|
Spasatel
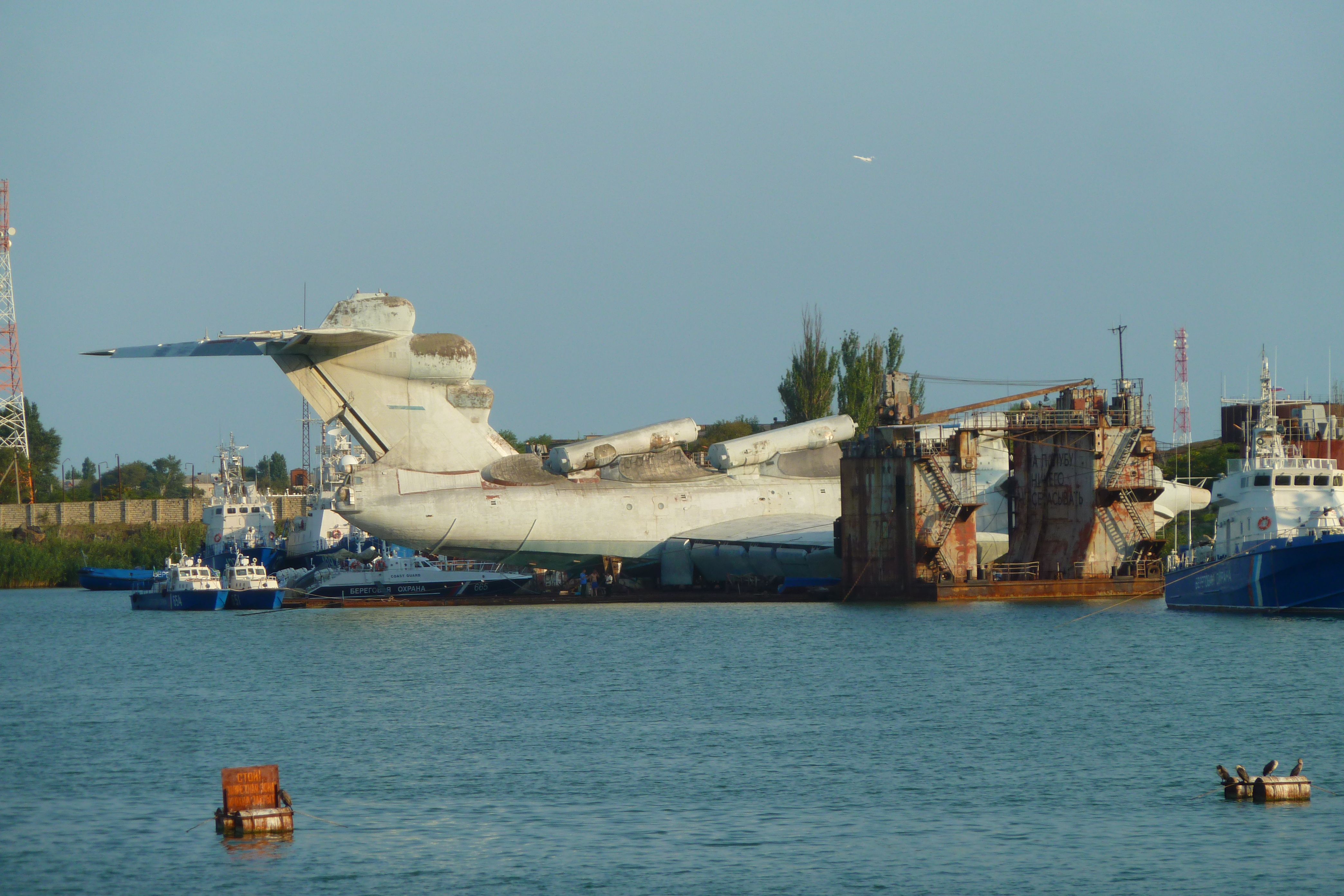
Spasatel (russian: Спасатель "Rescuer", "Lifesaver", Project 9038) is a ground-effect vehicle, originally planned by the Soviet Ministry of Defense. The vehicle was intended to serve as the missile carrier of the project ''Lun''-class ekranoplan, but was then converted into an ambulance craft. Following the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, construction was halted and the vehicle was never completed. By 2018, Russia had revived the project, with plans to use it for search and rescue operations in the Arctic and Pacific, as well as cargo and troop delivery (up to 550 troops) to remote military bases. Goals A military advantage of ground-effect vehicles over ships and submarines was that they did not have draft during operation, and therefore could not be detected by sonar and could not be hit by torpedoes. Advantages over aircraft include operation at low altitude, which makes radar acquisition difficult, and a larger payload. This was particularly interesting d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spasatel Ekranoplan Modell
Spasatel (russian: Спасатель "Rescuer", "Lifesaver", Project 9038) is a ground-effect vehicle, originally planned by the Soviet Ministry of Defense. The vehicle was intended to serve as the missile carrier of the project ''Lun''-class ekranoplan, but was then converted into an ambulance craft. Following the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, construction was halted and the vehicle was never completed. By 2018, Russia had revived the project, with plans to use it for search and rescue operations in the Arctic and Pacific, as well as cargo and troop delivery (up to 550 troops) to remote military bases. Goals A military advantage of ground-effect vehicles over ships and submarines was that they did not have draft during operation, and therefore could not be detected by sonar and could not be hit by torpedoes. Advantages over aircraft include operation at low altitude, which makes radar acquisition difficult, and a larger payload. This was particularly interesting du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lun-class Ekranoplan
The ''Lun''-class ekranoplan (also called Project 903) is the only ground effect vehicle (GEV) to ever be operationally deployed as a warship. designed by Rostislav Alexeyev in 1975 and used by the Soviet and Russian navies from 1987 until sometime in the late 1990s. It flew using lift generated by the ground effect acting on its large wings when within about above the surface of the water. Although they might look similar to traditional aircraft, ekranoplans like the ''Lun'' are not classified as aircraft, seaplanes, hovercraft, or hydrofoils. Rather, crafts like the ''Lun''-class ekranoplan are classified as maritime ships by the International Maritime Organization due to their use of the ground effect, in which the craft glides just above the surface of the water. The ground effect occurs when flying at an altitude of only a few meters above the ocean or ground; drag is greatly reduced by the proximity of the ground preventing the formation of wingtip vortices, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lun Class
The ''Lun''-class ekranoplan (also called Project 903) is the only ground effect vehicle (GEV) to ever be operationally deployed as a warship. designed by Rostislav Alexeyev in 1975 and used by the Soviet and Russian navies from 1987 until sometime in the late 1990s. It flew using lift generated by the ground effect acting on its large wings when within about above the surface of the water. Although they might look similar to traditional aircraft, ekranoplans like the ''Lun'' are not classified as aircraft, seaplanes, hovercraft, or hydrofoils. Rather, crafts like the ''Lun''-class ekranoplan are classified as maritime ships by the International Maritime Organization due to their use of the ground effect, in which the craft glides just above the surface of the water. The ground effect occurs when flying at an altitude of only a few meters above the ocean or ground; drag is greatly reduced by the proximity of the ground preventing the formation of wingtip vortices, thus in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground-effect Vehicle
A ground-effect vehicle (GEV), also called a wing-in-ground-effect (WIG), ground-effect craft, wingship, flarecraft or ekranoplan (russian: экранопла́н – "screenglider"), is a vehicle that is able to move over the surface by gaining support from the reactions of the air against the surface of the earth or water. Typically, it is designed to glide over a level surface (usually over the sea) by making use of ground effect, the aerodynamic interaction between the moving wing and the surface below. Some models can operate over any flat area such as frozen lakes or flat plains similar to a hovercraft. Design A ground-effect vehicle needs some forward velocity to produce lift dynamically, and the principal benefit of operating a wing in ground effect is to reduce its lift-dependent drag. The basic design principle is that the closer the wing operates to an external surface such as the ground, when it is said to be in ground effect, the less drag it feels. An airfoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ekranoplans
A ground-effect vehicle (GEV), also called a wing-in-ground-effect (WIG), ground-effect craft, wingship, flarecraft or ekranoplan (russian: экранопла́н – "screenglider"), is a vehicle that is able to move over the surface by gaining support from the reactions of the air against the surface of the earth or water. Typically, it is designed to glide over a level surface (usually over the sea) by making use of ground effect, the aerodynamic interaction between the moving wing and the surface below. Some models can operate over any flat area such as frozen lakes or flat plains similar to a hovercraft. Design A ground-effect vehicle needs some forward velocity to produce lift dynamically, and the principal benefit of operating a wing in ground effect is to reduce its lift-dependent drag. The basic design principle is that the closer the wing operates to an external surface such as the ground, when it is said to be in ground effect, the less drag it feels. An airfoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TTS-IS
TTS-IS (Russian Тяжелый транспортный самолет интегральной схемы (ТТС-ИС), heavy transport aircraft integrated circuit (HTA-IC)) is a project by TsAGI for a very large wing-in-ground-effect, lifting-body cargo aircraft with a take-off weight of 1000 tons, a payload of 500 tons, with a flight range of over 6000 km, a cruising speed of 500 km / h. Although the aircraft typically flies at above water, ice, or ground to reduce drag, it is designed to take off and land at conventional airports, unlike most ground effect vehicles but similar to the Boeing Pelican. As with the Airbus A380 and the Boeing 747-8, the aircraft is designed to land at airports that meet the Aerodrome Reference Code code 4F standard of the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO). It is also notable for the use of liquefied natural gas (LNG) as its aviation fuel source, and for the use of intermodal containers that are standardized in train, ship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alekseyev Central Hydrofoil Design Bureau
Alekseyev Central Hydrofoil Design Bureau (russian: Конструкторское бюро Алексеева) is a company based in Nizhniy Novgorod, Russia. It was named after Rostislav Alexeyev. This design bureau has been designing hydrofoils, air cushion craft, and air cavity vessels for many years. It designed and manufactured several designs for wing-in-ground-effect vehicles, including the 400-ton Lun-class ekranoplan, 140-ton A-90 Orlyonok, and 20-ton Utka. Vehicles * А-080-752 * Spasatel * А-300-538 * A-90 Orlyonok *Lun-class ekranoplan The ''Lun''-class ekranoplan (also called Project 903) is the only ground effect vehicle (GEV) to ever be operationally deployed as a warship. designed by Rostislav Alexeyev in 1975 and used by the Soviet and Russian navies from 1987 until ... * Utka References External links Official website Aircraft manufacturers of Russia Companies based in Nizhny Novgorod Ministry of the Shipbuilding Industry (Soviet Union) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draft (hull)
The draft or draught of a ship's hull is the vertical distance between the waterline and the bottom of the hull ( keel). The draught of the vessel is the maximum depth of any part of the vessel, including appendages such as rudders, propellers and drop keels if deployed. Draft determines the minimum depth of water a ship or boat can safely navigate. The related term air draft is the maximum height of any part of the vessel above the water. The more heavily a vessel is loaded, the deeper it sinks into the water, and the greater its draft. After construction, the shipyard creates a table showing how much water the vessel displaces based on its draft and the density of the water (salt or fresh). The draft can also be used to determine the weight of cargo on board by calculating the total displacement of water, accounting for the content of the ship's bunkers, and using Archimedes' principle. The closely related term "trim" is defined as the difference between the forward and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nizhny Novgorod
Nizhny Novgorod ( ; rus, links=no, Нижний Новгород, a=Ru-Nizhny Novgorod.ogg, p=ˈnʲiʐnʲɪj ˈnovɡərət ), colloquially shortened to Nizhny, from the 13th to the 17th century Novgorod of the Lower Land, formerly known as Gorky (, ; 1932–1990), is the administrative centre of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast and the Volga Federal District. The city is located at the confluence of the Oka and the Volga rivers in Central Russia, with a population of over 1.2 million residents, up to roughly 1.7 million residents in the urban agglomeration. Nizhny Novgorod is the sixth-largest city in Russia, the second-most populous city on the Volga, as well as the Volga Federal District. It is an important economic, transportation, scientific, educational and cultural center in Russia and the vast Volga-Vyatka economic region, and is the main center of river tourism in Russia. In the historic part of the city there are many universities, theaters, museums and churches. The city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proposed Aircraft Of Russia
Proposal(s) or The Proposal may refer to: * Proposal (business) * Research proposal * Proposal (marriage) * Proposition, a proposal in logic and philosophy Arts, entertainment, and media * ''The Proposal'' (album) Films * ''The Proposal'' (1957 film), an Australian television play based on Chekhov's 1890 play * ''The Proposal'' (2001 film), starring Nick Moran, Jennifer Esposito, and Stephen Lang * ''The Proposal'' (2009 film), starring Sandra Bullock and Ryan Reynolds * ''The Proposal'' (2022 film), starring Joe Joseph and Amara Raja * " La propuesta" ("The Proposal"), a short story in the 2014 Argentina anthology film ''Wild Tales'' Literature * ''Proposals (play)'', a 1997 play by Neil Simon * ''The Proposal'' (novel), 1999 and 35th book in the ''Animorphs'' series by K.A. Applegate * ''The Proposal'', alternative title of Chekhov's 1890 play '' A Marriage Proposal'' Television * ''The Proposal'' (American TV series), a 2018 reality dating series * The Proposal (Au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Manufactured In The Soviet Union
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, helicopters, airships (including blimps), gliders, paramotors, and hot air balloons. The human activity that surrounds aircraft is called ''aviation''. The science of aviation, including designing and building aircraft, is called ''aeronautics.'' Crewed aircraft are flown by an onboard pilot, but unmanned aerial vehicles may be remotely controlled or self-controlled by onboard computers. Aircraft may be classified by different criteria, such as lift type, aircraft propulsion, usage and others. History Flying model craft and stories of manned flight go back many centuries; however, the first manned ascent — and safe descent — in modern times took place by larger hot-a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Ministry Of Defense
The Ministry of Defense (Minoboron; russian: Министерство обороны СССР) was a government ministry in the Soviet Union. The first Minister of Defense was Nikolai Bulganin, starting 1953. The Krasnaya Zvezda (Red Star) was the official newspaper of the Ministry. The Ministry of Defense was disbanded on 16 March 1992. An agreement to set up a joint CIS military command was signed on 20 March 1992, but the idea was discarded as the post-Soviet states quickly built up separate national armies. Organization The Ministry of Defense, an all-union ministry, was technically subordinate to the Council of Ministers, as well as to the Supreme Soviet and the Central Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. In 1989 it was, however, larger than most other ministries and had special arrangements for party supervision of, and state participation in, its activities. The Ministry of Defense was made up of the General Staff, the Main Political Directorate of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |