|
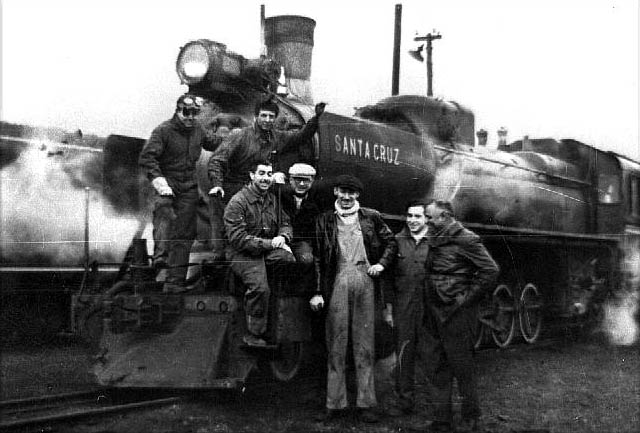
Southern Fuegian Railway
The Southern Fuegian Railway ( es, Ferrocarril Austral Fueguino (FCAF)) or the Train of the End of the World ( es, El Tren del Fin del Mundo) is a gauge steam railway in Tierra del Fuego Province, Argentina. It was originally built as a freight line to serve the prison of Ushuaia, specifically to transport timber. It now operates as a heritage railway into the Tierra del Fuego National Park and is considered the southernmost functioning railway in the world. History Origins century, Ushuaia on Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego developed as a penal colony, with the first prisoners arriving in 1884. In 1902, work began on a proper set of buildings for the prison by inmates, and a railway on wooden rails was constructed to assist the transport of materials, mainly local rock, sand and timber. Oxen pulled wagons along the narrow gauge of less than . In 1909, the prison governor informed the government of the need to upgrade the line and Decauville tracks at a narrow gauge wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
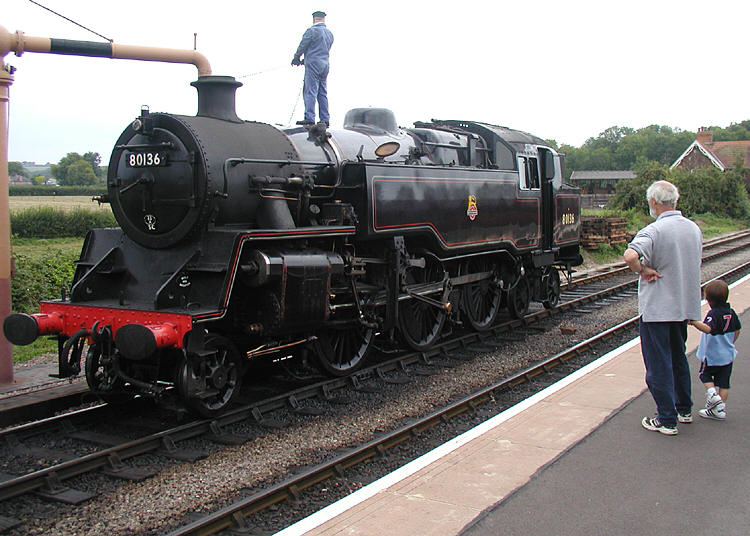
Heritage Railway
A heritage railway or heritage railroad (US usage) is a railway operated as living history to re-create or preserve railway scenes of the past. Heritage railways are often old railway lines preserved in a state depicting a period (or periods) in the history of rail transport. Definition The British Office of Rail and Road defines heritage railways as follows:...'lines of local interest', museum railways or tourist railways that have retained or assumed the character and appearance and operating practices of railways of former times. Several lines that operate in isolation provide genuine transport facilities, providing community links. Most lines constitute tourist or educational attractions in their own right. Much of the rolling stock and other equipment used on these systems is original and is of historic value in its own right. Many systems aim to replicate both the look and operating practices of historic former railways companies. Infrastructure Heritage railway lines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
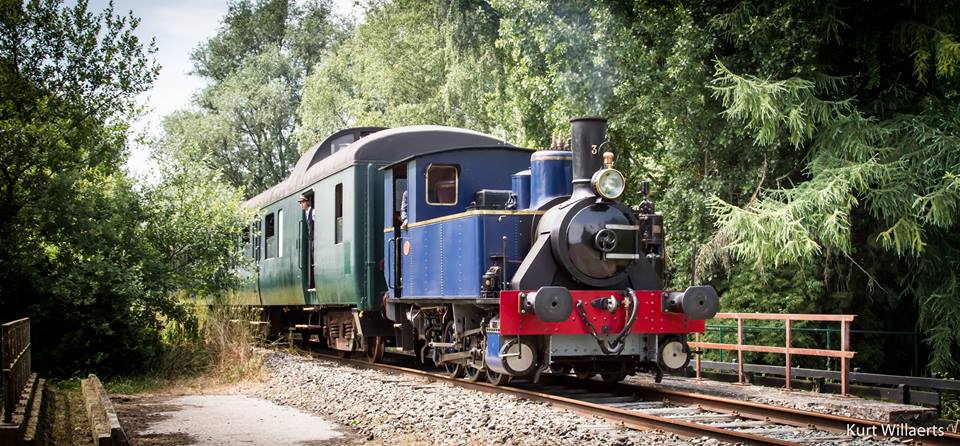
Track Gauge
In rail transport, track gauge (in American English, alternatively track gage) is the distance between the two rails of a railway track. All vehicles on a rail network must have wheelsets that are compatible with the track gauge. Since many different track gauges exist worldwide, gauge differences often present a barrier to wider operation on railway networks. The term derives from the metal bar, or gauge, that is used to ensure the distance between the rails is correct. Railways also deploy two other gauges to ensure compliance with a required standard. A '' loading gauge'' is a two-dimensional profile that encompasses a cross-section of the track, a rail vehicle and a maximum-sized load: all rail vehicles and their loads must be contained in the corresponding envelope. A ''structure gauge'' specifies the outline into which structures (bridges, platforms, lineside equipment etc.) must not encroach. Uses of the term The most common use of the term "track gauge" refers to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tren A Las Nubes
The Tren a las Nubes ( en, Train to the Clouds) is a tourist train service in Salta Province, Argentina. The service runs along the eastern part of the Salta–Antofagasta railway line of the Belgrano Railway (also known as the "C-14" line) that connects the Argentine Northwest with the border in the Andes mountain range, over above mean sea level, the fifth highest railway in the world. Originally built for economic and social reasons, it is now primarily of interest to tourists as a heritage railway, though cheaper tickets are also available for locals to use the train as transport. Overview The railway line has 29 bridges, 21 tunnels, 13 viaducts, 2 spirals and 2 zigzags. Because of the design decision not to use a rack-and-pinion for traction, the route had to be designed to avoid steep grades. The zigzags allow the train to climb up driving back and forth parallel to the slope of the mountain. The train departs from Salta every Saturday at 07:05, and returns around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainforest Ecological Train
The Rainforest Ecological Train or Waterfalls Train (''Tren Ecológico de la Selva'' or ''Tren de las Cataratas'') is a narrow gauge train that runs through the forest inside Iguazú National Park in the north of the province of Misiones of Argentina. The line is long and was built using rail track by French manufacturer Decauville.El chisporroteo de la chorbita mandó a vía muerta al “Trencito” de Yerba Buena on ''La Gazeta'', 11 Apr 2014 (archived) Characteristics [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Heritage Railways
This list of heritage railways includes heritage railways sorted by country, state, or region. A heritage railway is a preserved or tourist railroad which is run as a tourist attraction, is usually but not always run by volunteers, and often seeks to re-create railway scenes of the past. Europe Austria * Ampflwanger Bahn (Timelkam — Ampflwang) * Bockerlbahn Bürmoos (narrow gauge, original tracks removed) * Bregenzerwaldbahn (narrow gauge, remaining section Bezau — Schwarzenberg) * Erzbergbahn (section Vordernberg — Eisenerz) * Feistritztalbahn (narrow gauge, Weiz — Birkfeld) * Gurktalbahn (narrow gauge, remaining section Treibach-Althofen — Pöckstein-Zwischenwässern) * Höllental Railway (Lower Austria) (narrow gauge, Payerbach-Reichenau — Hirschwang an der Rax) * Landesbahn Feldbach — Bad Gleichenberg (some regular service remains) * Lavamünder Bahn (Lavamünd — St. Paul im Lavanttal, track removed) * Lokalbahn Ebelsberg — St. Florian (narrow gauge, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
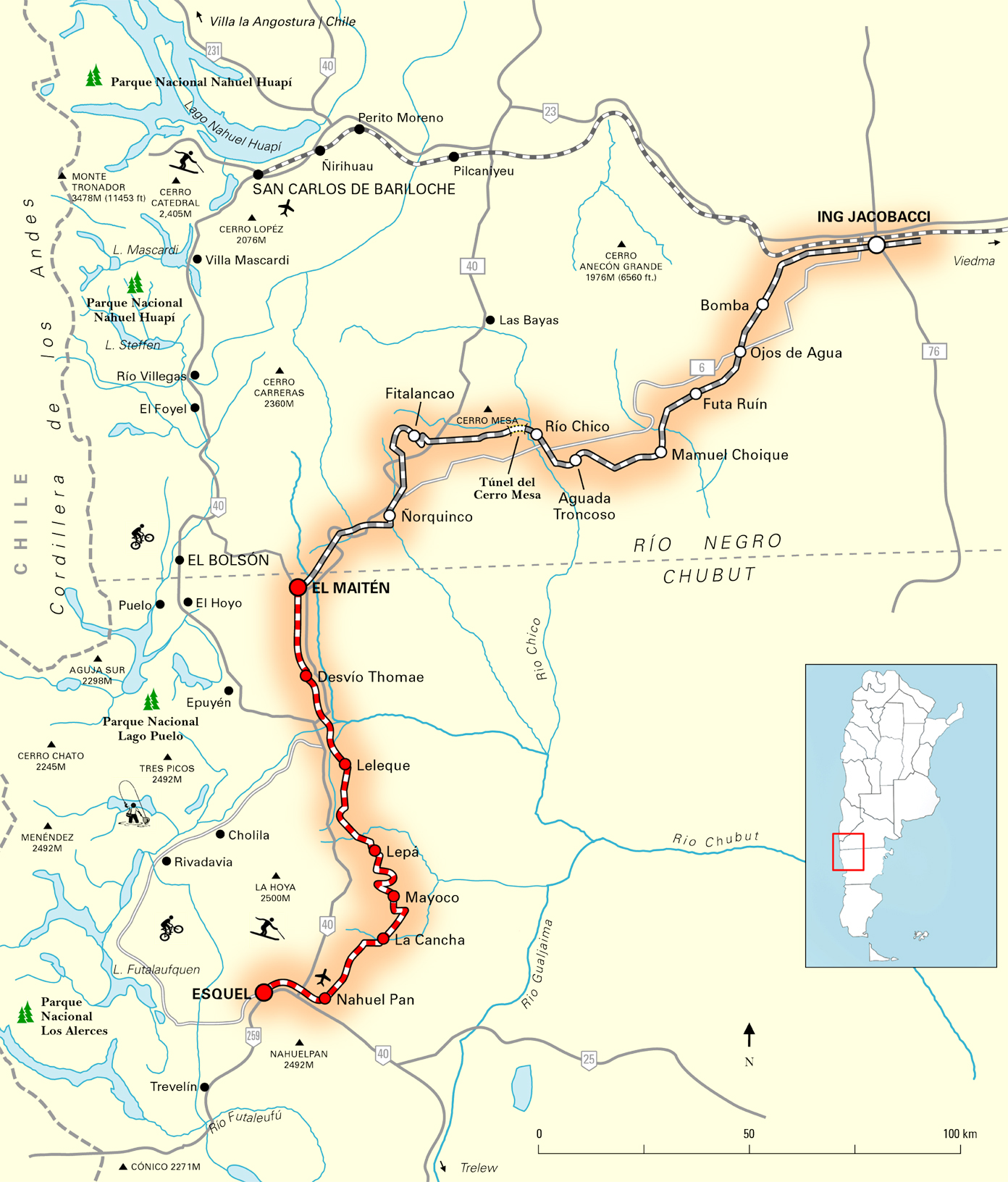
La Trochita
La Trochita (official name: ''Viejo Expreso Patagónico''), in English known as the Old Patagonian Express, is a narrow gauge railway in Patagonia, Argentina using steam locomotives. The nickname ''La Trochita'' means literally "The little gauge" though it is sometimes translated as "The Little Narrow Gauge" in Spanish while "trocha estrecha", "trocha angosta" in Argentina, is often used for a generic description of "narrow gauge." The Trochita railway is 402 km in length and runs through the foothills of the Andes between Esquel and El Maitén in Chubut Province and Ingeniero Jacobacci in Río Negro Province, originally it was part of Ferrocarriles Patagónicos, a network of railways in southern Argentina. Nowadays, with its original character largely unchanged, it operates as a heritage railway and was made internationally famous by the 1978 Paul Theroux book ''The Old Patagonian Express'', which described it as the railway almost at the end of the world. Theroux had soug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avellaneda Park Historic Train
The Avellaneda Park Historic Train (native name: Tren Histórico del Parque Avellaneda), colloquially known as "Expreso Alegría" ("Joy Express" in English language, English) is a narrow gauge railway, narrow gauge train that runs inside Avellaneda Park of Parque Avellaneda district, in the southwest of Buenos Aires, Argentina. History In 1908, the Buenos Aires Legislature carried out a public tender to build a railway that ran through the Buenos Aires Zoo, which was completed and opened one year later. The train was towed by Deutz AG, Deutz locomotives, manufactured in Germany. In 1929 the train was moved to Avellaneda Park, alleging that it would be useful to transport people to "polideportivo" (sports center) located in the park. The service was officially opened in 1936, being named ''"Expreso Alegría"'' and operated by Genoa, Genovese Juan Cugusi who was in charge of the service. The train departed from Clemente Onelli station. It was free for children going to the holida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michale Graves
Michael Emanuel (born March 21, 1975), better known by his stage name Michale Graves, is an American singer. He is best known as the lead vocalist for the 1990s re-incarnation of the horror punk band Misfits from 1995 to 2000, leaving briefly in 1998. Graves grew up in Dumont, New Jersey. He has also released several albums as a solo artist. Life and career Misfits Graves was recording a demo with his band the Mopes in Lodi, New Jersey, when their engineer, Bob Alecca, mentioned that the Misfits were reforming and holding auditions for a new singer. Graves bought the '' Collection I'' and ''Walk Among Us'' albums to familiarize himself with the band and became an official member about a year after trying out. In September 2008, Graves confirmed that he would return to the Misfits if asked: " Jerry and I do not have a dysfunctional working relationship. Him and I both know and I know he knows that I am on board. It is a phone call away. I won't step back into what I walked awa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tram
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are called tramways or simply trams/streetcars. Many recently built tramways use the contemporary term light rail. The vehicles are called streetcars or trolleys (not to be confused with trolleybus) in North America and trams or tramcars elsewhere. The first two terms are often used interchangeably in the United States, with ''trolley'' being the preferred term in the eastern US and ''streetcar'' in the western US. ''Streetcar'' or ''tramway'' are preferred in Canada. In parts of the United States, internally powered buses made to resemble a streetcar are often referred to as "trolleys". To avoid further confusion with trolley buses, the American Public Transportation Association (APTA) refers to them as "trolley-replica buses". In the Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yaghan People
