|
Spanish Romanesque
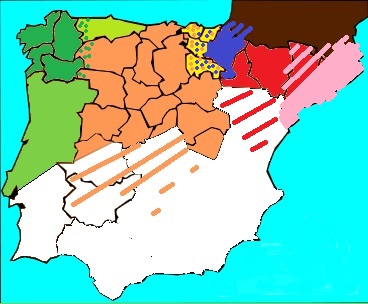
Spanish Romanesque designates the Romanesque art developed in the Chronology of the kingdoms on the Iberian peninsula, Hispanic-Christian kingdoms of the Iberian Peninsula in the 11th and 12th centuries. Its stylistic features are essentially common to the European Romanesque although it developed particular characteristics in the different regions of the peninsula. There is no Romanesque art in the southern half of the peninsula because it remained under Muslim rule (Al-Andalus). The examples of Romanesque buildings in the central area of the peninsula are sparse and of the latest period, with virtually no presence south of the Ebro and the Tagus. Most Romanesque buildings can be found in the northern third of the peninsula. Romanesque art was introduced into the peninsula from east to west, so scholars have usually defined regional characteristics accordingly: the "eastern kingdoms" comprising the Pyrenean areas, Catalan Romanesque, Aragonese Romanesque and Navarrese Romanesque, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Románico Español
An Esperantido (plural Esperantidoj) is a constructed language derived from Esperanto. ''Esperantido'' originally referred to the language which is now known as Ido. The word ''Esperantido'' contains the affix (''-ido''), which means a "child (''born to a parent''), young (''of an animal'') or offspring". Hence, ''Esperantido'' literally means an 'offspring or descendant of Esperanto'. A number of Esperantidoj have been created to address a number of perceived flaws or weaknesses in Esperanto (or in other Esperantidoj) by attempting to improve the lexicon, grammar, pronunciation, or orthography. Others were created as language games or to add variety to Esperanto literature. Language reforms These attempted improvements were intended to replace Esperanto. Limited suggestions for improvement within the framework of Esperanto, such as orthographic reforms and riism, are not considered Esperantidos. Mundolinco ''Mundolinco'' (1888) was the first Esperantido, created in 1888. Chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mozarabic Art And Architecture
Mozarabic art refers to art of Mozarabs (from ''musta'rab'' meaning “Arabized”), Iberian Christians living in Al-Andalus, the Muslim conquered territories in the period that comprises from the Arab invasion of the Iberian Peninsula (711) to the end of the 11th century, adopted some Arab customs without converting to Islam, preserving their religion and some ecclesiastical and judicial autonomy. Formerly used for the whole of the Iberian peninsula, the term is now usually restricted, at least in architecture, to the south, with Repoblación art and architecture used for the north. Art The Mozarabic communities maintained some of the Visigothic churches that were older than the Arab occupation for the practice of their religious rites and were rarely able to build new ones, because, even though a certain religious tolerance existed, the authorizations for building new churches were very limited. When permitted, new churches were always in rural areas or in the cities' suburbs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loarre Castle
The Castle of Loarre is a Romanesque Castle and Abbey located near the town of the same name, Huesca Province in the Aragon autonomous region of Spain. It is one of the oldest castles in Spain. History The castle was built largely during the 11th and 13th centuries, when its position on the frontier between Christian and Muslim lands gave it strategic importance. The first of the two major building programs began circa 1020, when Sancho el Mayor (r. 1063–94) reconquered the surrounding lands from the Muslims. After 1070, Loarre became increasingly important. In 1073, King Sancho Ramírez installed a community of Augustinian canons, and it was from Loarre that he prepared for the conquest of Huesca in 1094. In 1097, however, his successor, Peter I of Aragon and Navarre, donated all the goods of Loarre to a new royal monastery at Montearagon. This evidence suggests that the second major construction program was undertaken between 1073 and 1097, and much building evide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
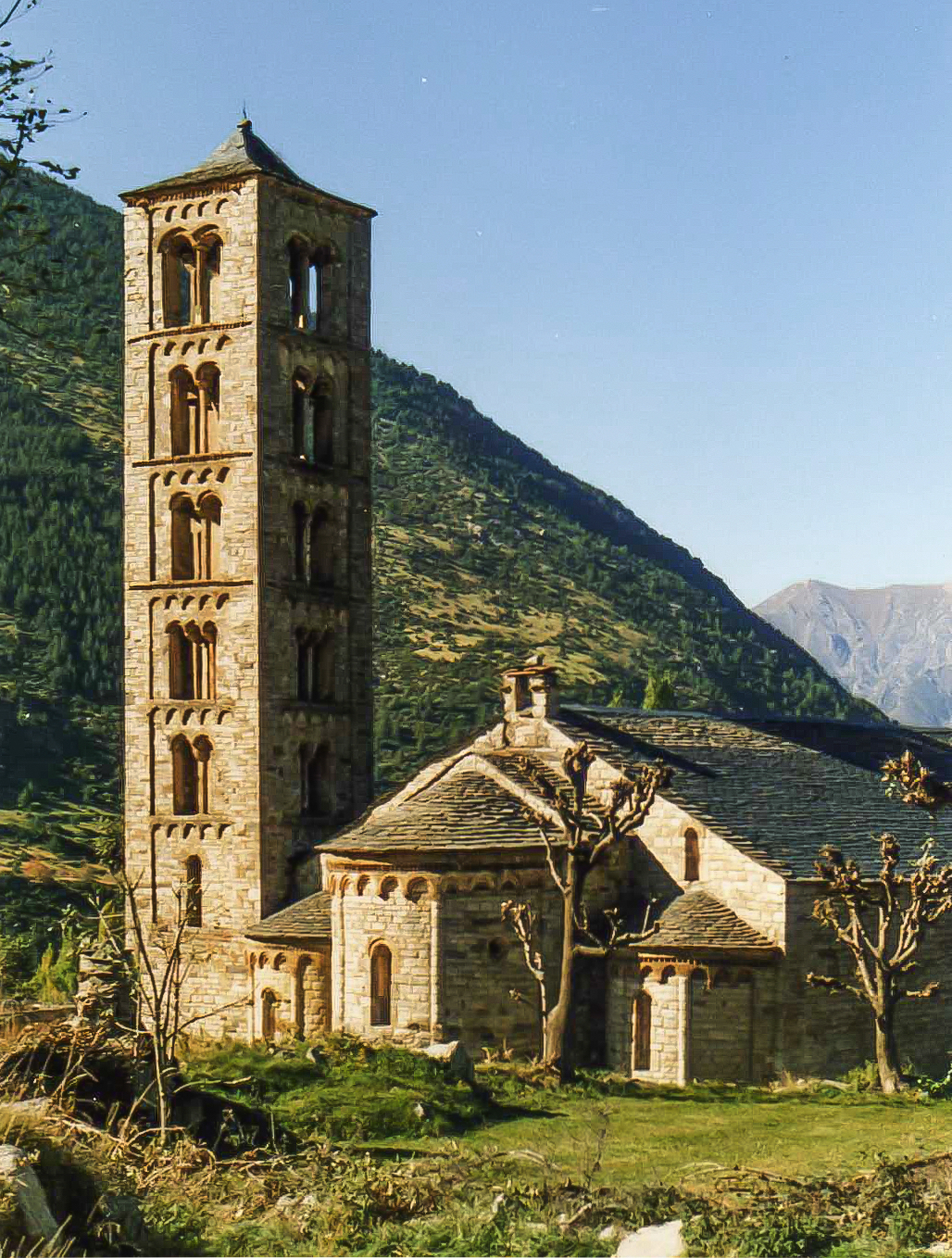
Catalan Romanesque Churches Of The Vall De Boí
The Churches of the Vall de Boí are a set of nine Early Romanesque churches declared World Heritage Site by UNESCO and located in the Vall de Boí, in the Catalan comarca of Alta Ribagorça (Province of Lleida). World Heritage Site UNESCO declared World Heritage Sites in 2000 to nine churches: History of the frescoes of the Vall de Boí During the early 20th century there was a major effort to study and catalog the Romanesque wall paintings in the churches of the Vall de Boí area. This activity was driven by both the academic interests of scholars, and by art dealers (whose motives were financial gain). In 1904 and 1906, the Hiking Club of Catalonia organised the first trips to ''inter-alia'' the Vall de Boí, with the aim of collecting plans, photographs and taking notes. Subsequently, in June 1907 an expedition by the Institute for Catalan Studies undertook to study, document and photograph culturally important buildings and art works the Vall d'Aran and Alta Ribagor� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Maria De Ripoll
The Monastery of Santa Maria de Ripoll is a Benedictine monastery, built in the Romanesque style, located in the town of Ripoll in Catalonia, Spain. Although much of the present church is 19th century rebuilding, the sculptured portico is a renowned work of Romanesque art. History The Monastery of Santa Maria de Ripoll was founded in 888 by Count Wilfred the Hairy (called Guifré el Pilós in Catalan) who used it as a centre to bring about the repopulation of the region after conquering it. Wilfred's son, Ridulph, was educated there and was later abbot of the monastery, as well as bishop of Urgell. The monastery grew rapidly, and was subsequently reconsecrated in 935, 977 and 1032, though the monks are known to have been established there permanently only from 1025 or 1032. The scriptorium and the monastic school quickly gained renown under Arnold Scholasticus. The monastery had several offshoots which included the abbeys of St. Martin-du-Canigou (now in France) and that of Santa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilica Of St
In Ancient Roman architecture Ancient Roman architecture adopted the external language of classical Greek architecture for the purposes of the ancient Romans, but was different from Greek buildings, becoming a new architectural style. The two styles are often considered one ..., a basilica is a large public building with multiple functions, typically built alongside the town's Forum (Roman), forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building gave its name to the architectural form of the basilica. Originally, a basilica was an ancient Roman architecture, ancient Roman public building, where courts were held, as well as serving other official and public functions. Basilicas are typically rectangular buildings with a central nave flanked by two or more longitudinal aisles, with the roof at two levels, being higher in the centre over the nave to admit a clerestory and lower over the side-aisles. An apse at one end, or less frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathedral Of Santiago De Compostela
The Santiago de Compostela Archcathedral Basilica (Spanish and Galician: ) is part of the Metropolitan Archdiocese of Santiago de Compostela and is an integral component of the Santiago de Compostela World Heritage Site in Galicia, Spain. The cathedral is the reputed burial place of Saint James the Great, one of the apostles of Jesus Christ. It is also among the remaining churches in the world built over the tomb of an apostle, the other ones being St Peter's Basilica in Vatican City, St Thomas Cathedral Basilica, Chennai in India and Basilica of St. John in Izmir, Turkey. The archcathedral basilica has historically been a place of pilgrimage on the Way of St James since the Early Middle Ages and marks the traditional end of the pilgrimage route. The building is a Romanesque structure, with later Gothic and Baroque additions. History According to the legend, the apostle Saint James the Great brought Christianity to the Iberian Peninsula. According to legend, this tomb was r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilica Of San Isidoro
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica is a large public building with multiple functions, typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building gave its name to the architectural form of the basilica. Originally, a basilica was an ancient Roman public building, where courts were held, as well as serving other official and public functions. Basilicas are typically rectangular buildings with a central nave flanked by two or more longitudinal aisles, with the roof at two levels, being higher in the centre over the nave to admit a clerestory and lower over the side-aisles. An apse at one end, or less frequently at both ends or on the side, usually contained the raised tribunal occupied by the Roman magistrates. The basilica was centrally located in every Roman town, usually adjacent to the forum and often opposite a temple in imperial-era forums. Basilicas were also built in private residences an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monastery Of Leyre
The Monastery of San Salvador of Leyre ( eu, Leireko San Salbatore monasterioa; es, Monasterio de San Salvador de Leire) is a religious complex to the south of the Sierra of Leyre, in northern Navarre, Spain, representing one of the most important historical monasteries of Spain. The oldest records of the site date from 842, when Íñigo Arista, considered the first king of Pamplona, and Wilesindo, Bishop of Pamplona, made a donation to the monastery. The monastery grew in importance thereafter, acquiring numerous properties and wealth during the first and middle stages of the Kingdom of Navarre, thanks to the privileges and donations made by the Navarrese kings. The monastery was expanded in the twelfth century. Several kings of Navarre were buried there. Since then it has been in various states of repair, undergoing many expansions and remodelling (the most extensive carried out in the sixteenth century, when almost the entire monastery was rebuilt). Romanesque architecture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaca Cathedral
The Cathedral of St Peter the Apostle ( es, Catedral de San Pedro Apóstol) is a Roman Catholic church located in Jaca, in Aragon, Spain. It is the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Jaca. It is the first Romanesque cathedral built in Aragon (1070s – early 12th century) and one of the oldest in the Iberian peninsula. Its current appearance is the result of later additions and modifications introduced especially in the early modern period (from the late 15th to late 18th century). The cathedral was erected on command of King Sancho Ramírez, who, after renovating in Rome his vassal oath to the Pope Alexander II (1068), had obtained from the latter the right to establish the episcopal seat in Jaca, then capital of the Kingdom of Aragon. History After Jaca became the capital of Aragon (1036), the city obtained the status of episcopal see in 1077. This made the construction of a cathedral church necessary. The starting date of the construction is unknown, but it is general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sant Pere De Rodes
Sant Pere de Rodes () is a former Benedictine monastery in the comarca of Alt Empordà, in the North East of Catalonia, Spain. Location Located in the municipal area of El Port de la Selva in the province of Girona, Spain, it was built on the slope of the Verdera Mountain, just below the Castle of Sant Verdera, which provided protection for the monastery but now lies in ruins at the very summit. It offers exceptional views over the bay of Llançà, to the north of Cap de Creus. Near the monastery Santa Creu de Rodes are the ruins of a medieval town, of which its pre-Romanesque-style church dedicated to Saint Helena is all that remains. File:Castell de Sant Salvador El Port de la Selva.jpg, Verdera Castle (inset: north tower). File:Santa Helena church.jpg, Santa Helena church, and remains of the medieval settlement at Santa Creu de Rodes. History The true origin of the monastery is not known, which has given rise to speculation and legend; such as its foundation by monk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

_3.jpg)

