|
South Hams
South Hams is a local government district on the south coast of Devon, England. Services divide between those provided by its own Council headquartered in Totnes, and those provided by Devon County Council headquartered in the city of Exeter. Beside Totnes are its towns of Dartmouth, Kingsbridge, Salcombe, and Ivybridge — the most populous with 11,851 residents, as at the 2011 Census. To the north, it includes part of Dartmoor National Park, to the east borders Torbay, and to the west Plymouth. It contains some of the most unspoilt coastline on the south coast, including the promontories of Start Point and Bolt Head. The entire coastline, along with the lower Avon and Dart valleys, form most of the South Devon Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. The South Hams, along with nearby Broadsands in Paignton, is the last British refuge of the cirl bunting. History The South Hams were formerly part of the Brythonic (Celtic) Kingdom of Dumnonia later reduced to the modern b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
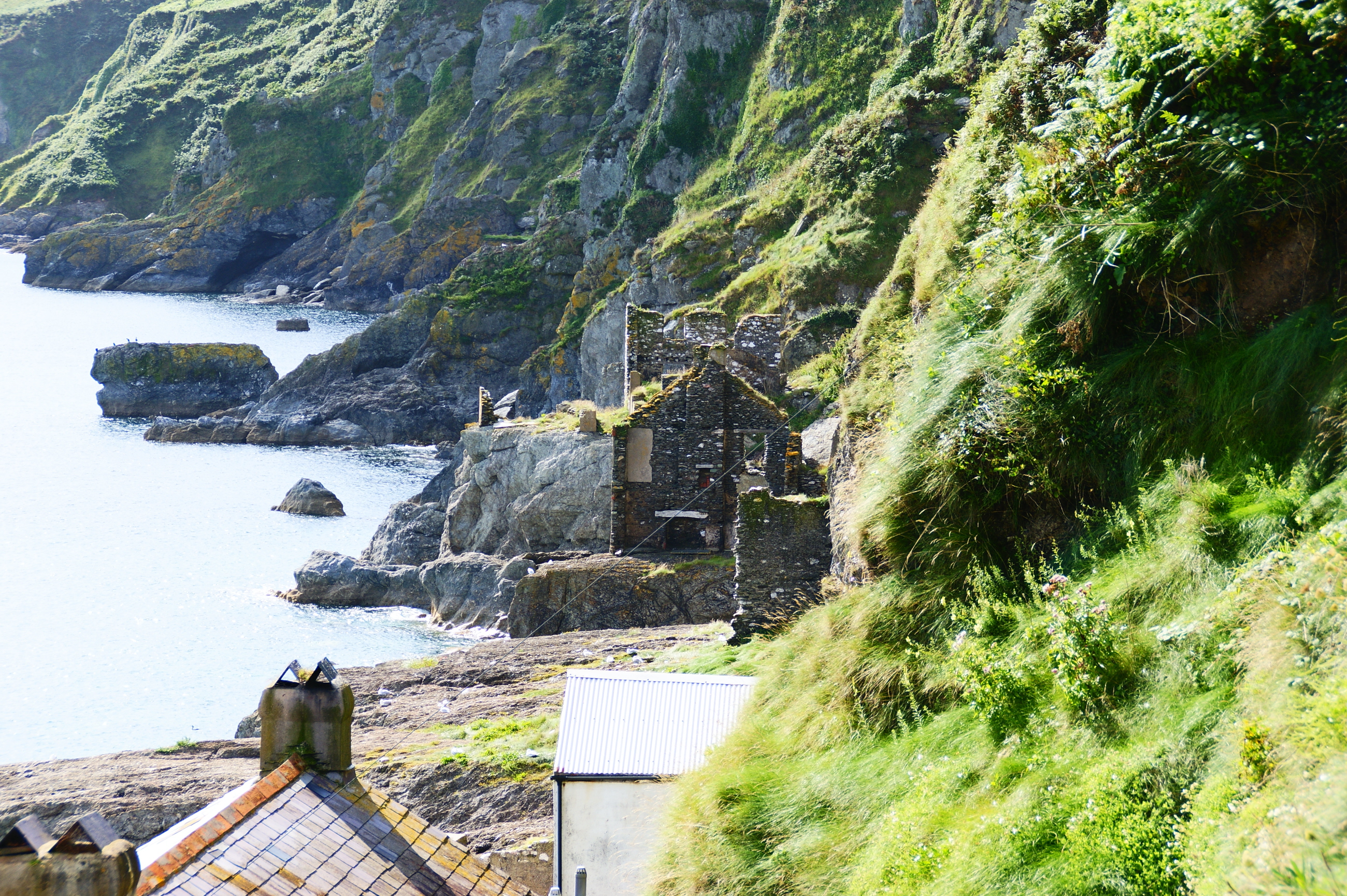 |
Hallsands
Hallsands is a village and beach in south Devon, England, in a precarious position between cliffs and the sea, between Beesands to the north and Start Point to the south. History The early history of Hallsands is unknown, but a chapel has existed there since at least 1506. The village was at a cave known as Poke Hole, and probably was not inhabited before 1600. The village grew in size during the 18th and 19th centuries, and by 1891 it had 37 houses, a spring, a public house called the ''London Inn'', and a population of 159. Most residents of Hallsands at that time depended on fishing for a living, particularly crab fishing on the nearby Skerries Bank. In the 1890s, following a scheme proposed by Sir John Jackson, it was decided to expand the naval dockyard at Keyham, near Plymouth, and dredging began offshore from Hallsands to provide sand and gravel for its construction. Soon, up to 1,600 tons of material was being removed each day, and the level of the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Local Government Act 1972
The Local Government Act 1972 (c. 70) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974. It was one of the most significant Acts of Parliament to be passed by the Heath Government of 1970–74. Its pattern of two-tier metropolitan and non-metropolitan county and district councils remains in use today in large parts of England, although the metropolitan county councils were abolished in 1986, and both county and district councils have been replaced with unitary authorities in many areas since the 1990s. In Wales, too, the Act established a similar pattern of counties and districts, but these have since been entirely replaced with a system of unitary authorities. Elections were held to the new authorities in 1973, and they acted as "shadow authorities" until the handover date. Elections to county councils were held on 12 April, for metropolitan and Welsh districts on 10 May, and for non-metropolitan distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
African British
Black British people are a multi-ethnic group of British citizens of either African or Afro-Caribbean descent.Gadsby, Meredith (2006), ''Sucking Salt: Caribbean Women Writers, Migration, and Survival'', University of Missouri Press, pp. 76–77. The term ''Black British'' developed in the 1950s, referring to the Black British West Indian people from the former Caribbean British colonies in the West Indies (ie, the New Commonwealth) now referred to as the Windrush Generation and people from Africa, who are residents of the United Kingdom and are British. The term ''black'' has historically had a number of applications as a racial and political label and may be used in a wider sociopolitical context to encompass a broader range of non-European ethnic minority populations in Britain. This has become a controversial definition. ''Black British'' is one of various self-designation entries used in official UK ethnicity classifications. Black residents constituted around 3 per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
British African-Caribbean Community
British African-Caribbean people are an ethnic group in the United Kingdom. They are British citizens whose ancestry originates from the Caribbean or they are nationals of the Caribbean who reside in the UK. There are some self-identified Afro-Caribbean people who are multi-racial. The most common and traditional use of the term African-Caribbean community is in reference to groups of residents continuing aspects of Caribbean culture, customs and traditions in the UK. The earliest generations of Afro-Caribbean people to migrate to Britain trace their ancestry to a wide range of Afro Caribbean ethnic groups. African Caribbean people descend from disparate groups of African peoples who were brought, sold and taken from West Africa as slaves to the colonial Caribbean. In addition British African Caribbeans may have ancestry from various indigenous Caribbean tribes, and from settlers of European and Asian ethnic groups. According to the National Library of Medicine the aver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Black British
Black British people are a multi-ethnic group of British citizens of either African or Afro-Caribbean descent.Gadsby, Meredith (2006), ''Sucking Salt: Caribbean Women Writers, Migration, and Survival'', University of Missouri Press, pp. 76–77. The term ''Black British'' developed in the 1950s, referring to the Black British West Indian people from the former Caribbean British colonies in the West Indies (ie, the New Commonwealth) now referred to as the Windrush Generation and people from Africa, who are residents of the United Kingdom and are British. The term ''black'' has historically had a number of applications as a racial and political label and may be used in a wider sociopolitical context to encompass a broader range of non-European ethnic minority populations in Britain. This has become a controversial definition. ''Black British'' is one of various self-designation entries used in official UK ethnicity classifications. Black residents constituted around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
British Bangladeshi
British Bangladeshis ( bn, বিলাতী বাংলাদেশী, Bilatī Bangladeshī) are people of Bangladeshi origin who have attained citizenship in the United Kingdom, through immigration and historical naturalisation. The term can also refer to their descendants. Bengali Muslims have prominently been migrating to the UK since the 1940s. Migration reached its peak during the 1970s, with most originating from the Sylhet Division. The largest concentration live in east London boroughs, such as Tower Hamlets. This large diaspora in London leads people in Sylhet to refer to British Bangladeshis as Londoni ( bn, লন্ডনী). Bangladeshis form one of the UK's largest group of people of overseas descent and are also one of the country's youngest and fastest growing communities. The 2011 UK Census recorded nearly half-a-million residents of Bangladeshi ethnicity. While in the 2021 UK census, Bangladeshis in England and Wales enumerated 644,881, or 1.1% of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Pakistani British
