons explored the area west of Lake Superior and established trading posts there. They were part of a process that added Western Canada to the original New France territory that was centred along the Saint Lawrence basin. He was the first known European to reach present-day North Dakota and the upper Missouri River in the United States. In the 1740s, two of his sons crossed the prairie as far as present-day Wyoming, United States and were the first Europeans to see the Rocky Mountains north of New Mexico. Early life Born in Trois-Rivières, New France, Pierre was the eldest son of René Gaultier de Varennes, who came to Canada as a soldier in 1665, and Marie, the daughter of Pierre Boucher, the first Governor of Trois-Rivières. The Gaultier family were minor nobility or landowne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sioux
The Sioux or Oceti Sakowin (; Dakota language, Dakota: Help:IPA, /otʃʰeːtʰi ʃakoːwĩ/) are groups of Native Americans in the United States, Native American tribes and First Nations in Canada, First Nations peoples in North America. The modern Sioux consist of two major divisions based on Siouan languages, language divisions: the Dakota people, Dakota and Lakota people, Lakota; collectively they are known as the Očhéthi Šakówiŋ ("Seven Council Fires"). The term "Sioux" is an exonym created from a French language, French transcription of the Ojibwe language, Ojibwe term "Nadouessioux", and can refer to any ethnic group within the Great Sioux Nation or to any of the nation's many language dialects. Before the 17th century, the Dakota people, Santee Dakota (; "Knife" also known as the Eastern Dakota) lived around Lake Superior with territories in present-day northern Minnesota and Wisconsin. They gathered wild rice, hunted woodland animals and used canoes to fish. Wars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cree
The Cree ( cr, néhinaw, script=Latn, , etc.; french: link=no, Cri) are a North American Indigenous people. They live primarily in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations. In Canada, over 350,000 people are Cree or have Cree ancestry. The major proportion of Cree in Canada live north and west of Lake Superior, in Ontario, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta and the Northwest Territories. About 27,000 live in Quebec. In the United States, Cree people historically lived from Lake Superior westward. Today, they live mostly in Montana, where they share the Rocky Boy Indian Reservation with Ojibwe (Chippewa) people. The documented westward migration over time has been strongly associated with their roles as traders and hunters in the North American fur trade. Sub-groups / Geography The Cree are generally divided into eight groups based on dialect and region. These divisions do not necessarily represent ethnic sub-divisions within the larger ethn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ojibwa
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains. According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of the largest tribal populations among Native American peoples. In Canada, they are the second-largest First Nations population, surpassed only by the Cree. They are one of the most numerous Indigenous Peoples north of the Rio Grande. The Ojibwe population is approximately 320,000 people, with 170,742 living in the United States , and approximately 160,000 living in Canada. In the United States, there are 77,940 mainline Ojibwe; 76,760 Saulteaux; and 8,770 Mississauga, organized in 125 bands. In Canada, they live from western Quebec to eastern British Columbia. The Ojibwe language is Anishinaabemowin, a branch of the Algonquian language family. They are part of the Council of Three Fires (which also include the Odawa and Potawatomi) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Winnipeg
Lake Winnipeg (french: Lac Winnipeg, oj, ᐑᓂᐸᑲᒥᐠᓴᑯ˙ᑯᐣ, italics=no, Weenipagamiksaguygun) is a very large, relatively shallow lake in North America, in the province of Manitoba, Canada. Its southern end is about north of the city of Winnipeg. Lake Winnipeg is Canada's sixth-largest freshwater lake and the third-largest freshwater lake contained entirely within Canada, but it is relatively shallow (mean depth of ) excluding a narrow deep channel between the northern and southern basins. It is the eleventh-largest freshwater lake on Earth. The lake's east side has pristine boreal forests and rivers that were in 2018 inscribed as Pimachiowin Aki, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The lake is from north to south, with remote sandy beaches, large limestone cliffs, and many bat caves in some areas. Manitoba Hydro uses the lake as one of the largest reservoirs in the world. There are many islands, most of them undeveloped. The Sagkeeng First Nation holds a rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |