|
Southern Mazghuna Pyramid
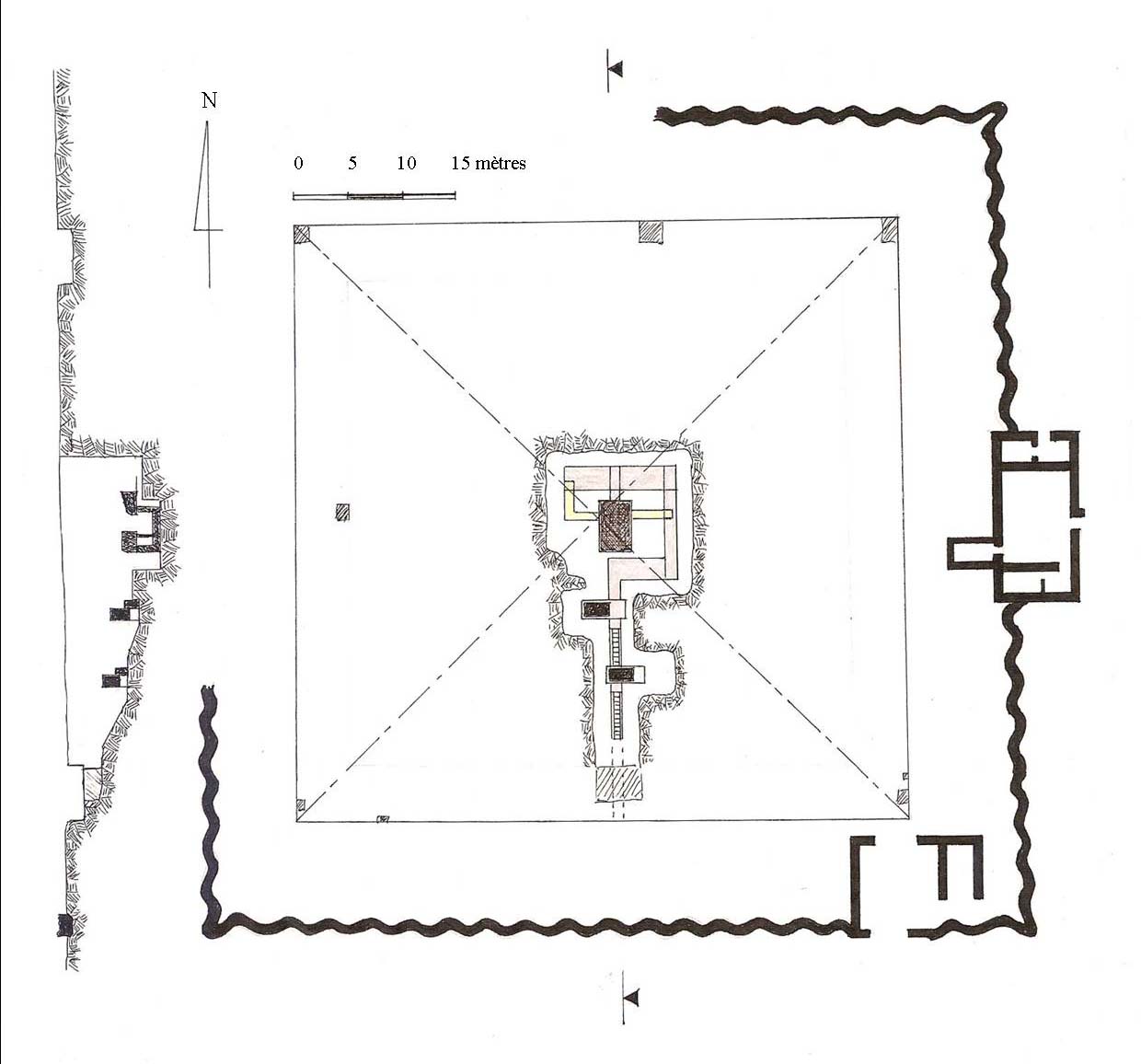
The Southern Mazghuna Pyramid is an ancient Egyptian royal tomb which was built during the 12th or the 13th Dynasty in Mazghuna Mazghuna (also known as ''Al Mazghunah'' or ''Al-Muzghumah''), 5 km to the south of Dahshur, is the site of several mudbrick pyramids dating from the 12th Dynasty. The area was explored by Ernest Mackay in 1910, and was excavated by Flinders ..., 5 km south of Dahshur, Egypt. The building was never finished, and is still unknown which pharaoh was the owner, since no appropriate inscription have been found. The pyramid was rediscovered in 1910 by Ernest Mackay and excavated in the following year by Flinders Petrie. Attribution The building shares some structural similarities to the Hawara, Hawara pyramid of Amenemhat III, and for this reason it is usually attributed to his son Amenemhat IV (around the end of the 19th-century BCE). In parallel, the near northern Mazghuna pyramid is considered to be the tomb of his sister Sobekneferu, the last ruler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amenemhat IV
:''See Amenemhat, for other individuals with this name.'' Amenemhat IV (also known as Amenemhet IV) was the seventh and penultimateJürgen von Beckerath: ''Handbuch der ägyptischen Königsnamen'', Münchner ägyptologische Studien, Heft 49, Mainz : Philip von Zabern, 1999, , see pp. 86–87, king No 7. and p. 283 for the dates of Amenemhat IV's reign. king of the Twelfth Dynasty of Egypt (c. 1990–1800 BC) during the late Middle Kingdom period (c. 2050–1710 BC), ruling for more than nine years in the late nineteenth century BC or the early eighteenth century BC.Darrell D. Baker: The Encyclopedia of the Pharaohs: Volume I – Predynastic to the Twentieth Dynasty 3300–1069 BC, Stacey International, , 2008, p. 30–32 K.S.B. Ryholt: ''The Political Situation in Egypt during the Second Intermediate Period, c. 1800–1550 BC'', Carsten Niebuhr Institute Publications, vol. 20. Copenhagen: Museum Tusculanum Press, 1997excerpts available online here./ref> Amenem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Mazghuna Pyramid
The Northern Mazghuna Pyramid is an ancient Egyptian royal tomb which was built during the 12th or 13th Dynasty in Mazghuna, 5 km south of Dahshur. The building remained unfinished, and it is still unknown which pharaoh was really intended to be buried here since no appropriate inscription has been found. The pyramid was rediscovered in 1910 by Ernest Mackay and excavated in the following year by Flinders Petrie. Attribution When the two Mazghuna pyramids were rediscovered, scholars noticed many structural similarities between those two and Amenemhat III's pyramid at Hawara; for this reason the southern pyramid was attributed to the son and successor of this king, Amenemhat IV. Subsequently, the northern pyramid was attributed to the female-pharaoh Sobekneferu, sister of Amenemhat IV and last ruler of the 12th Dynasty. However, some scholars such as William C. Hayes believed that the two Mazghuna pyramids were built during the 13th Dynasty, on the basis of some similarities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Egyptian Pyramids
This list presents the vital statistics of the pyramids listed in chronological order, when available. See also * Egyptian pyramids * Great Sphinx of Giza * Lepsius list of pyramids * List of Egyptian pyramidia * List of the oldest buildings in the world * Umm El Qa'ab Umm El Qaʻāb (sometimes romanised Umm El Gaʻab, ar, أم القعاب) is a necropolis of the Early Dynastic Period kings at Abydos, Egypt. Its modern name means "Mother of Pots" as the whole area is littered with the broken pot shards of of ... References and notes Bibliography * {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Egyptian Pyramids Pyramids, Egyptian Ancient Egypt-related lists Pyramids in Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soapstone
Soapstone (also known as steatite or soaprock) is a talc-schist, which is a type of metamorphic rock. It is composed largely of the magnesium rich mineral talc. It is produced by dynamothermal metamorphism and metasomatism, which occur in the zones where tectonic plates are subducted, changing rocks by heat and pressure, with influx of fluids, but without melting. It has been a medium for carving for thousands of years. Terminology The definitions of the terms "steatite" and "soapstone" vary with the field of study. In geology, steatite is a rock that is to a very large extent composed of talc. The mining industry will define steatite as a high-purity talc rock that is suitable for manufacturing of, for example, insulators, the lesser grades of the mineral can be called simply "talc rock". Steatite can be used both in lumps ("block steatite", "lava steatite", "lava grade talc"), and in the ground form. While the geologists logically will use "steatite" to designate both forms, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alabaster
Alabaster is a mineral or rock that is soft, often used for carving, and is processed for plaster powder. Archaeologists and the stone processing industry use the word differently from geologists. The former use it in a wider sense that includes varieties of two different minerals: the fine-grained massive type of gypsum and the fine-grained banded type of calcite.''More about alabaster and travertine'', brief guide explaining the different use of these words by geologists, archaeologists, and those in the stone trade. Oxford University Museum of Natural History, 2012/ref> Geologists define alabaster only as the gypsum type. Chemically, gypsum is a Water of crystallization, hydrous sulfur, sulfate of calcium, while calcite is a carbonate of calcium. The two types of alabaster have similar properties. They are usually lightly colored, translucent, and soft stones. They have been used throughout history primarily for carving decorative artifacts."Grove": R. W. Sanderson and Francis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grave Goods
Grave goods, in archaeology and anthropology, are the items buried along with the body. They are usually personal possessions, supplies to smooth the deceased's journey into the afterlife or offerings to the gods. Grave goods may be classed as a type of votive deposit. Most grave goods recovered by archaeologists consist of inorganic objects such as pottery and stone and metal tools but organic objects that have since decayed were also placed in ancient tombs. The grave goods were to be useful to the deceased in the afterlife; therefore their favorite foods or everyday objects were left with them. Often times social status played a role in what was left and how often it was left. Funerary art is a broad term but generally means artworks made specifically to decorate a burial place, such as miniature models of possessions including slaves or servants for "use" in the afterlife. Although, in ancient Egypt they would sometimes bury the real servants with the deceased. Where grave go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcophagus
A sarcophagus (plural sarcophagi or sarcophaguses) is a box-like funeral receptacle for a corpse, most commonly carved in stone, and usually displayed above ground, though it may also be buried. The word ''sarcophagus'' comes from the Greek σάρξ ' meaning "flesh", and φαγεῖν ' meaning "to eat"; hence ''sarcophagus'' means "flesh-eating", from the phrase ''lithos sarkophagos'' ( λίθος σαρκοφάγος), "flesh-eating stone". The word also came to refer to a particular kind of limestone that was thought to rapidly facilitate the decomposition of the flesh of corpses contained within it due to the chemical properties of the limestone itself. History of the sarcophagus Sarcophagi were most often designed to remain above ground. The earliest stone sarcophagi were used by Egyptian pharaohs of the 3rd dynasty, which reigned from about 2686 to 2613 B.C. The Hagia Triada sarcophagus is a stone sarcophagus elaborately painted in fresco; one style of later A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartzite
Quartzite is a hard, non- foliated metamorphic rock which was originally pure quartz sandstone.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak, p 182 Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tectonic compression within orogenic belts. Pure quartzite is usually white to grey, though quartzites often occur in various shades of pink and red due to varying amounts of hematite. Other colors, such as yellow, green, blue and orange, are due to other minerals. The term ''quartzite'' is also sometimes used for very hard but unmetamorphosed sandstones that are composed of quartz grains thoroughly cemented with additional quartz. Such sedimentary rock has come to be described as orthoquartzite to distinguish it from metamorphic quartzite, which is sometimes called metaquartzite to emphasize its metamorphic origins. Quartzite is very resistant to chemical weathering and often forms ridges and resistant hilltops. The nearly pure silica conte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gable Roof
A gable roof is a roof consisting of two sections whose upper horizontal edges meet to form its ridge. The most common roof shape in cold or temperate climates, it is constructed of rafters, roof trusses or purlins. The pitch of a gable roof can vary greatly. Distribution The gable roof is so common because of the simple design of the roof timbers and the rectangular shape of the roof sections. This avoids details which require a great deal of work or cost and which are prone to damage. If the pitch or the rafter lengths of the two roof sections are different, it is described as an 'asymmetrical gable roof'. A gable roof on a church tower (gable tower) is usually called a 'cheese wedge roof' (''Käsbissendach'') in Switzerland. Its versatility means that the gable roof is used in many regions of the world. In regions with strong winds and heavy rain, gable roofs are built with a steep pitch in order to prevent the ingress of water. By comparison, in alpine regions, gable roo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mudbrick
A mudbrick or mud-brick is an air-dried brick, made of a mixture of loam, mud, sand and water mixed with a binding material such as rice husks or straw. Mudbricks are known from 9000 BCE, though since 4000 BCE, bricks have also been fired, to increase their strength and durability. In warm regions with very little timber available to fuel a kiln, bricks were generally sun-dried. In some cases, brickmakers extended the life of mud bricks by putting fired bricks on top or covering them with stucco. Ancient world The history of mudbrick production and construction in the southern Levant may be dated as far back to the Pre-Pottery Neolithic A (e.g., PPNA Jericho). These sun dried mudbricks, also known as adobe or just mudbrick, were made from a mixture of sand, clay, water and frequently temper (e.g. chopped straw and chaff branches), and were the most common method/material for constructing earthen buildings throughout the ancient Near East for millennia. Unfired ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merneferre Ay
Merneferre Ay (also spelled Aya or Eje, sometimes known as Ay I) was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of the mid 13th Dynasty. The longest reigning pharaoh of the 13th Dynasty, he ruled a likely fragmented Egypt for over 23 years in the early to mid 17th century BC. A pyramidion bearing his name shows that he possibly completed a pyramid, probably located in the necropolis of Memphis. Merneferre Ay is the last pharaoh of the 13th Dynasty to be attested outside Upper Egypt. In spite of his long reign, the number of artefacts attributable to him is comparatively small. This may point to problems in Egypt at the time and indeed, by the end of his reign, "the administration f the Egyptian stateseems to have completely collapsed". It is possible that the capital of Egypt since the early Middle Kingdom, Itjtawy was abandoned during or shortly after Ay's reign. For this reason, some scholars consider Merneferre Ay to be the last pharaoh of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt. Chronology Chronolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_-_several_colored_samples.jpg)






