|
Spoof Surface Plasmon
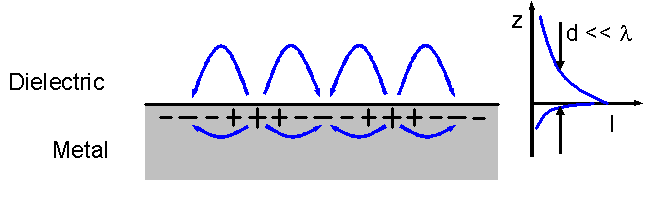
Spoof surface plasmons, also known as spoof surface plasmon polaritons and designer surface plasmons, are surface electromagnetic waves in microwave and terahertz regimes that propagate along planar interfaces with sign-changing permittivities. Spoof surface plasmons are a type of surface plasmon polariton, which ordinarily propagate along metal and dielectric interfaces in infrared and visible frequencies. Since surface plasmon polaritons cannot exist naturally in microwave and terahertz frequencies due to dispersion properties of metals, spoof surface plasmons necessitate the use of artificially-engineered metamaterials. Spoof surface plasmons share the natural properties of surface plasmon polaritons, such as dispersion characteristics and subwavelength field confinement. They were first theorized by John Pendry et al. Theory Surface plasmon polaritons (SPP) result from the coupling of delocalized electron oscillations ("surface plasmon") to electromagnetic waves ("polariton" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Wave
In physics, a surface wave is a mechanical wave that propagates along the Interface (chemistry), interface between differing media. A common example is gravity waves along the surface of liquids, such as ocean waves. Gravity waves can also occur within liquids, at the interface between two fluids with different densities. Elastic surface waves can travel along the surface of solids, such as ''Rayleigh wave, Rayleigh'' or ''Love wave, Love'' waves. Electromagnetic waves can also propagate as "surface waves" in that they can be guided along with a refractive index gradient or along an interface between two media having different dielectric constants. In radio transmission (telecommunications), transmission, a ''ground wave'' is a guided wave that propagates close to the surface of the Earth. Mechanical waves In seismology, several types of surface waves are encountered. Surface waves, in this mechanical sense, are commonly known as either ''Love waves'' (L waves) or ''Rayleigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evanescent Field
In electromagnetics, an evanescent field, or evanescent wave, is an oscillating electric and/or magnetic field that does not propagate as an electromagnetic wave but whose energy is spatially concentrated in the vicinity of the source (oscillating charges and currents). Even when there is a propagating electromagnetic wave produced (e.g., by a transmitting antenna), one can still identify as an evanescent field the component of the electric or magnetic field that cannot be attributed to the propagating wave observed at a distance of many wavelengths (such as the far field of a transmitting antenna). A hallmark of an evanescent field is that there is no net energy flow in that region. Since the net flow of electromagnetic energy is given by the average Poynting vector, this means that the Poynting vector in these regions, as averaged over a complete oscillation cycle, is zero. Use of the term In many cases one cannot simply say that a field is or is not "evanescent": Having Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drude Model
The Drude model of electrical conduction was proposed in 1900 by Paul Drude to explain the transport properties of electrons in materials (especially metals). Basically, Ohm's law was well established and stated that the current ''J'' and voltage ''V'' driving the current are related to the resistance ''R'' of the material. The inverse of the resistance is known as the conductance. When we consider a metal of unit length and unit cross sectional area, the conductance is known as the conductivity, which is the inverse of resistivity. The Drude model attempts to explain the resistivity of a conductor in terms of the scattering of electrons (the carriers of electricity) by the relatively immobile ions in the metal that act like obstructions to the flow of electrons. The model, which is an application of kinetic theory, assumes that the microscopic behaviour of electrons in a solid may be treated classically and behaves much like a pinball machine, with a sea of constantly jittering e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bravais Lattice
In geometry and crystallography, a Bravais lattice, named after , is an infinite array of discrete points generated by a set of discrete translation operations described in three dimensional space by : \mathbf = n_1 \mathbf_1 + n_2 \mathbf_2 + n_3 \mathbf_3, where the ''ni'' are any integers, and a''i'' are ''primitive translation vectors'', or ''primitive vectors'', which lie in different directions (not necessarily mutually perpendicular) and span the lattice. The choice of primitive vectors for a given Bravais lattice is not unique. A fundamental aspect of any Bravais lattice is that, for any choice of direction, the lattice appears exactly the same from each of the discrete lattice points when looking in that chosen direction. The Bravais lattice concept is used to formally define a ''crystalline arrangement'' and its (finite) frontiers. A crystal is made up of one or more atoms, called the ''basis'' or ''motif'', at each lattice point. The ''basis'' may consist of atoms, mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmon
In physics, a plasmon is a quantum of plasma oscillation. Just as light (an optical oscillation) consists of photons, the plasma oscillation consists of plasmons. The plasmon can be considered as a quasiparticle since it arises from the quantization of plasma oscillations, just like phonons are quantizations of mechanical vibrations. Thus, plasmons are collective (a discrete number) oscillations of the free electron gas density. For example, at optical frequencies, plasmons can couple with a photon to create another quasiparticle called a plasmon polariton. Derivation The plasmon was initially proposed in 1952 by David Pines and David Bohm and was shown to arise from a Hamiltonian for the long-range electron-electron correlations. Since plasmons are the quantization of classical plasma oscillations, most of their properties can be derived directly from Maxwell's equations. Explanation Plasmons can be described in the classical picture as an oscillation of electron densit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effective Medium Approximations
In materials science, effective medium approximations (EMA) or effective medium theory (EMT) pertain to analytical or theoretical modeling that describes the macroscopic properties of composite materials. EMAs or EMTs are developed from averaging the multiple values of the constituents that directly make up the composite material. At the constituent level, the values of the materials vary and are inhomogeneous. Precise calculation of the many constituent values is nearly impossible. However, theories have been developed that can produce acceptable approximations which in turn describe useful parameters including the effective permittivity and permeability of the materials as a whole. In this sense, effective medium approximations are descriptions of a medium (composite material) based on the properties and the relative fractions of its components and are derived from calculations, and effective medium theory.T.C. Choy, "Effective Medium Theory", Oxford University Press, (2016) 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfect Conductor
A perfect conductor or perfect electric conductor (PEC) is an idealized material exhibiting infinite electrical conductivity or, equivalently, zero resistivity (cf. perfect dielectric). While perfect electrical conductors do not exist in nature, the concept is a useful model when electrical resistance is negligible compared to other effects. One example is ideal magnetohydrodynamics, the study of perfectly conductive fluids. Another example is electrical circuit diagrams, which carry the implicit assumption that the wires connecting the components have no resistance. Yet another example is in computational electromagnetics, where PEC can be simulated faster, since the parts of equations that take finite conductivity into account can be neglected. Properties of perfect conductors Perfect conductors: *have exactly zero electrical resistance - a steady current within a perfect conductor will flow without losing energy to resistance. Resistance is what causes heating in conductors, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffraction-limited System
The resolution of an optical imaging system a microscope, telescope, or camera can be limited by factors such as imperfections in the lenses or misalignment. However, there is a principal limit to the resolution of any optical system, due to the physics of diffraction. An optical system with resolution performance at the instrument's theoretical limit is said to be diffraction-limited. The diffraction-limited angular resolution of a telescopic instrument is inversely proportional to the wavelength of the light being observed, and proportional to the diameter of its objective's entrance aperture. For telescopes with circular apertures, the size of the smallest feature in an image that is diffraction limited is the size of the Airy disk. As one decreases the size of the aperture of a telescopic lens, diffraction proportionately increases. At small apertures, such as f/22, most modern lenses are limited only by diffraction and not by aberrations or other imperfections in the cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subwavelength Optics
A superlens, or super lens, is a lens which uses metamaterials to go beyond the diffraction limit. For example, in 1995, Guerra combined a transparent grating having 50nm lines and spaces (the "metamaterial") with a conventional microscope immersion objective. The resulting "superlens" resolved a silicon sample also having 50nm lines and spaces, far beyond the classical diffraction limit imposed by the illumination having 650nm wavelength in air. The diffraction limit is a feature of conventional lenses and microscopes that limits the fineness of their resolution depending on the illumination wavelength and the numerical aperture NA of the objective lens. Many lens designs have been proposed that go beyond the diffraction limit in some way, but constraints and obstacles face each of them. History In 1873 Ernst Abbe reported that conventional lenses are incapable of capturing some fine details of any given image. The super lens is intended to capture such details. The limitation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed Of Light
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted , is a universal physical constant that is important in many areas of physics. The speed of light is exactly equal to ). According to the special theory of relativity, is the upper limit for the speed at which conventional matter or energy (and thus any signal carrying information) can travel through space. All forms of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, travel at the speed of light. For many practical purposes, light and other electromagnetic waves will appear to propagate instantaneously, but for long distances and very sensitive measurements, their finite speed has noticeable effects. Starlight viewed on Earth left the stars many years ago, allowing humans to study the history of the universe by viewing distant objects. When communicating with distant space probes, it can take minutes to hours for signals to travel from Earth to the spacecraft and vice versa. In computing, the speed of light fixes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Frequency
In physics, angular frequency "''ω''" (also referred to by the terms angular speed, circular frequency, orbital frequency, radian frequency, and pulsatance) is a scalar measure of rotation rate. It refers to the angular displacement per unit time (for example, in rotation) or the rate of change of the phase of a sinusoidal waveform (for example, in oscillations and waves), or as the rate of change of the argument of the sine function. Angular frequency (or angular speed) is the magnitude of the pseudovector quantity angular velocity.(UP1) One turn is equal to 2''π'' radians, hence \omega = \frac = , where: *''ω'' is the angular frequency (unit: radians per second), *''T'' is the period (unit: seconds), *''f'' is the ordinary frequency (unit: hertz) (sometimes ''ν''). Units In SI units, angular frequency is normally presented in radians per second, even when it does not express a rotational value. The unit hertz (Hz) is dimensionally equivalent, but by convention it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave Propagation
Wave propagation is any of the ways in which waves travel. Single wave propagation can be calculated by 2nd order wave equation ( standing wavefield) or 1st order one-way wave equation. With respect to the direction of the oscillation relative to the propagation direction, we can distinguish between longitudinal wave and transverse waves. For electromagnetic waves, propagation may occur in a vacuum as well as in the material medium. Other wave types cannot propagate through a vacuum and need a transmission medium to exist. Reflection of plane waves in a half-space The propagation and reflection of plane waves—e.g. Pressure waves (P-wave) or Shear waves (SH or SV-waves) are phenomena that were first characterized within the field of classical seismology, and are now considered fundamental concepts in modern seismic tomography. The analytical solution to this problem exists and is well known. The frequency domain solution can be obtained by first finding the Helmholtz deco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |