|
Speleoseismite
A speleoseismite is a damaged speleothem (cave deposit) argued to have been deformed by a seismic event (an earthquake). Speleoseismites can include severed stalagmites (those growing from the floor), fallen stalactites (those growing from the ceiling of caves), collapsed cave ceilings, tilted speleothems, change in growth axis of speleothems, stalactite-stalagmite pair displaced from one another and others. These seismite {{Earthquakes Seismites are sedimentary beds and structures deformed by seismic shaking. The German paleontologist Adolf Seilacher first used the term in 1969 to describe earthquake-deformed layers. Today, the term is applied to both sedimentary ...s can be used in paleoseismological studies of ancient earthquakes. References * ''Kagan, E.J., Agnon, A., Bar-Matthews, M., Ayalon, A., 2005, Dating large, infrequent earthquakes by damaged cave deposits. Geology, v. 33; no. 4; p. 261-264.'' * ''Gilli, E., Levret, A., Sollogoub, P., and Delange, P., 1999, Rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speleothem
A speleothem (; ) is a geological formation by mineral deposits that accumulate over time in natural caves. Speleothems most commonly form in calcareous caves due to carbonate dissolution reactions. They can take a variety of forms, depending on their depositional history and environment. Their chemical composition, gradual growth, and preservation in caves make them useful paleoclimatic proxies. Chemical and physical characteristics More than 300 variations of cave mineral deposits have been identified. The vast majority of speleothems are calcareous, composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) minerals (calcite or aragonite). Less commonly, speleothems are made of calcium sulfate (gypsum or mirabilite) or opal. Speleothems of pure calcium carbonate or calcium sulfate are translucent and colorless. The presence of iron oxide or copper provides a reddish brown color. The presence of manganese oxide can create darker colors such as black or dark brown. Speleothems can also be brown d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismite
{{Earthquakes Seismites are sedimentary beds and structures deformed by seismic shaking. The German paleontologist Adolf Seilacher first used the term in 1969 to describe earthquake-deformed layers. Today, the term is applied to both sedimentary ''layers'' and soft sediment deformation ''structures'' formed by shaking. This subtle change in usage accommodates structures that may not remain within a layer (i.e., clastic dikes or sand volcanos). Caution is urged when applying the term to features observed in the field, as similar-looking features may be products of either seismic or non-seismic perturbation. Several informal classification systems exist to help geologists distinguish seismites from other soft-sediment deformation features, though a formal, standardized system has not been developed. Geologists use seismites, in combination with other evidence, to better understand the earthquake history of an area. If age and distribution of seismically-generated features can be d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collapsed Cave Ceiling With Regrowth
''Into the Rush'' is the debut studio album by American pop rock duo Aly & AJ. The album was released on August 16, 2005, by Disney-owned label Hollywood Records. The album features 14 tracks, including the singles "Rush" and "Do You Believe in Magic". A deluxe edition of the album was released on August 8, 2006, featuring three all new songs, two new mixes of previous songs, and a bonus DVD. The album generally received positive reviews from critics and became a commercial success. ''Into the Rush'' had sold over 839,000 copies as of June 2013, and was certified Gold for sales over 500,000 copies on March 20, 2006. The album sold 1,000,000 copies worldwide. The album, combined with the sales of the Deluxe Edition, became one of the top best-selling albums in the United States in 2006; ''Into the Rush'' ranked at number 112 on the ''Billboard'' 200 Albums end-of-year charts of 2006. Chart performance ''Into the Rush'' debuted at number 36, selling 25,000 copies in its first we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismic
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other planet-like bodies. It also includes studies of earthquake environmental effects such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, glacial, fluvial, oceanic, atmospheric, and artificial processes such as explosions. A related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes is paleoseismology. A recording of Earth motion as a function of time is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist who does research in seismology. History Scholarly interest in earthquakes can be traced back to antiquity. Early speculations on the natural causes of earthquakes were included in the writings of Thales of Miletus (c. 585 BCE), Anaximenes of Miletus (c. 550 BCE), Aristotle (c. 340 BCE), and Zhan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those that are so weak that they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time period. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. The word ''tremor'' is also used for Episodic tremor and slip, non-earthquake seismic rumbling. At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and displacing or disrupting the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
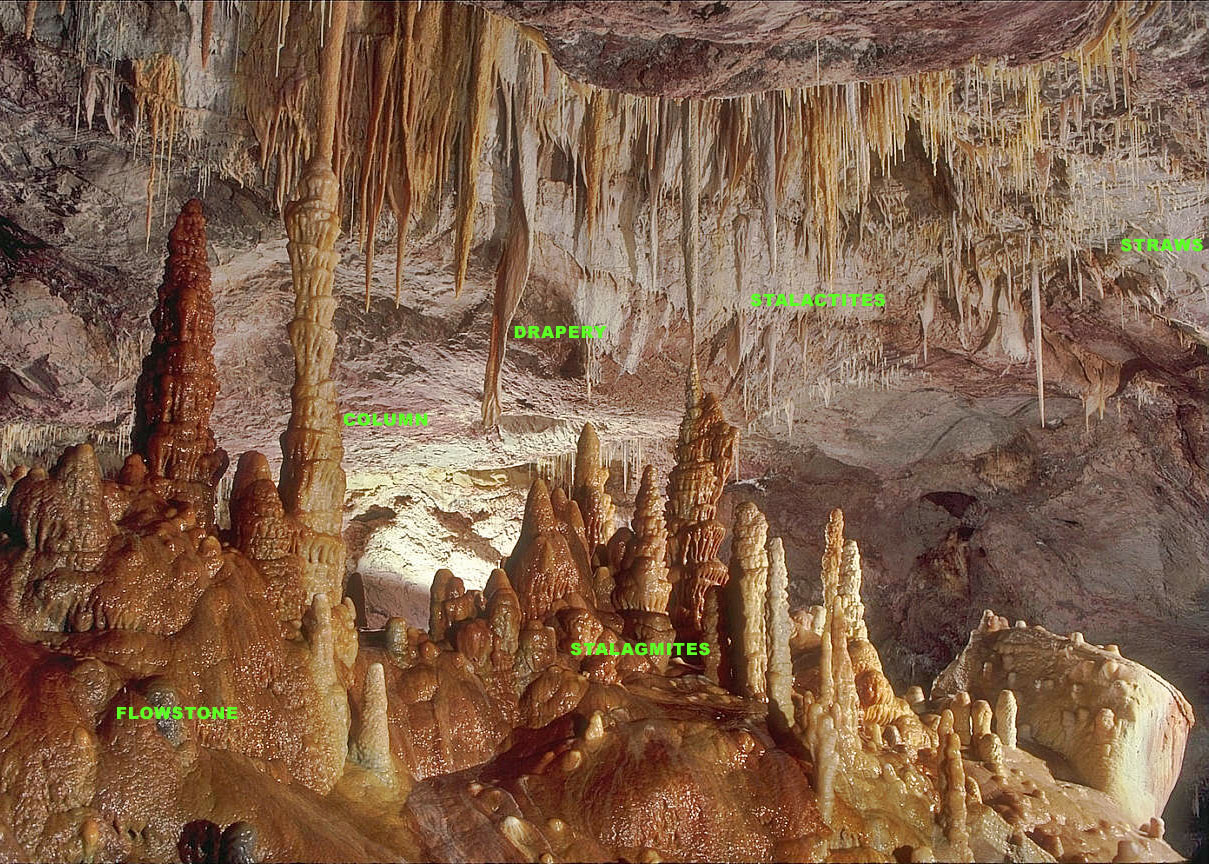
Stalagmite
A stalagmite (, ; from the Greek , from , "dropping, trickling") is a type of rock formation that rises from the floor of a cave due to the accumulation of material deposited on the floor from ceiling drippings. Stalagmites are typically composed of calcium carbonate, but may consist of lava, mud, peat, pitch, sand, sinter, and amberat (crystallized urine of pack rats). The corresponding formation hanging down from the ceiling of a cave is a stalactite. Mnemonics have been developed for which word refers to which type of formation; one is that ''stalactite'' has a C for "ceiling", and ''stalagmite'' has a G for "ground", another is that, as with ants in the pants, the mites go up and the tights (tites) come down. Formation and type Limestone stalagmites The most common stalagmites are speleothems, which usually form in limestone caves. Stalagmite formation occurs only under certain pH conditions within the cavern. They form through deposition of calcium carbonate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stalactite
A stalactite (, ; from the Greek 'stalaktos' ('dripping') via ''stalassein'' ('to drip') is a mineral formation that hangs from the ceiling of caves, hot springs, or man-made structures such as bridges and mines. Any material that is soluble and that can be deposited as a colloid, or is in suspension, or is capable of being melted, may form a stalactite. Stalactites may be composed of lava, minerals, mud, peat, pitch, sand, sinter, and amberat (crystallized urine of pack rats). A stalactite is not necessarily a speleothem, though speleothems are the most common form of stalactite because of the abundance of limestone caves. The corresponding formation on the floor of the cave is known as a stalagmite. Mnemonics have been developed for which word refers to which type of formation; one is that ''stalactite'' has a C for "ceiling", and ''stalagmite'' has a G for "ground". Another example is that ''stalactites'' "hang on ''T''ight" and ''stalagmites'' "''M''ight grow up" � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
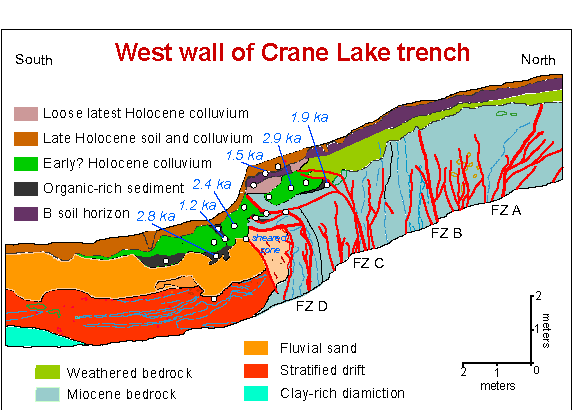
Paleoseismology
Paleoseismology looks at geologic sediments and rocks, for signs of ancient earthquakes. It is used to supplement seismic monitoring, for the calculation of seismic hazard. Paleoseismology is usually restricted to geologic regimes that have undergone continuous sediment creation for the last few thousand years, such as swamps, lakes, river beds and shorelines. In this typical example, a trench is dug in an active sedimentation regime. Evidence of thrust faulting can be seen in the walls of the trench. It becomes a matter of deducting the relative age of each fault, by cross-cutting patterns. The faults can be dated in absolute terms, if there is dateable carbon, or human artifacts. Many notable discoveries have been made using the techniques of paleoseismology. For example, there is a common misconception that having many smaller earthquakes can somehow 'relieve' a major fault such as the San Andreas Fault, and reduce the chance of a major earthquake. It is now known (u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |