|
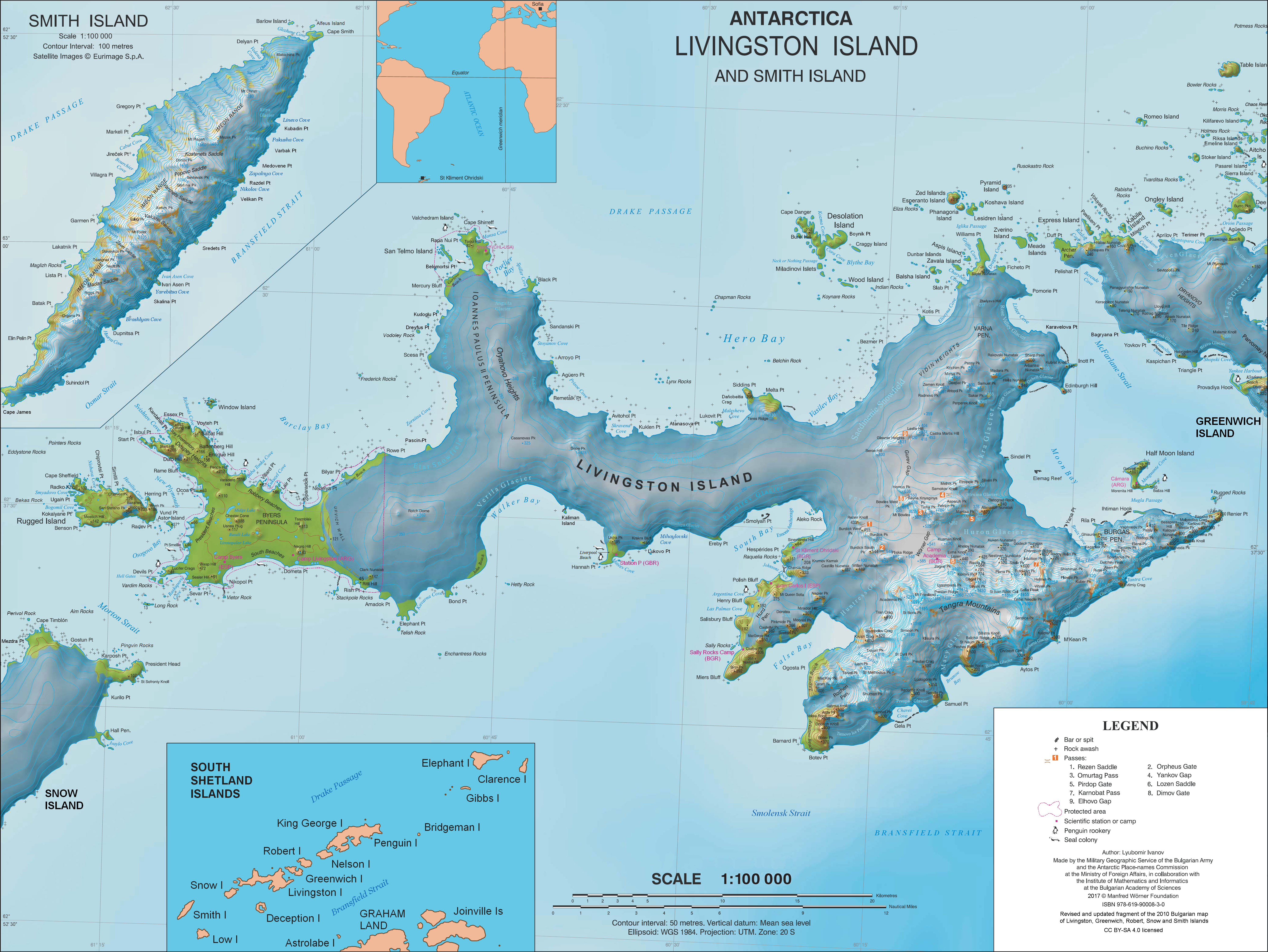
St. Boris Peak
St. Boris Peak ( bg, връх Св. Борис, vrah Sv. Boris, ) is an ice-covered mountain rising to 1,700 m in Friesland Ridge, Tangra Mountains on Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. It is the first or second highest peak of both the mountains and the island along with Mount Friesland (1,700.2 m). The two are connected by a short saddle of elevation 1649 m dominated by ‘The Synagogue’, a sharp-peaked rock-cored ice formation abutting upon the central summit of St. Boris Peak. The peak is also connected to Simeon Peak by Paril Saddle, and surmounts Huntress Glacier to the northwest and west, and Macy Glacier to the southeast. The peak's central summit is rising to 1,685 m,L. Ivanov and N. Ivanova''The World of Antarctica''.Generis Publishing, 2022. 241 pp. while its highest point ‘The Synagogue’ rises to 1,699 or 1,700 m. The local ice relief is subject to change; according to a Bulgarian GPS survey by D. Boyanov and N. Pet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Friesland
Mount Friesland is a mountain rising to in the homonymous Friesland Ridge, the summit of Tangra Mountains and Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Its north rib is connected to Pliska Ridge by Nesebar Gap on the west, and to Bowles Ridge by Wörner Gap on the north. On the east Mount Friesland is connected to Presian Ridge and further on to Catalunyan Saddle and Lyaskovets Peak. On the south-southwest it is connected by a short saddle to ‘ The Synagogue’ a sharp-peaked rock-cored ice formation abutting neighbouring St. Boris Peak. The peak is heavily glaciated and crevassed, surmounting Huntress Glacier to the west, Perunika Glacier to the north-northwest, Huron Glacier to the northeast and Macy Glacier to the southeast. The local weather is notoriously unpleasant and challenging; according to the seasoned Antarctic mountaineer Damien Gildea who climbed in the area, 'just about the worst weather in the world'. History The feature was known to Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliska Ridge
Pliska Ridge ( bg, връх Плиска, vrah Pliska, ) is a three-peaked ridge rising to 667 m in eastern Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Its central and highest summit, ''Pliska Peak'', is located 2.48 km east-northeast of Willan Nunatak (449 m), 1.81 km southeast of Burdick Peak (773 m, summit of Burdick Ridge), 3.53 km south-southwest of Mount Bowles, 3.68 km west-southwest of Kuzman Knoll, and 3.61 km northwest of Mount Friesland. The feature is 1.6 km long and 500 m wide, its axis trending due east-west, with precipitous southern slopes. It is ice-covered except for segments of its easternmost peak (646 m) and is bounded to the northwest by Orpheus Gate, to the north by the head of Perunika Glacier, to the east by Nesebar Gap, and to the south and west by the head of Huntress Glacier, the latter flowing 6 km southwestwards into False Bay. First ascent by the Bulgarian Lyubomir Ivanov from Camp Academia on 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Gazetteer Of Antarctica
The Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica (CGA) of the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is the authoritative international gazetteer containing all Antarctic toponyms published in national gazetteers, plus basic information about those names and the relevant geographical features. The Gazetteer includes also parts of the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans (GEBCO) gazetteer for under-sea features situated south of 60° south latitude. , the overall content of the CGA amounts to 37,893 geographic names for 19,803 features including some 500 features with two or more entirely different names, contributed by the following sources: {, class="wikitable sortable" ! Country ! Names , - , United States , 13,192 , - , United Kingdom , 5,040 , - , Russia , 4,808 , - , New Zealand , 2,597 , - , Australia , 2,551 , - , Argentina , 2,545 , - , Chile , 1,866 , - , Norway , 1,706 , - , Bulgaria , 1,450 , - , Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Orkney Islands
The South Orkney Islands are a group of islands in the Southern Ocean, about north-east of the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula''Antarctica: Secrets of the Southern Continent'' p. 122 David McGonigal, 2009 and south-west of . They have a total area of about . The islands are claimed both by Britain (as part of the since 1962, previously as a [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Powell (sealer)
George Powell (1794–1824) was an English sealer, explorer and amateur naturalist. He captained three sealing expeditions to the Antarctic Ocean between 1818 and 1822. Powell was born in London. During his first expedition, in 1818 and 1819, he captained the sloop ''Dove'' and visited South Georgia and Kerguelen Islands. His second expedition, captaining ''Eliza'', lasted from 1819 until 1821, during which time he visited the Falkland Islands and the South Shetland Islands. In 1821 and 1822 he took both ''Dove'', which he captained, and ''Eliza'', captained by John Wright, on another sealing expedition to the South Shetland Islands, for which he produced a very fine chartL. Ivanov and N. Ivanova. Sealing period. In''The World of Antarctica''.Generis Publishing, 2022. pp. 78-84. based on his own observations of the north coast of the group and the observations of others for the southern coast. On 6 December 1821, he co-discovered the South Orkney Islands along with American N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desolation Island (South Shetland Islands)
Desolation Island is one of the minor islands in the South Shetlands archipelago, Antarctica situated at the entrance to Hero Bay, Livingston Island. The island is V-shaped with its northern coast indented by Kozma Cove. Surface area .L.L. Ivanov. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands. Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2010. (First edition 2009. ) The island was discovered on 15 October 1819 by Captain William Smith in the English merchant brig ''Williams'' during his second visit to the islands. The anchorage Blythe Bay at the southeast side of Desolation Island was frequented by the early Nineteenth century English and American sealers. Location The island's midpoint is located at , with the island lying northwest of Kotis Point, west of Williams Point and north-northeast of Siddins Point. British mapping in 1820 and 1968, Chilean in 1971, Argentine in 1980, and Bulgarian in 2005 and 2009. Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyaskovets Peak
Lyaskovets Peak ( bg, връх Лясковец, vrah Lyaskovets, ) is the easternmost peak of Friesland Ridge in the Tangra Mountains, eastern Livingston Island and has an elevation of 1,473 m. The peak is bounded by Catalunyan Saddle on the west and Shipka Saddle on the east, and is heavily glaciated and crevassed, with precipitous western, southern and eastern slopes. It surmounts Huron Glacier to the northwest and northeast, and Macy Glacier and Brunow Bay area to the south. Its northern offshoot forms Zograf Peak, and is linked to Lozen Nunatak, Erma Knoll and Aheloy Nunatak in Huron Glacier. The peak is named after Lyaskovets, a town in central northern Bulgaria. Location Lyaskovets Peak is located at , which is 2.3 km east-northeast of Mount Friesland (the summit of Friesland Ridge and Livingston Island, 1,700 m), 3.2 km south-southeast of Kuzman Knoll, 1.33 km south by east of Zograf Peak, 1.3 km west of Levski Peak, and 4.6 km west by nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levski Peak (Antarctica)
Levski Peak ( bg, връх Левски, vrah Levski, ) is a mountain in Antarctica, rising to approximately in the western extremity of Levski Ridge, Tangra Mountains on Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. It surmounts Huron Glacier to the north and Macy Glacier to the south. The peak was named after Vasil Levski (1837–1873), a national hero of the Bulgarian liberation movement. Location The peak is located to the east of Shipka Saddle, east of Lyaskovets Peak, southeast of Kuzman Knoll, south of Atanasoff Nunatak, west by north of Great Needle Peak (Falsa Aguja), and km north by west of St. Naum Peak St. Naum Peak ( bg, връх Св. Наум, vrah Sv. Naum, ) is a rocky peak of elevation 560 m in the east extremity of Peshev Ridge, Tangra Mountains, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Separated from Balchik Ridge a .... Maps Chart of South Shetland including Coronation Island, &c.from the exploration of the slo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Needle Peak
Great Needle Peak ( bg, Голям Иглен връх, Golyam Iglen vrah, ; variant name in es, pico Falsa Aguja, lit=False Needle Peak) is the summit of the central Levski Ridge in Tangra Mountains on Livingston Island, Antarctica. Rising to 1,679.5 m, it is the third highest peak of both the mountains and the island after Mount Friesland (1700.2 m) and St. Boris Peak (1685 m). Great Needle Peak surmounts Huron Glacier and its tributary draining Devnya Valley to the north, Magura Glacier to the east, Srebarna Glacier to the south, and Macy Glacier to the southwest. History The peak's name derives from the Spanish name form ''pico Falsa Aguja'' (False Needle Peak) that probably dates back to 1957, with ‘great’ becoming established in usage and considered more suitable than ‘false’ as this heavily glaciated, major peak could hardly be associated with the ‘true’ Needle Peak (''pico Aguja''), a sharp rocky peak of elevation just 370 m situated near S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bransfield Strait
Bransfield Strait or Fleet Sea ( es, Estrecho de Bransfield, Mar de la Flota) is a body of water about wide extending for in a general northeast – southwest direction between the South Shetland Islands and the Antarctic Peninsula. History The strait was named in about 1825 by James Weddell, Master, Royal Navy, for Edward Bransfield, Master, RN, who charted the South Shetland Islands in 1820. It is called ''Mar de la Flota'' by Argentina. On 23 November 2007, the MS ''Explorer'' struck an iceberg and sank in the strait; all 154 passengers were rescued and no injuries were reported. Description The undersea trough through the strait is known as Bransfield Trough (). The basin is about 400 km long and 2 km deep, between the South Shetland Island Arc and the Antarctic Peninsula. It was formed by rifting behind the islands, which began about 4 million years ago. Ongoing rifting has caused recent earthquakes and volcanism. The Strait hosts a chain of submerged seam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |