|
St. George (crater)
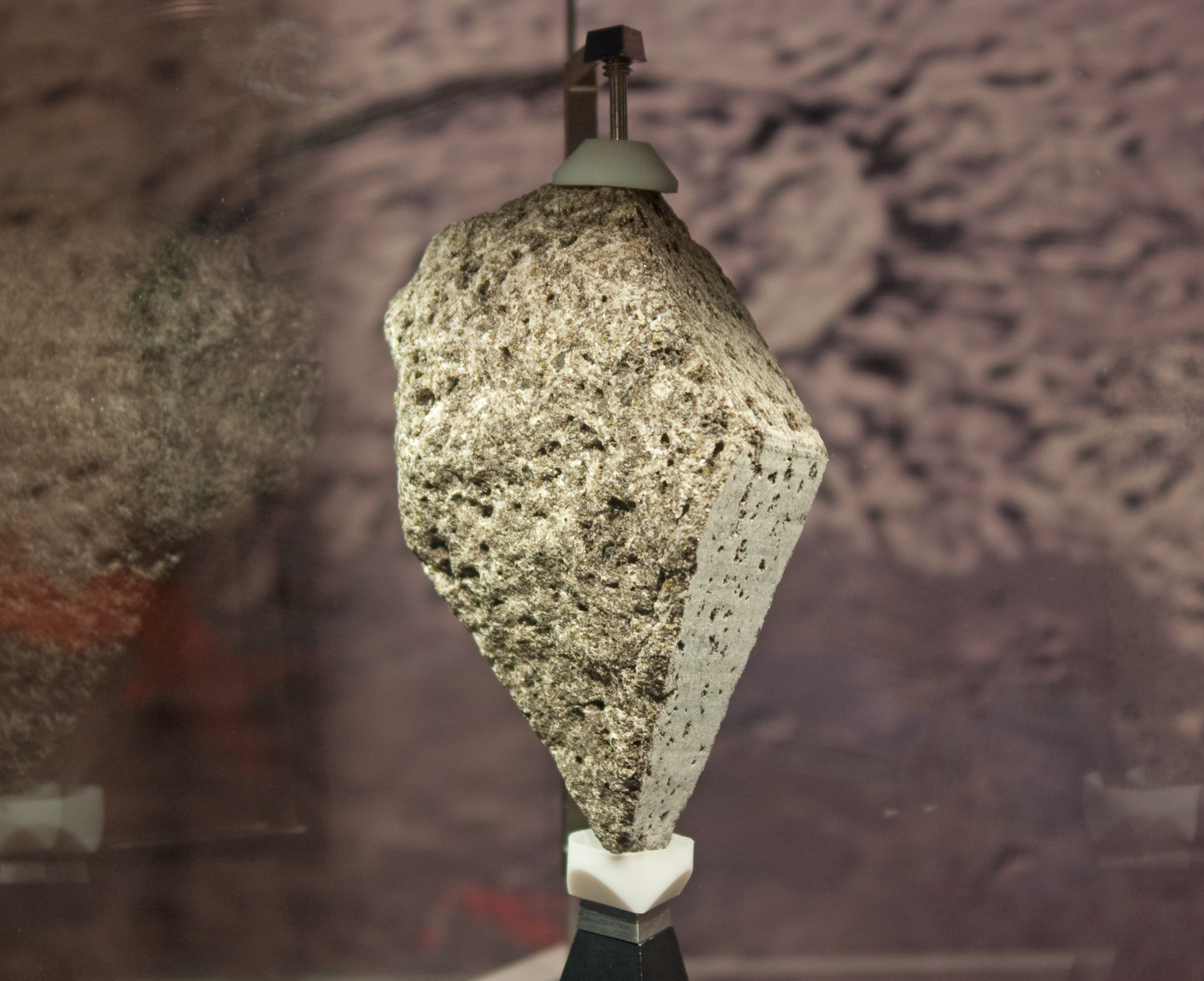
St. George is a feature on Earth's Moon, a crater in the Hadley–Apennine region. Astronauts David Scott and James Irwin drove their rover onto what was suspected to be its ejecta blanket in 1971, on the Apollo 15 mission, during EVA 1. They collected samples to the northeast of the crater, at Geology Station 2 of the mission. St. George crater is located on the west slope of Mons Hadley Delta and approximately 4 km southwest of the Apollo 15 landing point. Bridge crater is to the northwest and Elbow crater is to the northeast. The name of the crater was formally adopted by the IAU in 1973. St. George is a crater of Upper (Late) Imbrian age. Station 2 File:Apollo 15 Scott Station 2 boulder.jpg, David Scott collecting samples from a boulder down the northeast slope from the rim of St. George File:Apollo 15 St. 2 boulder.jpg, The boulder at Station 2 File:A15 PSR Fig 5-65 Planimetric map Station 2.jpg, Station 2 map. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadley Rille St
Hadley may refer to: Places Canada * Hadley Bay, on the north of Victoria Island, Nunavut England * Hadley, London, a former civil parish within Barnet Urban District from 1894 to 1965 * Hadley, Shropshire, part of the new town of Telford, Shropshire * Hadley Wood in the London Borough of Enfield * Monken Hadley, suburb of Barnet, in the London Borough of Barnet United States * Hadley Township, Pike County, Illinois * Hadley, Indiana * Hadley, Kentucky * Hadley, Massachusetts ** South Hadley, Massachusetts * Hadley Township, Michigan * Hadley, Minnesota * Hadley, Missouri * Hadley, Nevada * Hadley's Purchase, New Hampshire, an uninhabited township of Coos County * Hadley, New York, town in Saratoga County ** Hadley (CDP), New York, the main hamlet in the town * Hadley, Pennsylvania, a place in Mercer County * Branchland, West Virginia, an unincorporated community in West Virginia also known as Hadley Other * Hadley (crater), a crater on Mars * Hadley (name), an Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridge (crater)
Bridge is a feature on Earth's Moon, a crater in the Hadley–Apennine region. The name of the crater was formally adopted by the International Astronomical Union, IAU in 1973. Location Bridge crater is located within Hadley–Apennine, Hadley Rille, also known as the Hadley-Apennine region, and its ejecta indeed forms a bridge of sorts across the rille. It lies at the base of Mons Hadley Delta and is approximately 4 km southwest of the Apollo 15 landing point. Adjacent craters The larger St. George (crater), St. George crater is to the southeast and the smaller Elbow (lunar crater), Elbow crater is due east. References {{reflist External links Apollo 15 Traverses Lunar Photomap 41B4S4(25) Impact craters on the Moon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Crater
An impact crater is a circular depression in the surface of a solid astronomical object formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact craters typically have raised rims and floors that are lower in elevation than the surrounding terrain. Lunar impact craters range from microscopic craters on lunar rocks returned by the Apollo Program and small, simple, bowl-shaped depressions in the lunar regolith to large, complex, multi-ringed impact basins. Meteor Crater is a well-known example of a small impact crater on Earth. Impact craters are the dominant geographic features on many solid Solar System objects including the Moon, Mercury, Callisto, Ganymede and most small moons and asteroids. On other planets and moons that experience more active surface geological processes, such as Earth, Venus, Europa, Io and Titan, visible impact craters are less common because they become eroded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Receiving Laboratory
The Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) was a facility at NASA's Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center (Building 37) that was constructed to quarantine astronauts and material brought back from the Moon during the Apollo program to reduce the risk of back-contamination. After recovery at sea, crews from Apollo 11, Apollo 12, and Apollo 14 walked from their helicopter to the Mobile Quarantine Facility on the deck of an aircraft carrier and were brought to the LRL for quarantine. Samples of rock and regolith that the astronauts collected and brought back were flown directly to the LRL and initially analyzed in glovebox vacuum chambers. ::: The quarantine requirement was dropped for Apollo 15 and later missions. The LRL was used for study, distribution, and safe storage of the lunar samples. Between 1969 and 1972, six Apollo space flight missions brought back 382 kilograms (842 pounds) of lunar rocks, core samples, pebbles, sand, and dust from the lunar surface—in all, 2,200 sample ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Don Wilhelms
Don Edward Wilhelms (born July 5, 1930) is a former United States Geological Survey geologist who contributed to geologic mapping of the Earth's moon and to the geologic training of the Apollo astronauts. He is the author of '' To a Rocky Moon: A Geologist's History of Lunar Exploration'' (1993), ''The geologic history of the Moon'' (1987), and he co-authored the ''Geologic Map of the Near Side of the Moon'' (1971) with John F. McCauley. Wilhelms also contributed to ''Apollo Over the Moon: A View from Orbit'' (NASA SP-362). He has also contributed to the study of Mars (including Mariner 9), Mercury, and Ganymede. Biography He was born July 5, 1930. Wilhelms was the recipient of the G. K. Gilbert Award in 1988. He received the Shoemaker Distinguished Lunar Scientist Award in 2010 at the Ames Research Center The Ames Research Center (ARC), also known as NASA Ames, is a major NASA research center at Moffett Federal Airfield in California's Silicon Valley. It was founded in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USGS
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredth anniv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imbrian
The Imbrian is a lunar geologic period divided into two epochs, the Early and Late. Early Imbrian In the lunar geologic timescale, the Early Imbrian epoch occurred from 3,850 million years ago to about 3,800 million years ago. It overlaps the end of the Late Heavy Bombardment of the Inner Solar System. The impact that created the huge Mare Imbrium basin occurred at the start of the epoch. The other large basins that dominate the lunar near side (such as Mare Crisium, Mare Tranquillitatis, Mare Serenitatis, and Mare Fecunditatis) were also formed in this period. These basins filled with basalt mostly during the subsequent Late Imbrian epoch. The Early Imbrian was preceded by the Nectarian. Late Imbrian In the Lunar geologic timescale, the Late Imbrian epoch occurred between 3800 million years ago to about 3200 million years ago. It was the epoch during which the mantle below the lunar basins partially melted and filled them with basalt. The melting is thought to have occurred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and development through global cooperation. It was founded in 1919 and is based in Paris, France. The IAU is composed of individual members, who include both professional astronomers and junior scientists, and national members, such as professional associations, national societies, or academic institutions. Individual members are organised into divisions, committees, and working groups centered on particular subdisciplines, subjects, or initiatives. As of 2018, the Union had over 13,700 individual members, spanning 90 countries, and 82 national members. Among the key activities of the IAU is serving as a forum for scientific conferences. It sponsors nine annual symposia and holds a triannual General Assembly that sets policy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
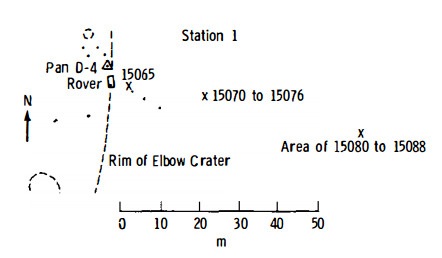
Elbow (lunar Crater)
Elbow is a feature on Earth's Moon, a crater in the Hadley–Apennine region. Astronauts David Scott and James Irwin visited the east rim of it in 1971, on the Apollo 15 mission, during EVA 1. The east rim of Elbow was designated Geology Station 1 of the mission. Geology Station 2 was to the southwest of the crater, up the slope of Mons Hadley Delta. Elbow is located on the edge of Hadley Rille, about 1 km northeast of the larger St. George crater, and about 3.2 km southwest of the Apollo 15 landing site itself. The ''Apollo 15 Preliminary Science Report''Apollo 15 Preliminary Science Report 1972, NASA SP-289, Scientific and Technical Information Office, NATIONAL AERONAUTICS AND SPACE ADMINISTRATION, Washington, D.C. describes Elbow as follows: The crater was named by the astronauts after its loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mons Hadley Delta
Mons Hadley Delta (δ) is a massif in the northern portion of the Montes Apenninus, a range in the northern hemisphere of the Moon adjacent to Mare Imbrium. It has a height of 3.6 km above the plains to the north and west. To the north of this mountain is a valley that served as the landing site for the Apollo 15 expedition. To the northeast of this same valley is the slightly larger Mons Hadley peak with a height of about 4.6 km. To the west of these peaks is the sinuous Rima Hadley rille. These features were named after the English mathematician and inventor of the octant John Hadley. On the Apollo 15 mission in 1971, the astronauts David Scott and James Irwin explored the lower reaches of the north slope of Mons Hadley Delta, and collected many samples which were returned to earth. Station 2 was near St. George crater, and Stations 6, 6A, and 7 were at or near Spur crater. They found the famous "Genesis Rock", sample 15415, at Spur. A clast of anorthosite with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of Australia). The Moon is a planetary-mass object with a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under the geophysical definitions of the term and larger than all known dwarf planets of the Solar System. It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's at , with Jupiter's moon Io being the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density. The Moon orbits Earth at an average distance of , or about 30 times Earth's diameter. Its gravitational influence is the main driver of Earth's tides and very slowly lengthens Earth's day. The Moon's orbit around Earth has a sidereal period of 27.3 days. During each synodic period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extra-vehicular Activity
Extravehicular activity (EVA) is any activity done by an astronaut in outer space outside a spacecraft. In the absence of a breathable Earthlike atmosphere, the astronaut is completely reliant on a space suit for environmental support. EVA includes ''spacewalks'' and lunar or planetary surface exploration (commonly known from 1969 to 1972 as ''moonwalks''). In a stand-up EVA (SEVA), an astronaut stands through an open hatch but does not fully leave the spacecraft. EVA has been conducted by the Soviet Union/Russia, the United States, Canada, the European Space Agency and China. On March 18, 1965, Alexei Leonov became the first human to perform a spacewalk, exiting the Voskhod 2 capsule for 12 minutes and 9 seconds. On July 20, 1969, Neil Armstrong became the first human to perform a moonwalk, outside his lunar lander on Apollo 11 for 2 hours and 31 minutes. On the last three Moon missions, astronauts also performed deep-space EVAs on the return to Earth, to retrieve film canis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |