|
St. Johns Park (Brooklyn)
St. John's Park was a 19th-century park and square, and the neighborhood of townhouses around it, in what is now the Tribeca neighborhood of Lower Manhattan, New York City. The square was bounded by Varick Street, Laight Street, Hudson Street and Beach Street, now also known for that block as Ericsson Place. Although the name "St. John's Park" is still in use, it is no longer a park and is inaccessible to the public. The land was part of a plantation owned by an early settler to New Netherland and was later owned by the English Crown, who deeded it to Trinity Church. The church built St. John's Chapel and laid out "Hudson Square", creating New York City's first development of townhouses around a private park. By 1827 the neighborhood had become known as "St. John's Park" and remained fashionable until about 1850. In 1866 it was sold to Cornelius Vanderbilt's Hudson River Railway Company and became the location of St. John's Park Freight Depot, the railroad's southern t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Townhouse
A townhouse, townhome, town house, or town home, is a type of terraced housing. A modern townhouse is often one with a small footprint on multiple floors. In a different British usage, the term originally referred to any type of city residence (normally in London) of someone whose main or largest residence was a country house. History Historically, a townhouse was the city residence of a noble or wealthy family, who would own one or more country houses in which they lived for much of the year. From the 18th century, landowners and their servants would move to a townhouse during the social season (when major balls took place). Europe In the United Kingdom, most townhouses are terraced. Only a small minority of them, generally the largest, were detached, but even aristocrats whose country houses had grounds of hundreds or thousands of acres often lived in terraced houses in town. For example, the Duke of Norfolk owned Arundel Castle in the country, while his London house, N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roeloff Jansen
The Roeliff Jansen Kill is a major tributary to the Hudson River. Roeliff Jansen Kill was the traditional boundary between the Native American Mahican and Wappinger tribes. Its source is in the town of Austerlitz, New York, and its mouth is at the Hudson River at Linlithgo in the town of Livingston. The stream flows for U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed October 3, 2011 through Dutchess and Columbia counties before entering the Hudson River about south of Hudson. Most of the watershed lies in Columbia County, although parts of the northern Dutchess County towns of North East, Stanford, Pine Plains, Milan, and Red Hook are within the stream's watershed of approximately . A major tributary is Shekomeko Creek. Tributaries * Klein Kill * Doove Kill * Fall Kill * Ham Brook * Shekomeko Creek - Native American ''Che-co-min-go'', "place of eels". ** Bean River * Punch Brook * Noster Kill ** Preechey Hollow Broo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgian Architecture
Georgian architecture is the name given in most English-speaking countries to the set of architectural styles current between 1714 and 1830. It is named after the first four British monarchs of the House of Hanover—George I, George II, George III, and George IV—who reigned in continuous succession from August 1714 to June 1830. The so-called great Georgian cities of the British Isles were Edinburgh, Bath, pre-independence Dublin, and London, and to a lesser extent York and Bristol. The style was revived in the late 19th century in the United States as Colonial Revival architecture and in the early 20th century in Great Britain as Neo-Georgian architecture; in both it is also called Georgian Revival architecture. In the United States the term "Georgian" is generally used to describe all buildings from the period, regardless of style; in Britain it is generally restricted to buildings that are "architectural in intention", and have stylistic characteristics that are typical o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West End Of London
The West End of London (commonly referred to as the West End) is a district of Central London, west of the City of London and north of the River Thames, in which many of the city's major tourist attractions, shops, businesses, government buildings and entertainment venues, including West End theatres, are concentrated. The term was first used in the early 19th century to describe fashionable areas to the west of Charing Cross.Mills, A., ''Oxford Dictionary of London Place Names'', (2001) The West End covers parts of the boroughs of Westminster and Camden.Greater London Authority, The London Plan: The Sub Regions'' While the City of London is the main business and financial district in London, the West End is the main commercial and entertainment centre of the city. It is the largest central business district in the United Kingdom, comparable to Midtown Manhattan in New York City, the 8th arrondissement in Paris, Causeway Bay in Hong Kong, or Shibuya in Tokyo. It is one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
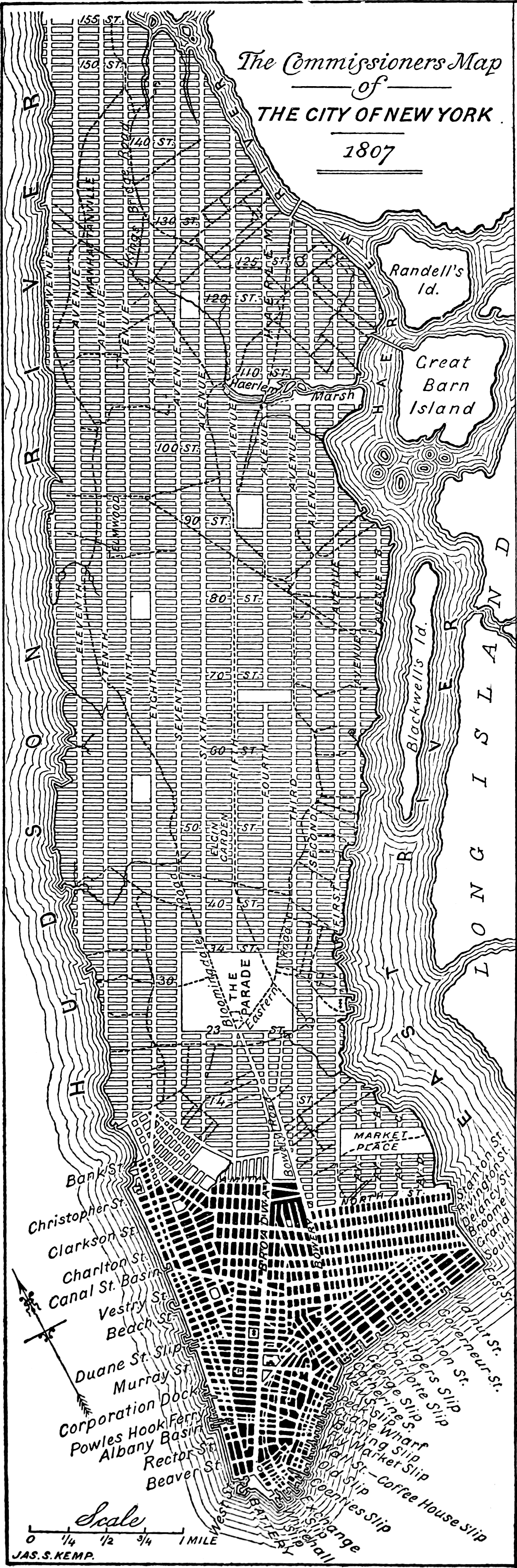
Commissioners Plan Of 1811
The Commissioners' Plan of 1811 was the original design for the streets of Manhattan above Houston Street and below 155th Street, which put in place the rectangular grid plan of streets and lots that has defined Manhattan on its march uptown until the current day. It has been called "the single most important document in New York City's development,"Augustyn & Cohen, pp.100–06 and the plan has been described as encompassing the "republican predilection for control and balance ... nddistrust of nature". It was described by the Commission that created it as combining "beauty, order and convenience." The plan originated when the Common Council of New York City, seeking to provide for the orderly development and sale of the land of Manhattan between 14th Street and Washington Heights, but unable to do so itself for reasons of local politics and objections from property owners, asked the New York State Legislature to step in. The legislature appointed a commission with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Moore Street
North Moore Street is a moderately trafficked street in TriBeCa, a neighborhood in the New York City borough of Manhattan. It runs roughly east–west between West Broadway and West Street. Automotive traffic is westbound only. Naming On street signs and maps, the street is usually written as "N. Moore Street". The street was named in 1790 for Benjamin Moore (1748–1816), the second bishop of the Episcopal Diocese of New York, the president of Columbia College (now Columbia University), and the father of Clement Clarke Moore. Bishop Moore is remembered for having given Holy Communion to Alexander Hamilton on his deathbed. The addition of "North" or "N" avoids confusion with the older Moore Street, a short street near the Battery at the southern tip of Manhattan across from 1 New York Plaza. Based on North Moore Street's abbreviation, "Nathaniel Moore Street" has been given as an incorrect name for the street. According to a 1984 article in ''The New York Times'', some city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national " newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anne, Queen Of Great Britain
