|
Spalling
Spall are fragments of a material that are broken off a larger solid body. It can be produced by a variety of mechanisms, including as a result of projectile impact, corrosion, weathering, cavitation, or excessive rolling pressure (as in a ball bearing). Spalling and spallation both describe the process of surface failure in which spall is shed. The terms ''spall'', ''spalling'', and ''spallation'' have been adopted by particle physicists; in neutron scattering instruments, neutrons are generated by bombarding a uranium (or other) target with a stream of atoms. The neutrons that are ejected from the target are known as "spall". Mechanical spalling Mechanical spalling occurs at high stress contact points, for example, in a ball bearing. Spalling occurs in preference to brinelling where the maximal shear stress occurs not at the surface, but just below, shearing the spall off. One of the simplest forms of mechanical spalling is plate impact, in which two waves of compression ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
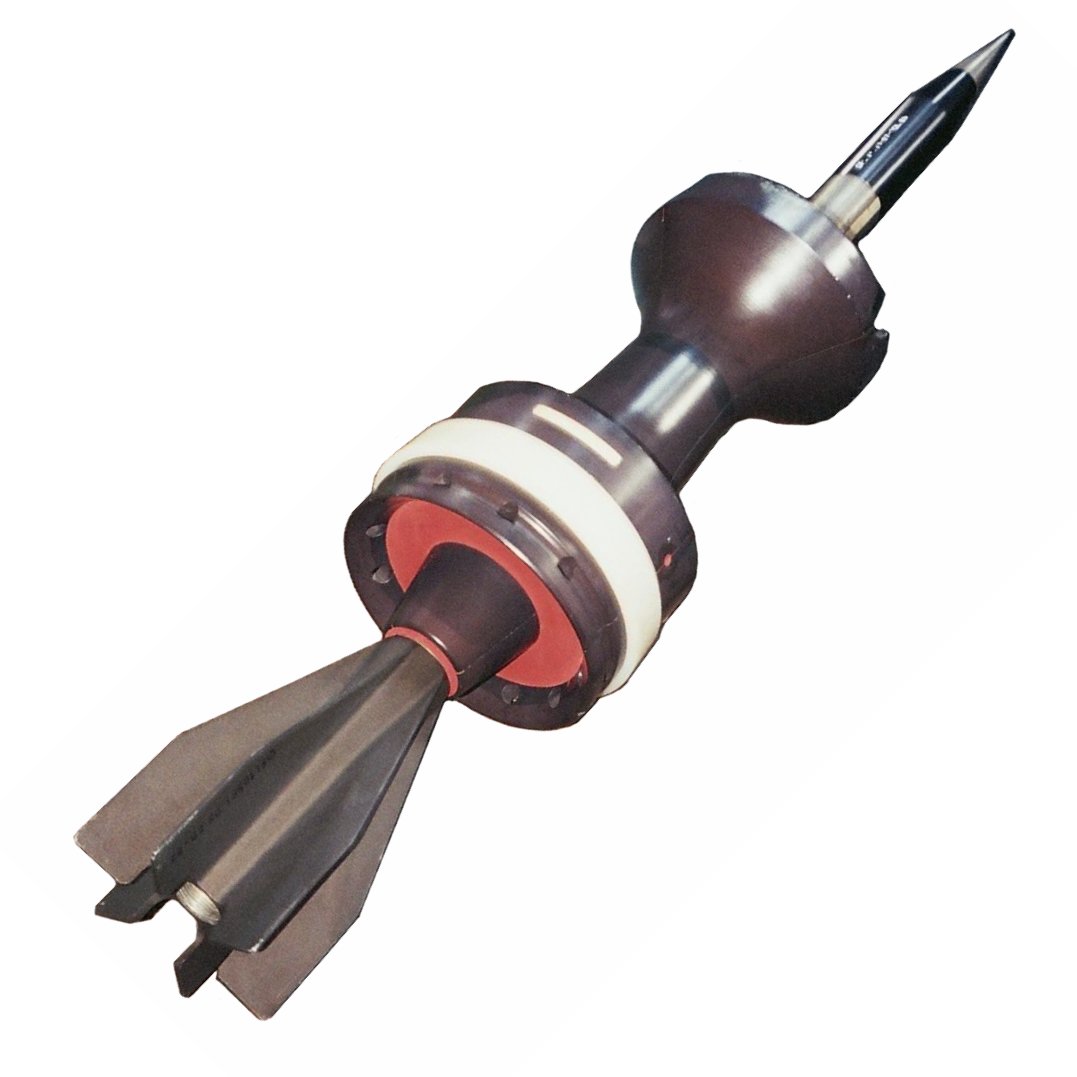
High-explosive Squash Head
High explosive squash head (HESH) in British terminology, or high explosive plastic/plasticized (HEP) in American terminology, is a type of explosive projectile which uses a plastic explosive that conforms to the surface of a target before detonating, to improve the transfer of explosive energy to the target. Squash head projectiles are similar to high explosive projectiles and are well suited to many of the same targets. However, while HESH projectiles are not armour-piercing, they can defeat armored targets by causing spall which can injure or kill a vehicle's occupants, and detonate some types of ammunition. Design Function HESH rounds are thin metal shells filled with inert material (like coal-tar pitch), plastic explosive and a delayed-action base fuze. On impact, the inert material, followed by plastic explosive, is "squashed" against the surface of the target and spreads out to form a disc or "pat" of explosive. The inert material helps prevent premature detonation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with water, atmospheric gases, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs ''in situ'' (on site, with little or no movement), and so is distinct from erosion, which involves the transport of rocks and minerals by agents such as water, ice, snow, wind, waves and gravity. Weathering processes are divided into ''physical'' and ''chemical weathering''. Physical weathering involves the breakdown of rocks and soils through the mechanical effects of heat, water, ice, or other agents. Chemical weathering involves the chemical reaction of water, atmospheric gases, and biologically produced chemicals with rocks and soils. Water is the principal agent behind both physical and chemical weathering, though atmospheric oxygen and carbon dioxide and the activities of biological organisms are also important. Chemical weathering by biological action is also known as biological wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freeze–thaw Weathering
Frost weathering is a collective term for several mechanical weathering processes induced by stresses created by the freezing of water into ice. The term serves as an umbrella term for a variety of processes such as frost shattering, frost wedging and cryofracturing. The process may act on a wide range of spatial and temporal scales, from minutes to years and from dislodging mineral grains to fracturing boulders. It is most pronounced in high-altitude and high-latitude areas and is especially associated with alpine, periglacial, subpolar maritime and polar climates, but may occur anywhere at sub-freezing temperatures (between -3 and -8 °C) if water is present. Ice segregation Certain frost-susceptible soils expand or heave upon freezing as a result of water migrating via capillary action to grow ice lenses near the freezing front. This same phenomenon occurs within pore spaces of rocks. The ice accumulations grow larger as they attract liquid water from the surrounding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with water, atmospheric gases, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs ''in situ'' (on site, with little or no movement), and so is distinct from erosion, which involves the transport of rocks and minerals by agents such as water, ice, snow, wind, waves and gravity. Weathering processes are divided into ''physical'' and ''chemical weathering''. Physical weathering involves the breakdown of rocks and soils through the mechanical effects of heat, water, ice, or other agents. Chemical weathering involves the chemical reaction of water, atmospheric gases, and biologically produced chemicals with rocks and soils. Water is the principal agent behind both physical and chemical weathering, though atmospheric oxygen and carbon dioxide and the activities of biological organisms are also important. Chemical weathering by biological action is also known as biological wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desquamation Of Dunite
Desquamation occurs when the outermost layer of a tissue, such as the skin, is shed. The term is . Physiologic desquamation Keratinocytes are the predominant cells of the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Living keratinocytes reside in the basal, spinous, or granular layers of the epidermis. The outermost layer of the epidermis is called the Stratum corneum and it is composed of terminally differentiated keratinocytes, the Corneocytes. In the absence of disease, desquamation occurs when corneocytes are individually shed unnoticeably from the surface of the skin. Typically the time it takes for a corneocyte to be formed and then shed is about 14 weeks but this time can vary depending on the anatomical location that the skin is covering. For example, desquamation occurs more slowly at acral (palm and sole) surfaces and more rapidly where the skin is thin, such as the eyelids. Normal desquamation can be visualized by immersing skin in warm or hot water. This induces the oute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetic Energy Penetrator
A kinetic energy penetrator (KEP), also known as long-rod penetrator (LRP), is a type of ammunition designed to penetrate vehicle armour using a flechette-like, high-sectional density projectile. Like a bullet or kinetic energy weapon, this type of ammunition does not contain explosive payloads and uses purely kinetic energy to penetrate the target. Modern KEP munitions are typically of the armour-piercing fin-stabilized discarding sabot (APFSDS) type. History Early cannons fired kinetic energy ammunition, initially consisting of heavy balls of worked stone and later of dense metals. From the beginning, combining high muzzle energy with projectile weight and hardness have been the foremost factors in the design of such weapons. Similarly, the foremost purpose of such weapons has generally been to defeat protective shells of armored vehicles or other defensive structures, whether it is stone walls, sailship timbers, or modern tank armour. Kinetic energy ammunition, in its vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vehicle Armour
Military vehicles are commonly armoured (or armored; see spelling differences) to withstand the impact of shrapnel, bullets, shells, rockets, and missiles, protecting the personnel inside from enemy fire. Such vehicles include armoured fighting vehicles like tanks, aircraft, and ships. Civilian vehicles may also be armoured. These vehicles include cars used by officials (e.g., presidential limousines), reporters and others in conflict zones or where violent crime is common. Civilian armoured cars are also routinely used by security firms to carry money or valuables to reduce the risk of highway robbery or the hijacking of the cargo. Armour may also be used in vehicles to protect from threats other than a deliberate attack. Some spacecraft are equipped with specialised armour to protect them against impacts from micrometeoroids or fragments of space debris. Modern aircraft powered by jet engines usually have them fitted with a sort of armour in the form of an aramid composite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brinelling
Brinelling {{IPAc-en, ˈ, b, r, ɪ, n, ə, l, ɪ, ŋ is the permanent indentation of a hard surface. It is named after the Brinell scale of hardness, in which a small ball is pushed against a hard surface at a preset level of force, and the depth and diameter of the mark indicates the Brinell hardness of the surface. Brinelling is permanent plastic deformation of a surface, and usually occurs while two surfaces in contact are stationary (such as rolling elements and the raceway of a bearings) and the material yield strength has been exceeded. Brinelling is undesirable, as the parts often mate with other parts in very close proximity. The very small indentations can quickly lead to improper operation, such as chattering or excess vibration, which in turn can accelerate other forms of wear, such as spalling and ultimately, failure of the bearing. Introduction Brinelling is a material surface failure caused by Hertz contact stress that exceeds the material limit. It usually occurs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium Plate Spalling
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has a great affinity towards oxygen, and forms a protective layer of oxide on the surface when exposed to air. Aluminium visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, non-magnetic and ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al; this isotope is very common, making aluminium the twelfth most common element in the Universe. The radioactivity of 26Al is used in radiodating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ is small and highly charged; as such, it is polarizing, and bonds aluminium forms tend towards covalency. The strong affinity towards oxyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape, area, volume, and density in response to a change in temperature, usually not including phase transitions. Temperature is a monotonic function of the average molecular kinetic energy of a substance. When a substance is heated, molecules begin to vibrate and move more, usually creating more distance between themselves. Substances which contract with increasing temperature are unusual, and only occur within limited temperature ranges (see examples below). The relative expansion (also called strain) divided by the change in temperature is called the material's coefficient of linear thermal expansion and generally varies with temperature. As energy in particles increases, they start moving faster and faster weakening the intermolecular forces between them, therefore expanding the substance. Overview Predicting expansion If an equation of state is available, it can be used to predict the values of the thermal expan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
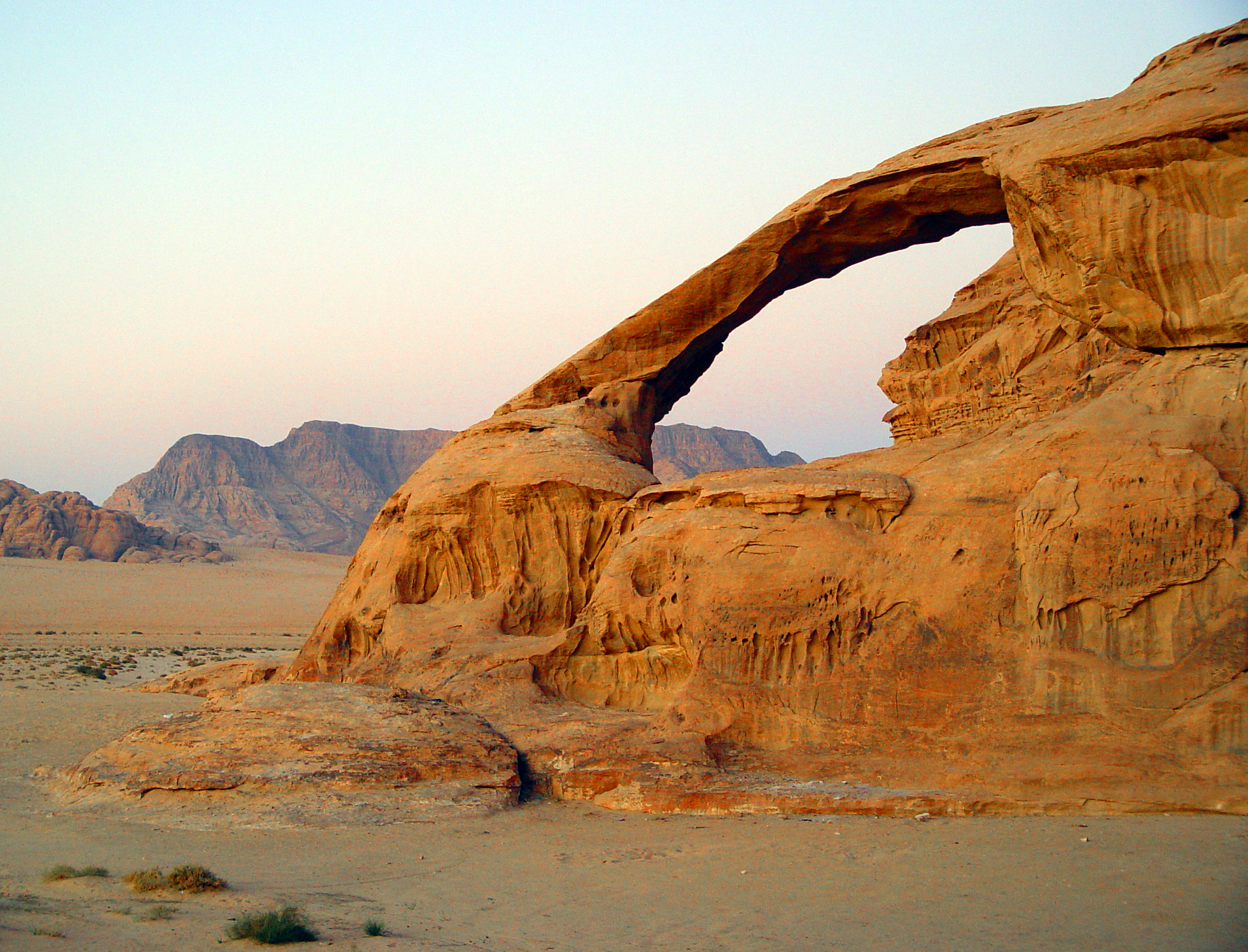
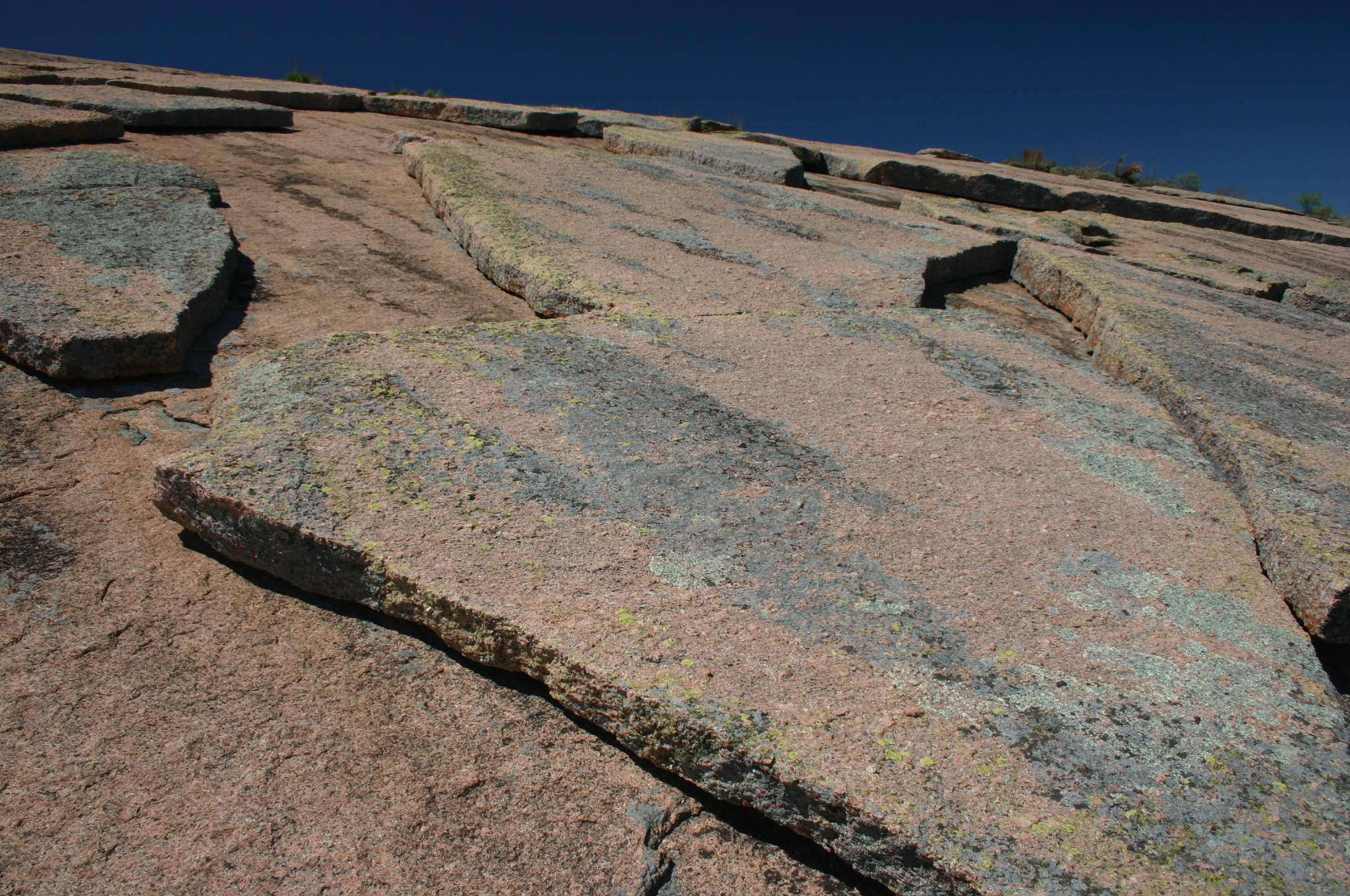
Exfoliation (geology)
Exfoliation joints or sheet joints are surface-parallel fracture systems in rock, and often leading to erosion of concentric slabs. ''(See Joint (geology)).'' General characteristics of exfoliation joints * Commonly follow topography. * Divide the rock into sub-planar slabs. * Joint spacing increases with depth from a few centimeters near the surface to a few meters * Maximum depth of observed occurrence is around 100 meters. * Deeper joints have a larger radius of curvature, which tends to round the corners of the landscape as material is eroded * Fracture mode is tensile * Occur in many different lithologies and climate zones, not unique to glaciated landscapes. * Host rock is generally sparsely jointed, fairly isotropic, and has high compressive strength. * Can have concave and convex upwards curvatures. * Often associated with secondary compressive forms such as arching, buckling, and A-tents (buckled slabs) Formation of exfoliation joints Despite their common occurrenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |