|
Special Pleading
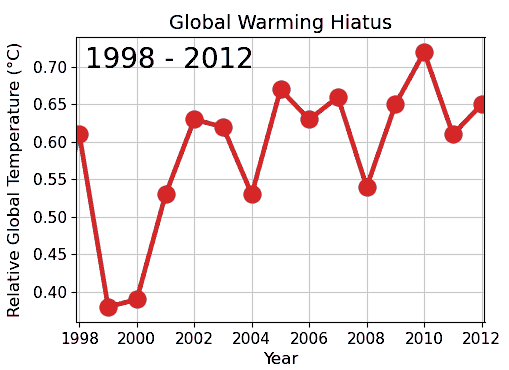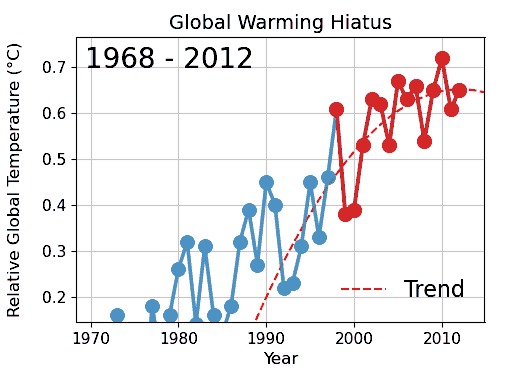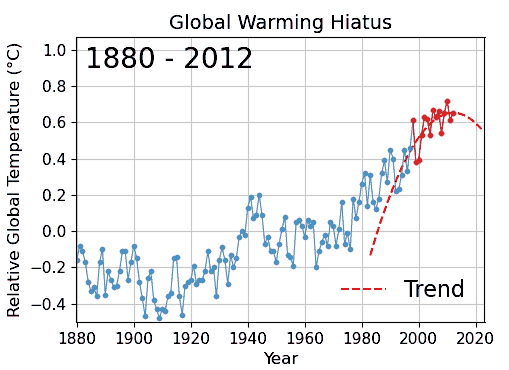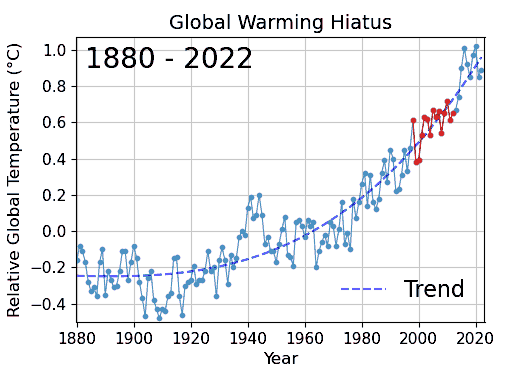
Special pleading is an informal fallacy wherein one cites something as an exception to a general or universal principle, without justifying the special exception. It is the application of a double standard. In the classic distinction among material fallacies, cognitive fallacies, and formal fallacies, special pleading most likely falls within the category of a cognitive fallacy, because it would seem to relate to "lip service", rationalization, and diversion (abandonment of discussion). Special pleading also often resembles the "appeal to" logical fallacies. In medieval philosophy, it was not presumed that wherever a distinction is claimed, a relevant basis for the distinction should exist and be substantiated. Special pleading subverts a presumption of existential import. Examples A difficult case is when a possible criticism is made relatively immune to investigation. This immunity may take the forms of: * unexplained claims of exemption from principles commonly though ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fallacy
A fallacy is the use of invalid or otherwise faulty reasoning, or "wrong moves," in the construction of an argument which may appear stronger than it really is if the fallacy is not spotted. The term in the Western intellectual tradition was introduced in the Aristotelian '' De Sophisticis Elenchis''. Some fallacies may be committed intentionally to manipulate or persuade by deception. Others may be committed unintentionally because of human limitations such as carelessness, cognitive or social biases and ignorance, or, potentially, as the inevitable consequence of the limitations of language and understanding of language. This includes ignorance of the right reasoning standard, but also ignorance of relevant properties of the context. For instance, the soundness of legal arguments depends on the context in which the arguments are made. Fallacies are commonly divided into "formal" and "informal." A formal fallacy is a flaw in the structure of a deductive argument which ren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ad Hoc Hypothesis
In science and philosophy, an ''ad hoc'' hypothesis is a hypothesis added to a theory in order to save it from being falsified. Often, ''ad hoc'' hypothesizing is employed to compensate for anomalies not anticipated by the theory in its unmodified form. In the scientific community Scientists are often skeptical of theories that rely on frequent, unsupported adjustments to sustain them. This is because, if a theorist so chooses, there is no limit to the number of ''ad hoc'' hypotheses that they could add. Thus the theory becomes more and more complex, but is never falsified. This is often at a cost to the theory's predictive power, however. ''Ad hoc'' hypotheses are often characteristic of pseudoscientific subjects. An ''ad hoc'' hypothesis is not necessarily incorrect; in some cases, a minor change to a theory was all that was necessary. For example, Albert Einstein's addition of the cosmological constant to general relativity in order to allow a static universe was ''ad hoc''. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
No True Scotsman
No True Scotsman, or appeal to purity, is an informal fallacy in which one attempts to protect their universal generalization from a falsifying counterexample by excluding the counterexample improperly.Antony Flew, ''God & Philosophy''p. 104 Hutchinson, 1966. Rather than abandoning the falsified universal generalization or providing evidence that would disqualify the falsifying counterexample, a slightly modified generalization is constructed ad-hoc to definitionally exclude the undesirable specific case and counterexamples like it by appeal to rhetoric. This rhetoric takes the form of emotionally charged but nonsubstantive purity platitudes such as "true", "pure", "genuine", "authentic", "real", etc. Philosophy professor Bradley Dowden explains the fallacy as an " ad hoc rescue" of a refuted generalization attempt. The following is a simplified rendition of the fallacy: Person A: "No Scotsman puts sugar on his porridge." Person B: "But my uncle Angus is a Scotsman and he puts s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moving The Goalposts
