|
Spathognathodus
''Spathognathodus'' is an extinct conodont genus in the family Spathognathodontidae. It is a non-Platform conodont, from the Pennsylvanian (Carboniferous).Pennsylvanian Nonplatform Conodont Genera, I: Spathognathodus. Glen K. Merrill, Journal of Paleontology, Vol. 47, No. 2 (Mar., 1973), pages 289-314Stable URL retrieved 04 May 2016) References External links ''Spathognathodus''at fossilworks Fossilworks is a portal which provides query, download, and analysis tools to facilitate access to the Paleobiology Database The Paleobiology Database is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals ....org (retrieved 4 May 2016) Ozarkodinida genera Pennsylvanian conodonts Fossil taxa described in 1941 Taxa named by Edward Branson Taxa named by Maurice Mehl Paleozoic life of Yukon {{Conodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spathognathodontidae
Spathognathodontidae is an extinct conodont family ranging from the Silurian to the Devonian.On Classification of Pridoli (Silurian)-Lochkovian (Devonian) Spathognathodontidae (Conodonts). Murphy M.A., Valenzuela-Ríos J.I. and Carls P., 2004, University of California, Riverside Campus Museum Contribution, 6, pp. 1-25, 3 FigsPDF/ref> Genera Genera are: * †'' Flajsella'' * †'' Lanea'' * †''Ozarkodina'' * †'' Spathognathodus'' * †'' Tortodus'' * †'' Wurmiella'' * †''Zieglerodina'' References * A new Ludlow (Late Silurian) Spathognathodontidae (Conodonta) from Bohemia with incipient alternating denticulation. P. Carls, L. Slavík and José Ignacio Valenzuela-Ríos, Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Monatshefte, September 2005, 9, pages 547–565. External links * * Spathognathodontidaeat fossilworks Fossilworks is a portal which provides query, download, and analysis tools to facilitate access to the Paleobiology Database The Paleobiolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvanian (geology)
The Pennsylvanian ( , also known as Upper Carboniferous or Late Carboniferous) is, in the International Commission on Stratigraphy, ICS geologic timescale, the younger of two period (geology), subperiods (or upper of two system (stratigraphy), subsystems) of the Carboniferous Period. It lasted from roughly . As with most other geochronology, geochronologic units, the stratum, rock beds that define the Pennsylvanian are well identified, but the exact date of the start and end are uncertain by a few hundred thousand years. The Pennsylvanian is named after the U.S. state of Pennsylvania, where the coal-productive beds of this age are widespread. The division between Pennsylvanian and Mississippian (geology), Mississippian comes from North American stratigraphy. In North America, where the early Carboniferous beds are primarily marine limestones, the Pennsylvanian was in the past treated as a full-fledged geologic period between the Mississippian and the Permian. In parts of Europe, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Edward Branson
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 1941
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvanian Conodonts
Pennsylvanian may refer to: * A person or thing from Pennsylvania * Pennsylvanian (geology) The Pennsylvanian ( , also known as Upper Carboniferous or Late Carboniferous) is, in the International Commission on Stratigraphy, ICS geologic timescale, the younger of two period (geology), subperiods (or upper of two system (stratigraphy), s ..., a geological subperiod of the Carboniferous Period * ''Pennsylvanian'' (train), an Amtrak train {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozarkodinida Genera
Ozarkodinida is an extinct conodont order. It is part of the clade Prioniodontida, also known as the "complex conodonts". Name Ozarkodinida is named after the Ozark Mountains of Missouri Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee ..., United States. Elements The feeding apparatus of ozarkodinids is composed at the front of an axial Sa element, flanked by two groups of four close-set elongate Sb and Sc elements which were inclined obliquely inwards and forwards. Above these elements lay a pair of arched and inward pointing (makellate) M elements. Behind the S-M array lay transversely oriented and bilaterally opposed (pectiniform, i.e. comb-shaped) Pb and Pa elements. References External links * * Prehistoric jawless fish orders {{Conodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossilworks
Fossilworks is a portal which provides query, download, and analysis tools to facilitate access to the Paleobiology Database The Paleobiology Database is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms. History The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) originated in the NCEAS-funded Phanerozoic Marine Pale ..., a large relational database assembled by hundreds of paleontologists from around the world. History Fossilworks was created in 1998 by John Alroy and is housed at Macquarie University. It includes many analysis and data visualization tools formerly included in the Paleobiology Database.{{cite web, title=Frequently asked questions, url=http://www.fossilworks.org/cgi-bin/bridge.pl?page=FAQ, publisher=Fossilworks, access-date=17 December 2021 References {{Reflist External links {{Wikidata property, P842 * [Baidu] |
Spathodus
''Spathodus'' is a small genus of cichlids endemis to Lake Tanganyika in east Africa. Species There are currently two recognized species in this genus: * ''Spathodus erythrodon'' Boulenger, 1900 * ''Spathodus marlieri'' Poll Poll, polled, or polling may refer to: Figurative head counts * Poll, a formal election ** Election verification exit poll, a survey taken to verify election counts ** Polling, voting to make decisions or determine opinions ** Polling places o ..., 1950 References Eretmodini Freshwater fish genera * Cichlid genera Taxa named by George Albert Boulenger {{Cichlidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
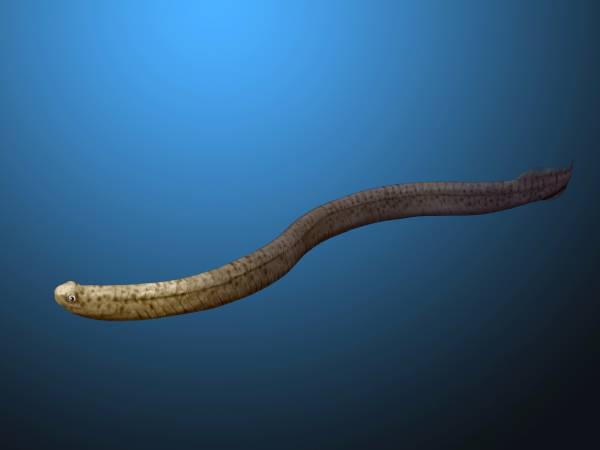
Conodont
Conodonts (Greek ''kōnos'', "cone", + ''odont'', "tooth") are an extinct group of agnathan (jawless) vertebrates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from their tooth-like oral elements, which are usually found in isolation and are now called conodont elements. Knowledge about soft tissues remains limited. They existed in the world's oceans for over 300 million years, from the Cambrian to the beginning of the Jurassic. Conodont elements are widely used as index fossils, fossils used to define and identify geological periods. The animals are also called Conodontophora (conodont bearers) to avoid ambiguity. Discovery and understanding of conodonts The teeth-like fossils of the conodont were first discovered by Heinz Christian Pander and the results published in Saint Petersburg, Russia, in 1856. The name ''pander'' is commonly used in scientific names of conodonts. It was only in the early 1980s that the first fossil evidence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordata
A chordate () is an animal of the phylum Chordata (). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five synapomorphies, or primary physical characteristics, that distinguish them from all the other taxa. These five synapomorphies include a notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail. The name “chordate” comes from the first of these synapomorphies, the notochord, which plays a significant role in chordate structure and movement. Chordates are also Bilateral symmetry, bilaterally symmetric, have a coelom, possess a circulatory system, and exhibit Metameric, metameric segmentation. In addition to the morphological characteristics used to define chordates, analysis of genome sequences has identified two conserved signature indels (CSIs) in their proteins: cyclophilin-like protein and mitochondrial inner membrane protease ATP23, which are exclusively shared by all vertebrates, tunicates and cep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willi Ziegler
Willi Ziegler (born 13 March 1929 in the neighborhood of Villingen in Hungen, Hessen; died 8 August 2002) was a German paleontologist. Works In 1969, he described the conodont genus ''Protognathodus''. In 1984, with Charles A. Sandberg, he described the conodont genus ''Alternognathus''. In 2002, with IA Bardashev and K Weddige, he described the conodont genus ''Eolinguipolygnathus''.The phylomorphogenesis of some Early Devonian platform conodonts. IA Bardashev, K Weddige and W Ziegler, Senckenbergiana lethaea, December 2002, volume 82, issue 2, pages 375-451, Ziegler's Catalogue of Conodonts * Ziegler's Catalogue of Conodonts. Schweizerbart Science Publisherslink to editor website retrieved 7 May 2016) ** Volume I, 1973 ** Volume II, 1975 ** Volume III, 1977 ** Volume IV, 1981 ** Volume V, 1991 Awards and tributes In 1998, he received the Goethe-Plakette des Landes Hessen, the highest award by the Hessian Ministry for Science and the Arts in Hesse, Germany. He w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |