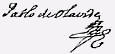|
Spanish Confiscation
The Spanish confiscation was the Spanish government's seizure and sale of property, including from the Catholic Church, from the late 18th century to the early 20th century. It was a long historical, economic, and social process beginning with the so-called "Confiscation of Godoy" in 1798—although there was an earlier precedent during the reign of Charles III of Spain—and ending on 16 December 1924. Confiscation consisted of the forced expropriation of land and property from the "mortmains" (i.e., the Catholic Church and religious orders, which had accumulated it from grants, wills, and intestates) and from municipalities. The government then sold the property on the market or through public auctions. A similar phenomenon occurred in other countries, such as Mexico.For example, in Mexico, the ''Law of confiscation of the rural and urban properties of the civil and religious corporations of Mexico'', nicknamed the lerdo law, was issued on 25 June 1856 by President Ignacio C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pablo Olavide
Pablo is a Spanish form of the name Paul. People *Pablo Alborán, Spanish singer *Pablo Aimar, Argentine footballer *Pablo Armero, Colombian footballer * Pablo Bartholomew, Indian photojournalist *Pablo Brandán, Argentine footballer * Pablo Brenes, Costa Rican footballer *Pablo Alborán, Spanish singer-songwriter *Pablo Casals, Catalan cello virtuoso *Pablo Couñago, Spanish footballer *Pablo Cuevas, Uruguayan tennis player *Pablo Eisenberg (born 1932), American scholar, social justice advocate, and tennis player *Pablo Escobar, Colombian drug lord *Pablo Iglesias Turrión, Spanish politician *Pablo Francisco, Chilean American comedian * Pablo Galdames, Chilean footballer *Pablo P. Garcia, Filipino politician *Pablo Hernández Domínguez, Spanish footballer *Pablo Ibañez, Spanish footballer *Pablo Iglesias Simón, Spanish theatre director, sound designer and playwright *Pablo Lombi, Argentine field hockey player *Pablo Darío López, Argentine footballer *Pablo Iglesias Posse, Spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Librorum Prohibitorum
The ''Index Librorum Prohibitorum'' ("List of Prohibited Books") was a list of publications deemed heretical or contrary to morality by the Sacred Congregation of the Index (a former Dicastery of the Roman Curia), and Catholics were forbidden to read them.Grendler, Paul F. "Printing and censorship" in ''The Cambridge History of Renaissance Philosophy'' Charles B. Schmitt, ed. (Cambridge University Press, 1988, ) pp. 45–46 There were attempts to ban heretical books before the sixteenth century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Castile
The Council of Castile ( es, Real y Supremo Consejo de Castilla), known earlier as the Royal Council ( es, Consejo Real), was a ruling body and key part of the domestic government of the Crown of Castile, second only to the monarch himself. It was established under Queen Isabella I in 1480 as the chief body dealing with administrative and judicial matters of the realm. With the 1516 ascension of King Charles I (later Holy Roman Emperor Charles V) to the throne of both Castile and Aragon, the Royal Council came to be known as the Council of Castile because Charles was king of many dominions other than Castile, while the Council retained responsibility only over Castile. During periods in which there was no monarch, an absent monarch, or an incompetent monarch, the Royal Council would rule as a regency council in his place. The Council weakened in the 19th century, where it was abolished and re-established several times before being dissolved permanently. History Origins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francisco Tomás Y Valiente
Francisco Tomás y Valiente (8 December 1932 – 14 February 1996) was a Spanish jurist, historian, and writer. He was professor of history of law in the Autonomous University of Madrid. He presided Spain's Constitutional Court from 1986 to 1992. He was assassinated by ETA in 1996. His killing led to between 850,000 and 1 million people marching in protest through Madrid, headed by the then Prime Minister, Felipe González (PSOE), and the leaders of all mainstream political parties. Regarding the definition of "state", Tomás y Valiente declared that without a state there could be neither Law nor rights, only chaos ("Sin Estado no hay ni Derecho ni derechos, solo hay caos"). Likewise, as an expert in the history of Law, he was convinced that the Law does not suffice without goodwill, and he was especially concerned about two particular risks, of four, that he perceived in Spain's political system: the lack of goodwill in co-operating and the autonomous communities' haste in rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Liberalism
Economic liberalism is a political and economic ideology that supports a market economy based on individualism and private property in the means of production. Adam Smith is considered one of the primary initial writers on economic liberalism, and his writing is generally regarded as representing the economic expression of 19th-century liberalism up until the Great Depression and rise of Keynesianism in the 20th century. Historically, economic liberalism arose in response to feudalism and mercantilism. Economic liberalism is associated with markets and private ownership of capital assets. Economic liberals tend to oppose government intervention and protectionism in the market economy when it inhibits free trade and competition, but tend to support government intervention where it protects property rights, opens new markets or funds market growth, and resolves market failures. An economy that is managed according to these precepts may be described as a liberal eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francisco De Goya Y Lucientes - Gaspar Melchor De Jovellanos
Francisco is the Spanish and Portuguese form of the masculine given name '' Franciscus''. Nicknames In Spanish, people with the name Francisco are sometimes nicknamed " Paco". San Francisco de Asís was known as ''Pater Comunitatis'' (father of the community) when he founded the Franciscan order, and "Paco" is a short form of ''Pater Comunitatis''. In areas of Spain where Basque is spoken, " Patxi" is the most common nickname; in the Catalan areas, "Cesc" (short for Francesc) is often used. In Spanish Latin America and in the Philippines, people with the name Francisco are frequently called " Pancho". " Kiko" is also used as a nickname, and " Chicho" is another possibility. In Portuguese, people named Francisco are commonly nicknamed " Chico" (''shíco''). This is also a less-common nickname for Francisco in Spanish. People with the given name * Pope Francis is rendered in the Spanish and Portuguese languages as Papa Francisco * Francisco Acebal (1866–1933), Spanish writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savings Bank (Spain)
In Spain, a savings bank ( es, caja de ahorros or informally just ''caja'', ca, caixa d'estalvis, gl, caixa de aforros, informally caixa, eu, aurrezki kutxa) is a financial institution that specializes in accepting savings deposits and granting loans. Spanish banks fall into two categories: Privately owned banks (''bancos'') and government owned banks (''cajas''—literally pay office, or pay desk). The original aim was to encourage thrift among the very poor, but they evolved to compete with and rival commercial banks. Over time, most cajas colluded with regional political establishments to create a self-serving system of unscrupulous financing for regional governments provided by politically stuffed savings banks' boards which, in turn, thrived in what has been defined as "a culture of greed, cronyism and political meddling". This system was exposed in the aftermath of the global financial crisis. As a result, out of the 45 cajas in existence at the start of the crisis in 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar (Spanish Term)
In Spanish urban development a ''solar'' is a plot of land that meets minimum conditions to be built on , RAE. Retrieved on July 11, 2012. and developed properly according to existing land use regulations. These conditions relate primarily to and access to the , disposal or purification of and [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaspar Melchor De Jovellanos
Gaspar Melchor de Jovellanos (born Gaspar Melchor de Jove y Llanos, 5 January 1744 – 27 November 1811) was a Spanish neoclassical statesman, author, philosopher and a major figure of the Age of Enlightenment in Spain. Life and influence of his works Gaspar Melchor de Jovellanos (pseudonym Jovino) was born at Gijón in Asturias, Spain. Selecting law as his profession, he studied at Oviedo, Ávila, and the University of Alcalá, before becoming a criminal judge at Seville in 1767. His integrity and ability were rewarded in 1778 by a judgeship in Madrid, and in 1780 by appointment to the council of military orders. In the capital Jovellanos was a respected member of the literary and scientific societies; he was commissioned by the Society of Friends of the Country (Madrid's economic society) in 1787 to write his most well-known and influential work, ''Informe en el expediente de ley agraria'' ("A report on the dossier of the Agrarian Law"), a project which he completed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pablo De Olavide
Pablo de Olavide y Jáuregui (Lima, Viceroyalty of Peru, 25 January 1725 – Baeza, Spain, 25 February 1803) was a Spanish politician, lawyer and writer. Biography He was born in a rich and influential creole Liman Basque family and studied at the San Marcos University of Lima. He earned a doctorate in Theology in 1740 and a degree in Law in 1742. He was appointed assistant of the Consulate Tribunal and ''oidor'' (judge) of the Audiency of Lima. In 1746, he was indicted for embezzlement and he had to go to Spain to be prosecuted by the Council of the Indies in 1750. He was imprisoned briefly in 1754, but he was finally condemned in 1757 just to temporary disqualification for public offices. In 1755 he married a rich widow and traveled through Italy and France. He met the most outstanding European enlightened philosophers and writers, like Voltaire (who he said was "A Spaniard who thinks") and his Madrid house was one of the most notable meeting points of the Spanish enli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
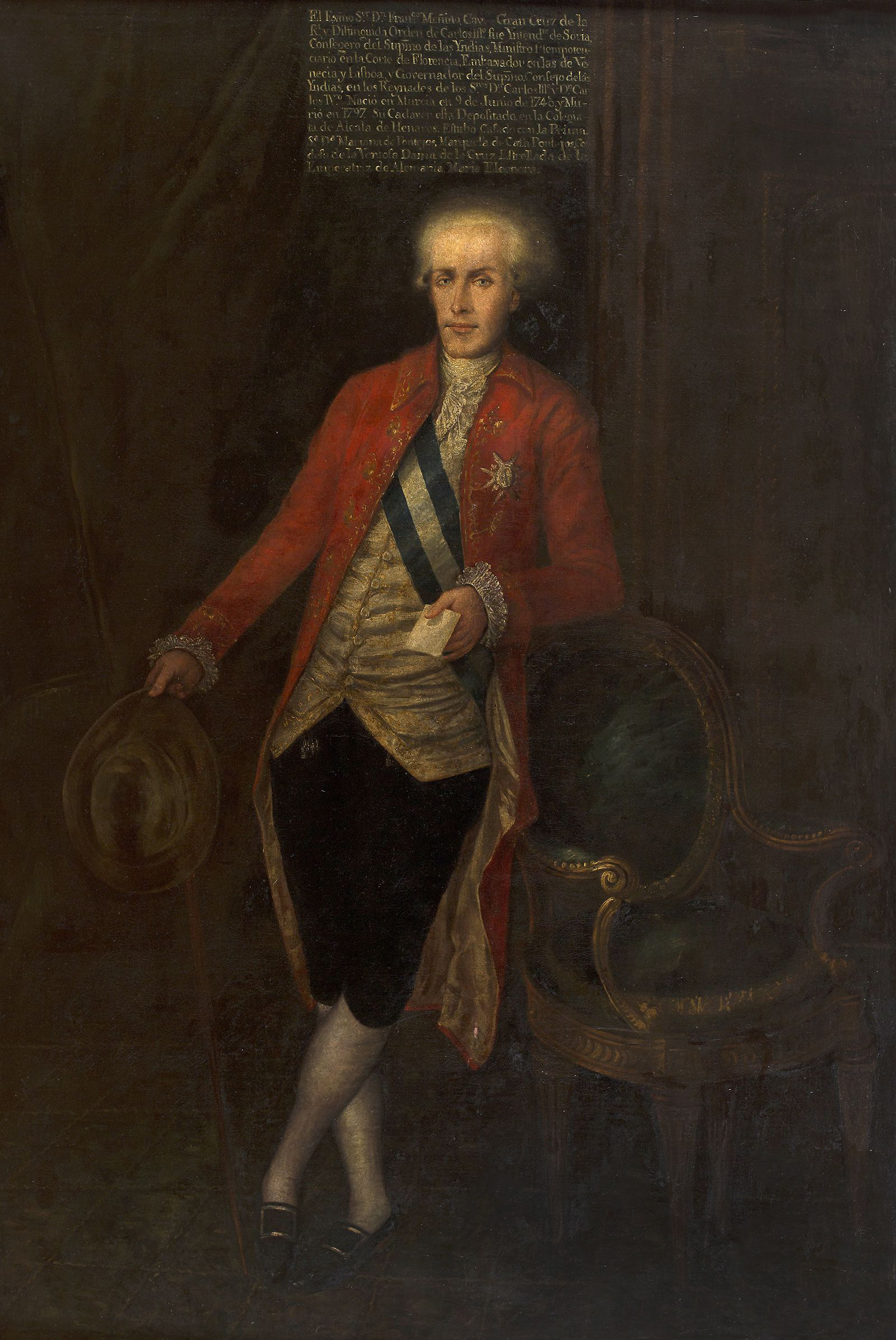
José Moñino, 1st Count Of Floridablanca
José Moñino y Redondo, 1st Count of Floridablanca (October 21, 1728 – December 30, 1808) was a Spanish statesman. He was the reformist chief minister of King Charles III of Spain, and also served briefly under Charles IV. He was arguably Spain's most effective statesman in the eighteenth century. In Spain, he is simply known as ''Conde de Floridablanca''. Early life He was born at Murcia in 1728 as the son of a retired army officer. He studied in Murcia and Orihuela, and later law at the University of Salamanca and was an esteemed advocate in the Spanish courts. He became a criminal prosecutor in Castile in 1766. He was given the task of investigating the Esquilache riots that same year and acquired a reputation as a supporter of the king's reformist policies. He defended the expulsion of the Jesuits in 1767. The chief minister at the time, the Marquis of Esquilache, recognized his ability and made Moñino Spanish ambassador to Pope Clement XIV in 1772. He was rewarded w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_01.jpg)