Anne (6 February 1665 – 1 August 1714) was Queen of England, Scotland and Ireland from 8 March 1702 until 1 May 1707. On 1 May 1707, under the Acts of Union, the kingdoms of England and Scotland united as a single sovereign state known as Great Britain. Anne continued to reign as Queen of Great Britain and Ireland until her death. Anne was born in the reign of Charles II to his younger brother and heir presumptive, James, whose suspected Roman Catholicism was unpopular in England. On Charles's instructions, Anne and her elder sister Mary were raised as Anglicans. Mary married their Dutch Protestant cousin, William III of Orange, in 1677, and Anne married Prince George of Denmark in 1683. On Charles's death in 1685, James succeeded to the throne, but just three years later he was deposed in the Glorious Revolution of 1688. Mary and William became joint monarchs. Although the sisters had been close, disagreements over Anne's finances, status, and choice of acquaintances ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of York
Duke of York is a title of nobility in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. Since the 15th century, it has, when granted, usually been given to the second son of English (later British) monarchs. The equivalent title in the Scottish peerage was Duke of Albany. However, King George II and King George III granted the titles ''Duke of York and Albany''. Initially granted in the 14th century in the Peerage of England, the title ''Duke of York'' has been created eight times. The title ''Duke of York and Albany'' has been created three times. These occurred during the 18th century, following the 1707 unification of the Kingdom of England and Kingdom of Scotland into a single, united realm. The double naming was done so that a territorial designation from each of the previously separate realms could be included. The current Duke of York is Prince Andrew, the younger brother of Charles III. The present Duke's marriage produced two daughters, and he has remained unmarried since his 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmund Andros
Sir Edmund Andros (6 December 1637 – 24 February 1714) was an English colonial administrator in British America. He was the governor of the Dominion of New England during most of its three-year existence. At other times, Andros served as governor of the provinces of New York, East and West Jersey, Virginia, and Maryland. Before his service in North America, he served as Bailiff of Guernsey. His tenure in New England was authoritarian and turbulent, as his views were decidedly pro-Anglican, a negative quality in a region home to many Puritans. His actions in New England resulted in his overthrow during the 1689 Boston revolt. He became governor of Virginia three years later. Andros was considered to have been a more effective governor in New York and Virginia, although he became the enemy of prominent figures in both colonies, many of whom worked to remove him from office. Despite these enmities, he managed to negotiate several treaties of the Covenant Chain with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Lovelace
Francis Lovelace (c. 1621–1675) was an English Royalist and the second Governor of New York colony. Early life Lovelace was born circa 1621. He was the third son of Sir William Lovelace (1584–1627) and his wife Anne Barne of Lovelace Place, Bethersden and Woolwich, Kent. He was the younger brother of Richard Lovelace, the Cavalier poet. The Bethersden Lovelace lineage was founded in 1367 by John Lovelace, six generations before Francis, and has been confused over the years with the Hurley Lovelaces who were raised to the House of Lords. Career The five Lovelace brothers supported Charles I in the English Civil War. Francis was a Colonel in the Royalist army and was governor of Carmarthen Castle in Wales from June 1644 until it was surrendered to Parliamentary troops in October 1645 after a fierce battle in which his brother, William, was killed. He and another brother, Dudley, migrated to Europe and served with the French army later in the 1640s. The brothers later su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)