Moving the goalposts (or shifting the goalposts) is a metaphor, derived from goal-based sports, that means to change the rule or criterion (goal) of a process or competition while it is still in progress, in such a way that the new goal offers one side an advantage or disadvantage. In sports Deliberately moving the goalposts constitutes a professional foul in rugby football and an unfair act in gridiron football. The officials are granted ''carte blanche'' to assess whatever penalty they see fit, including awarding the score for any attempt at a goal missed or invalidating any goal scored as a result of the moved goalposts. In both rugby and gridiron, goalposts are anchored into the ground; the distance they can be moved (most easily in gridiron by pulling down on one end of the crossbar to tilt both posts either to the left or the right) is far more restricted. Inadvertently moving the goalposts in a touchdown celebration is an unsportsmanlike conduct penalty of 15 yards against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Cases Make Bad Law
Hard cases make bad law is an adage or legal maxim meaning that an extreme case is a poor basis for a general law that would cover a wider range of less extreme cases. In other words, a general law is better drafted for the average circumstance as this will be more common. The original meaning of the phrase concerned cases in which the law had a hard impact on some person whose situation aroused sympathy. The expression dates at least to 1837. It was used in 1904 by US Supreme Court Justice Oliver Wendell Holmes Jr. Its validity has since been questioned and dissenting variations include the phrase "Bad law makes hard cases", and even its opposite, "Hard cases make good law". Discussion The maxim dates at least to 1837, when a judge, ruling in favor of a parent against the maintenance of her children, said, "We have heard that hard cases make bad law." The judge's wording suggests that the phrase was not new then. Oliver Wendell Holmes Jr. made a utilitarian argument for this in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exception That Proves The Rule
"The exception that proves the rule" is a saying whose meaning is contested. Henry Watson Fowler's ''Modern English Usage'' identifies five ways in which the phrase has been used, and each use makes some sort of reference to the role that a particular case or event takes in relation to a more general rule. Two original meanings of the phrase are usually cited. The first, preferred by Fowler, is that the presence of an exception applying to a ''specific'' case establishes ("proves") that a ''general'' rule exists. A more explicit phrasing might be "the exception that proves ''the existence of'' the rule". Most contemporary uses of the phrase emerge from this origin, although often in a way which is closer to the idea that all rules have their exceptions. The alternative origin given is that the word "prove" is used in the archaic sense of "test". In this sense, the phrase does not mean that an exception demonstrates a rule to be true or to exist, but that it tests the rule, thereby ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courtier's Reply
The courtier's reply is a type of informal fallacy, coined by American biologist PZ Myers, in which a respondent to criticism claims that the critic lacks sufficient knowledge, credentials, or training to pose any sort of criticism whatsoever.Myers, PZ (December 24, 2006)"The Courtier's Reply" Pharyngula. It may be considered an inverted form of argument from authority, where a person without authority disagreeing with authority is presumed incorrect ''prima facie''. A key element of a courtier's reply, which distinguishes it from an otherwise valid response that incidentally points out the critic's lack of established authority on the topic, is that the respondent never shows how the work of these overlooked experts invalidates the arguments that were advanced by the critic. Critics of the idea that the courtier's reply is a real fallacy have called it the "Myers shuffle", implying calling someone out for an alleged courtier's reply is a kind of rhetorical dodge or trick. Usage h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherry Picking (fallacy)
Cherry picking, suppressing evidence, or the fallacy of incomplete evidence is the act of pointing to individual cases or data that seem to confirm a particular position while ignoring a significant portion of related and similar cases or data that may contradict that position. Cherry picking may be committed intentionally or unintentionally. The term is based on the perceived process of harvesting fruit, such as cherries. The picker would be expected to select only the ripest and healthiest fruits. An observer who sees only the selected fruit may thus wrongly conclude that most, or even all, of the tree's fruit is in a likewise good condition. This can also give a false impression of the quality of the fruit (since it is only a sample and is not a representative sample). A concept sometimes confused with cherry picking is the idea of gathering only the fruit that is easy to harvest, while ignoring other fruit that is higher up on the tree and thus more difficult to obtain (see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Existential Import
A syllogism ( grc-gre, συλλογισμός, ''syllogismos'', 'conclusion, inference') is a kind of logical argument that applies deductive reasoning to arrive at a conclusion based on two propositions that are asserted or assumed to be true. In its earliest form (defined by Aristotle in his 350 BCE book '' Prior Analytics''), a syllogism arises when two true premises (propositions or statements) validly imply a conclusion, or the main point that the argument aims to get across. For example, knowing that all men are mortal (major premise) and that Socrates is a man (minor premise), we may validly conclude that Socrates is mortal. Syllogistic arguments are usually represented in a three-line form: All men are mortal. Socrates is a man. Therefore, Socrates is mortal.In antiquity, two rival syllogistic theories existed: Aristotelian syllogism and Stoic syllogism. From the Middle Ages onwards, ''categorical syllogism'' and ''syllogism'' were usually used interchangeably. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Standard
A double standard is the application of different sets of principles for situations that are, in principle, the same. It is often used to describe treatment whereby one group is given more latitude than another. A double standard arises when two or more people, groups, organizations, circumstances, or events are treated differently even though they should be treated the same way. A double standard "implies that two things which are the same are measured by different standards". Applying different principles to similar situations may or may not indicate a double standard. To distinguish between the application of a double standard and a valid application of different standards toward circumstances that only ''appear'' to be the same, several factors must be examined. One is the sameness of those circumstances – what are the parallels between those circumstances, and in what ways do they differ? Another is the philosophy or belief system informing which principles should be appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association Fallacy
An association fallacy is an informal inductive fallacy of the hasty-generalization or red-herring type and which asserts, by irrelevant association and often by appeal to emotion, that qualities of one thing are inherently qualities of another. Two types of association fallacies are sometimes referred to as guilt by association and honor by association. Form In notation of first-order logic, this type of fallacy can be expressed as ( ∃''x'' ∈ ''S'' : ''φ''(''x'')) ⇒ ( ∀''x'' ∈ ''S'' : ''φ''(''x'')), meaning "if there exists any ''x'' in the set ''S'' so that a property ''φ'' is true for ''x'', then for all ''x'' in ''S'' the property ''φ'' must be true." :Premise: A is a B :Premise: A is also a C :Conclusion: Therefore, all Bs are Cs The fallacy in the argument can be illustrated through the use of an Euler diagram: "A" satisfies the requirement that it is part of both sets "B" and "C", but if one represent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fallacies
A fallacy is reasoning that is logically invalid, or that undermines the logical validity of an argument. All forms of human communication can contain fallacies. Because of their variety, fallacies are challenging to classify. They can be classified by their structure ( formal fallacies) or content (informal fallacies). Informal fallacies, the larger group, may then be subdivided into categories such as improper presumption, faulty generalization, and error in assigning causation and relevance, among others. The use of fallacies is common when the speaker's goal of achieving common agreement is more important to them than utilizing sound reasoning. When fallacies are used, the premise should be recognized as not well-grounded, the conclusion as unproven (but not necessarily false), and the argument as unsound. Formal fallacies A formal fallacy is an error in the argument's form. All formal fallacies are types of . * Appeal to probability – a statement that takes something ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |