|
South Walls
South Walls ( sco, Sooth Waas), often referred to as Walls, is an inhabited island adjacent to Hoy in Orkney, Scotland. The name is a corruption of "Sooth Was", which means the "southern voes" – as with Kirkwall, it was assumed that it was a mispronunciation of "walls". South Walls forms the southern side of the harbour of Longhope. It was a tidal island until a narrow causeway, was constructed over the sandbank in 1912, which was known as the Ayre, although this name has become transferred to the causeway itself. Although sometimes considered to be a peninsula, it is an island in all but name. South Walls is a popular stopping off place for barnacle geese. Geography and geology The island, like most of the Orkney archipelago, is made up of old red sandstone with the Rousay Flagstone Group predominating. The island is more or less oval in shape, but there is a small promontory, called Cantick Head in the south east, which is created by Kirk Hope (Church Bay). It is separat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantick Head Lighthouse
The Cantick Head Lighthouse is an active 19th century lighthouse on the Scottish island of South Walls in the Orkney Islands. It is located at the end of Cantick Head, a long peninsula on the south-eastern coast of South Walls that overlooks the Pentland Firth and the Sound of Hoxa, which forms the southern entry to the natural harbour of Scapa Flow. South Walls is joined to the larger island of Hoy by a narrow causeway, allowing road access to the village of Longhope, Hackness and then the lighthouse further to the south-east. History The need for the lighthouse was first raised by the Northern Lights Commissioners in 1854 and was quickly approved, but delays in agreeing the details for the light and that of the buildings meant that construction did not start until two years later in 1856. The design and construction was overseen by the notable lighthouse engineers Thomas and David Stevenson. The light first entered service in 1858, and consists of a high cylinder-shap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sutherland
Sutherland ( gd, Cataibh) is a historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area in the Highlands of Scotland. Its county town is Dornoch. Sutherland borders Caithness and Moray Firth to the east, Ross-shire and Cromartyshire (later combined into Ross and Cromarty) to the south and the Atlantic to the north and west. Like its southern neighbour Ross-shire, Sutherland has some of the most dramatic scenery in Europe, especially on its western fringe where the mountains meet the sea. These include high sea cliffs, and very old mountains composed of Precambrian and Cambrian rocks. The name ''Sutherland'' dates from the era of Norwegian Viking rule and settlement over much of the Highlands and Islands, under the rule of the jarl of Orkney. Although it contains some of the northernmost land in the island of Great Britain, it was called ' ("southern land") from the standpoint of Orkney and Caithness. In Gaelic, the area is referred to according to its traditional areas: ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaman
Shamanism is a religious practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with what they believe to be a spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct spirits or spiritual energies into the physical world for the purpose of healing, divination, or to aid human beings in some other way. Beliefs and practices categorized as "shamanic" have attracted the interest of scholars from a variety of disciplines, including anthropologists, archeologists, historians, religious studies scholars, philosophers and psychologists. Hundreds of books and academic papers on the subject have been produced, with a peer-reviewed academic journal being devoted to the study of shamanism. In the 20th century, non-Indigenous Westerners involved in countercultural movements, such as hippies and the New Age created modern magicoreligious practices influenced by their ideas of various Indigenous religions, creating what has been ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Völva
In Germanic paganism, a seeress is a woman said to have the ability to foretell future events and perform sorcery. They are also referred to with many other names meaning "prophetess", "staff bearer", "wise woman" and "sorceress", and they are frequently called ''witches'' or ''priestesses'' both in early sources and in modern scholarship. They were an expression of the pre-Christian shamanic traditions of Europe, and they held an authoritative position in Germanic society. Mentions of Germanic seeresses occur as early as the Roman era, when, for example, they at times led armed resistance against Roman rule and acted as envoys to Rome. After the Roman Era, seeresses occur in records among the North Germanic people, where they form a reoccurring motif in Norse mythology. Both the classical and the Norse accounts imply that they used wands, and describe them as sitting on raised platforms during séances. Ancient Roman and Greek literature records the name of several Germanic s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigurd Hloðvisson
Sigurd Hlodvirsson (23 April 1014), popularly known as Sigurd the Stout from the Old Norse ''Sigurðr digri'',Thomson (2008) p. 59 was an Earl of Orkney. The main sources for his life are the Norse Sagas, which were first written down some two centuries or more after his death. These engaging stories must therefore be treated with caution rather than as reliable historical documents. Sigurd was the son of Hlodvir Thorfinnsson and (according to the Norse sagas) a direct descendant of Torf-Einarr Rognvaldson. Sigurd's tenure as earl was apparently free of the kin-strife that beset some other incumbents of this title and he was able to pursue his military ambitions over a wide area. He also held lands in the north of mainland Scotland and in the '' Sudrøyar'', and he may have been instrumental in the defeat of Gofraid mac Arailt, King of the Isles. The '' Annals of Ulster'' record his death at the Battle of Clontarf in 1014, the earliest known reference to the earldom of Orkn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of Norway. Bouvet Island, located in the Subantarctic, is a dependency of Norway; it also lays claims to the Antarctic territories of Peter I Island and Queen Maud Land. The capital and largest city in Norway is Oslo. Norway has a total area of and had a population of 5,425,270 in January 2022. The country shares a long eastern border with Sweden at a length of . It is bordered by Finland and Russia to the northeast and the Skagerrak strait to the south, on the other side of which are Denmark and the United Kingdom. Norway has an extensive coastline, facing the North Atlantic Ocean and the Barents Sea. The maritime influence dominates Norway's climate, with mild lowland temperatures on the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
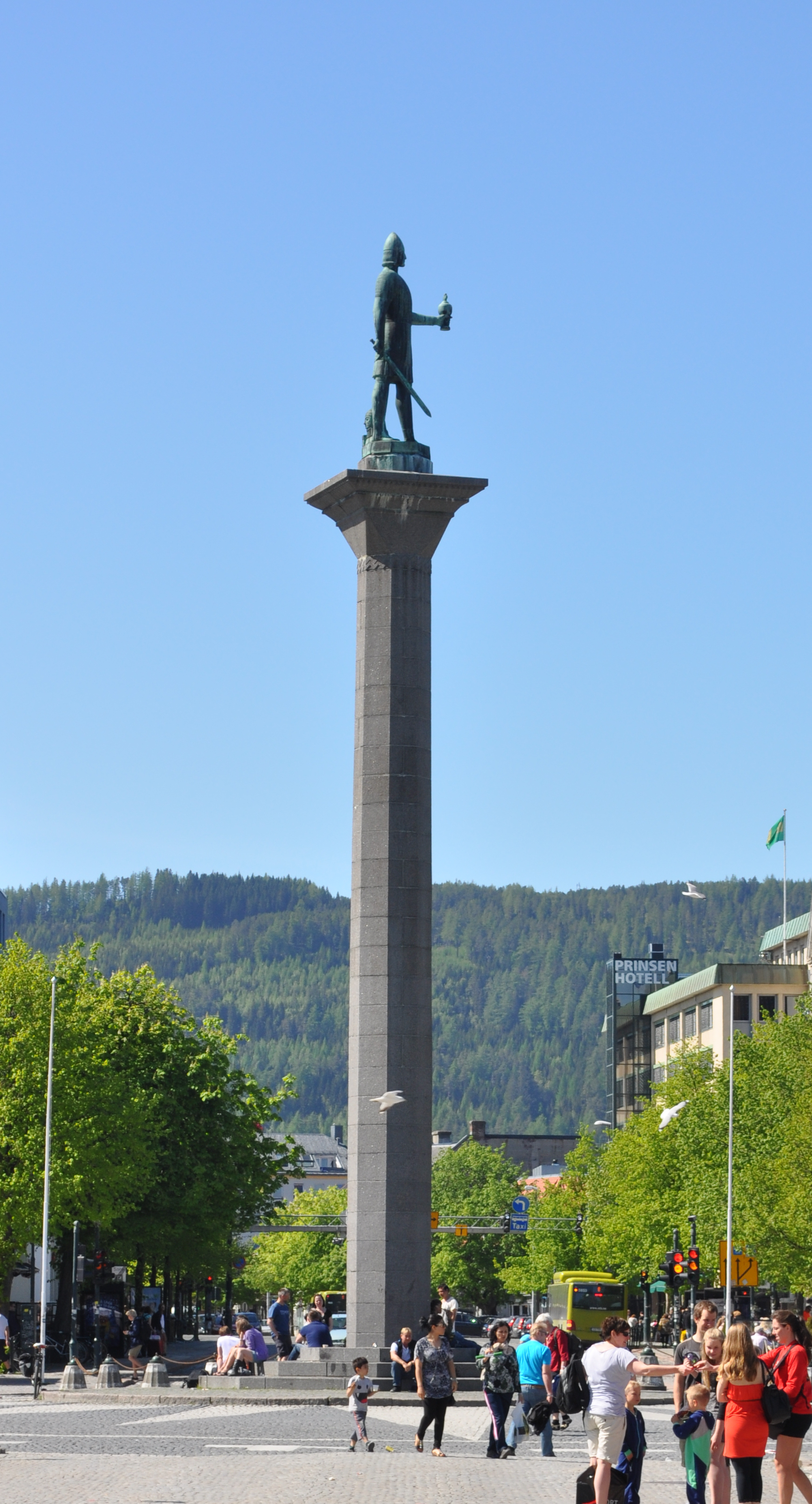
Olaf I Of Norway
Olaf Tryggvason (960s – 9 September 1000) was King of Norway from 995 to 1000. He was the son of Tryggvi Olafsson, king of Viken (Vingulmark, and Rånrike), and, according to later sagas, the great-grandson of Harald Fairhair, first King of Norway. He is numbered as Olaf I. Olaf is seen as an important factor in the conversion of the Norse to Christianity. He is said to have built the first Christian church in Norway, in 995, and to have founded the city of Trondheim in 997. A statue of Olaf Tryggvason is located in the city's central plaza. Historical information on Olaf is sparse. He is mentioned in some contemporary English sources, and some skaldic poems. The oldest narrative source mentioning him briefly is Adam of Bremen's ''Gesta Hammaburgensis ecclesiae pontificum'' of ''circa'' 1070. In the 1190s, two Latin versions of ''" Óláfs saga Tryggvasonar"'' were written in Iceland, by Oddr Snorrason and by Gunnlaugr Leifsson – these are now lost, but are thought to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon's-mas
Simon the Zealot (, ) or Simon the Canaanite or Simon the Canaanean (, ; grc-gre, Σίμων ὁ Κανανίτης; cop, ⲥⲓⲙⲱⲛ ⲡⲓ-ⲕⲁⲛⲁⲛⲉⲟⲥ; syc, ܫܡܥܘܢ ܩܢܢܝܐ) was one of the most obscure among the apostles of Jesus. A few pseudepigraphical writings were connected to him, but Saint Jerome does not include him in ''De viris illustribus'' written between 392 and 393 AD. Identity The name Simon occurs in all of the Synoptic Gospels and the Book of Acts each time there is a list of apostles, without further details: The Zealot To distinguish him from Simon Peter he is called ''Kananaios'' or ''Kananites'', depending on the manuscript ( ), and in the list of apostles in Luke 6:15, repeated in Acts 1:13, ''Zelotes,'' the "Zealot". Both ''Kananaios'' and ''Kananites'' derive from the Hebrew word קנאי ''qanai'', meaning ''zealous'', although Jerome and others mistook the word to signify the apostle was from the town of קנה Cana, in w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assynt
Assynt ( gd, Asainn or ) is a sparsely populated area in the south-west of Sutherland, lying north of Ullapool on the west coast of Scotland. Assynt is known for its landscape and its remarkable mountains, which have led to the area, along with neighbouring Coigach, being designated as the Assynt-Coigach National scenic area (Scotland), National Scenic Area, one of 40 such areas in Scotland. The western part of Assynt has many distinctively shaped mountains, including Quinag, Canisp, Suilven and Ben More Assynt, that rise steeply from the surrounding "cnoc and lochan" scenery. These can often appear higher than their actual height would indicate due to their steep sides and the contrast with the moorland from which they rise. Many of the most distinctive peaks such as Suilven were formed during the last Ice age, Ice Age, when they were left exposed above the ice sheet as nunataks, and they now remain as inselbergs of highly eroded Torridonian sandstone sitting on a bedrock of mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rögnvald Brusason
Rognvald Brusason (died 1046), son of Brusi Sigurdsson, was Earl of Orkney jointly with Thorfinn Sigurdsson from about 1037 onwards. His life is recorded in the ''Orkneyinga Saga''. History Rognvald was taken by his father to Norway, to the court of Olaf II of Norway, Olaf Haraldsson, when Brusi and Thorfinn went there to have the inheritance of Einar Sigurdsson, Earl of Orkney, Einar Wry-mouth's third-share of the Earldom settled. Olaf kept Einar's share for himself, appointing Brusi to administer it, and kept Rognvald at his court. The ''Orkneyinga Saga'' says of Rognvald:Rognvald was one of the handsomest of men, with a fine head of golden hair, smooth as silk. At an early age he grew to be tall and strong, earning a great reputation for his shrewdness and courtesy ... Rognvald was a supporter of Olaf Haraldsson, later Saint Olaf, sharing his exile in Kievan Rus, and helping his brother Harald III of Norway, Harald Sigurdsson, better known as Harald Hardraade, escape after th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
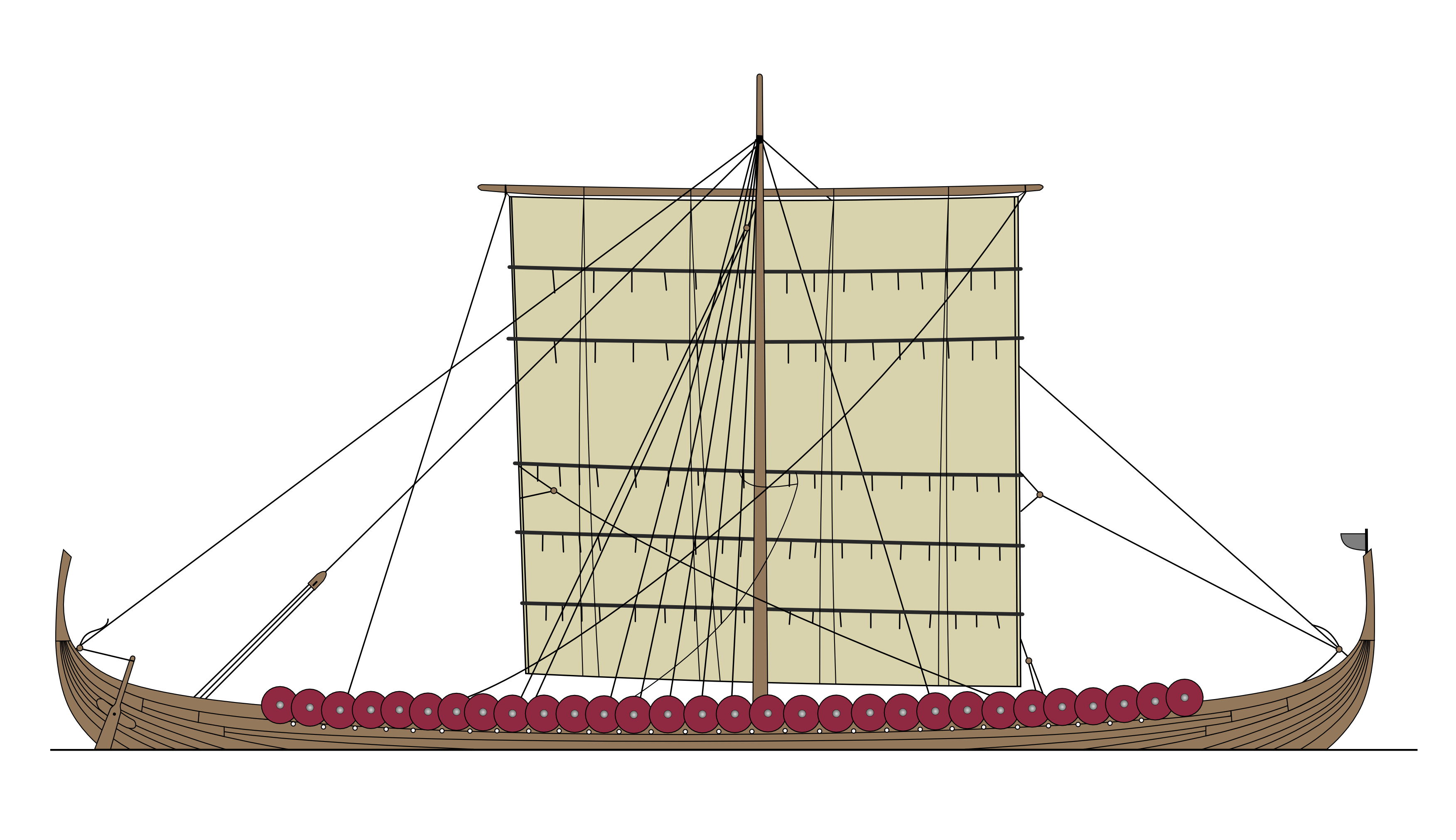
Long-ship
Longships were a type of specialised Scandinavian warships that have a long history in Scandinavia, with their existence being archaeologically proven and documented from at least the fourth century BC. Originally invented and used by the Norsemen (commonly known as the Vikings) for commerce, exploration, and warfare during the Viking Age, many of the longship's characteristics were adopted by other cultures, like Anglo-Saxons, and continued to influence shipbuilding for centuries. The longship's design evolved over many centuries, and continuing up until the sixth century with clinker-built ships like Nydam. The longship appeared in its complete form between the ninth and 13th centuries. The character and appearance of these ships have been reflected in Scandinavian boatbuilding traditions to the present day. The particular skills and methods employed in making longships are still used worldwide, often with modern adaptations. They were all made out of wood, with cloth sails ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)