The Yahgan (also called Yagán, Yaghan, Yámana, Yamana or Tequenica) are a group of indigenous peoples in the Southern Cone. Their traditional territory includes the islands south of Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego, extending their presence into Cape Horn, making them the world's southernmost human population. In the 19th century, the Yahgan were known in English as “Fuegians”. The term is now avoided as it can also refer to several other indigenous peoples of Tierra del Fuego, for example the Selk'nam. The Yahgan language, also known as Yámana, is considered a language isolate. Cristina Calderón (1928–2022), who was born on Navarino Island, Chile, was known as the last full-blooded Yahgan and last native speaker of the Yahgan language. Most Yahgans speak Spanish. The Yahgan were traditionally nomads and hunter-gatherers who traveled by canoe between islands to collect food. The men hunted sea lions and the women dove to collect shellfish. The Yahgan share some similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livio Dante Porta
Livio Dante Porta (21 March 1922 – 10 June 2003) was an Argentine steam locomotive engineer. He is particularly remembered for his innovative modifications to existing locomotive systems in order to obtain better performance and energy efficiency, and reduced pollution. He developed the Kylpor and Lempor exhaust systems. The Lemprex was under development at the time of his death. Early years Porta was born in Paraná, Entre Ríos, and studied civil engineering, concluding his studies in 1946, at a time when steam was already giving way to diesel and electric locomotives in Europe and North America. Career Naturally, Porta's first projects were in Argentina. Taking the work of Andre Chapelon in France as his starting point, he set out to demonstrate that the steam locomotive was far from reaching its maximum potential. His first locomotive project in 1948 took the remains of a 4-6-2 converting it into a 4-cylinder compound 4-8-0 named 'Presidente Peron'/'Argentina'. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garratt
A Garratt (often referred to as a Beyer Garratt) is a type of steam locomotive invented by British engineer Herbert William Garratt that is articulated into three parts. Its boiler, firebox, and cab are mounted on a centre frame or "bridge". The two other parts, one at each end, have a pivot to support the central frame; they consist of a steam engine unit – with driving wheels, trailing wheels, valve gear, and cylinders, and above it, fuel and/or water storage. Articulation permits locomotives to negotiate curves that might restrict large rigid-framed locomotives. The design also provides more driving wheels per unit of locomotive weight, permitting operation on lightly engineered track. Garratt locomotives produced as much as twice the power output of the largest conventional locomotives of railways that introduced them, reducing the need for multiple locomotives and crews. Advantages of the Garratt concept The principal benefit of the Garratt design is that the boil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)


.gif)