British Pakistanis ( ur, (Bratānia men maqīm pākstānī); also known as Pakistani British people or Pakistani Britons) are citizens or residents of the United Kingdom whose ancestral roots lie in Pakistan. This includes people born in the UK who are of Pakistani descent, Pakistani-born people who have migrated to the UK and those of Pakistani origin from overseas who migrated to the UK. The UK is home to the largest Pakistani community in Europe, with the population of British Pakistanis exceeding 1.17 million based on the 2011 census. British Pakistanis are the second-largest ethnic minority population in the United Kingdom and also make up the second-largest sub-group of British Asians. In addition, they are one of the largest overseas Pakistani communities, similar in number to the Pakistani diaspora in Saudi Arabia. The majority of British Pakistanis originate from the Azad Kashmir and Punjab regions, with a smaller number from other parts of Pakistan includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Indian British
British Indians are citizens of the United Kingdom (UK) whose ancestral roots are from India. This includes people born in the UK who are of Indian origin as well as Indians who have migrated to the UK. Today, Indians comprise about 1.4 million people in the UK, making them the single largest visible ethnic minority population in the country. They make up the largest subgroup of British Asians and are one of the largest Indian communities in the Indian diaspora, mainly due to the Indian–British relations (including historical links such as India having been part of the British Empire and still being part of the Commonwealth of Nations). The British Indian community is the sixth largest in the Indian diaspora, behind the Indian communities in the United States, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Malaysia and Nepal. The majority of British Indians are of Punjabi, Gujarati, Bengali and Malayali descent, with smaller Tamil, Telugu, Konkani, and Marathi communities. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
British Asian
British Asians (also referred to as Asian Britons) are British citizens of Asian descent. They constitute a significant and growing minority of the people living in the United Kingdom, with 6.9% of the population identifying as Asian/Asian British in the 2011 United Kingdom census. This represented a national demographic increase from a 4.4% share of UK population in 2001. Represented predominantly by South Asian ethnic groups, census data regarding birthplace and ethnicity demonstrate around a million Asian British people derive their ancestry between East Asia, Southeast Asia, Central Asia, and West Asia. Since the 2001 census, British people of general Asian descent have been included in the "Asian/Asian British" grouping ("Asian, Asian Scottish or Asian British" grouping in Scotland) of the UK census questionnaires. Categories for British Indians, British Pakistanis, British Bangladeshis, British Chinese, and other Asians have existed under an Asian British heading si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
White Other (United Kingdom Census)
The term Other White is a classification of ethnicity in the United Kingdom and has been used in documents such as the 2011 UK Census to describe people who self-identify as white (chiefly European) persons who are not of the English, Welsh, Scottish, Romani or Irish ethnic groupings. The category does not comprise a single ethnic group but is instead a method of identification for white people who are not represented by other white census categories. This means that the Other White group contains a diverse collection of people with different countries of birth, languages and religions. In 2011, the Scottish Government introduced the category White Polish to differentiate Polish Britons, and Polish residents, living in Scotland from this broad grouping. The categorisation was primarily intended to cover people with ancestry from Continental Europe, with the largest represented ethnic groups being Poles (except in Scotland since 2011), Germans, Romanians, Italians and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
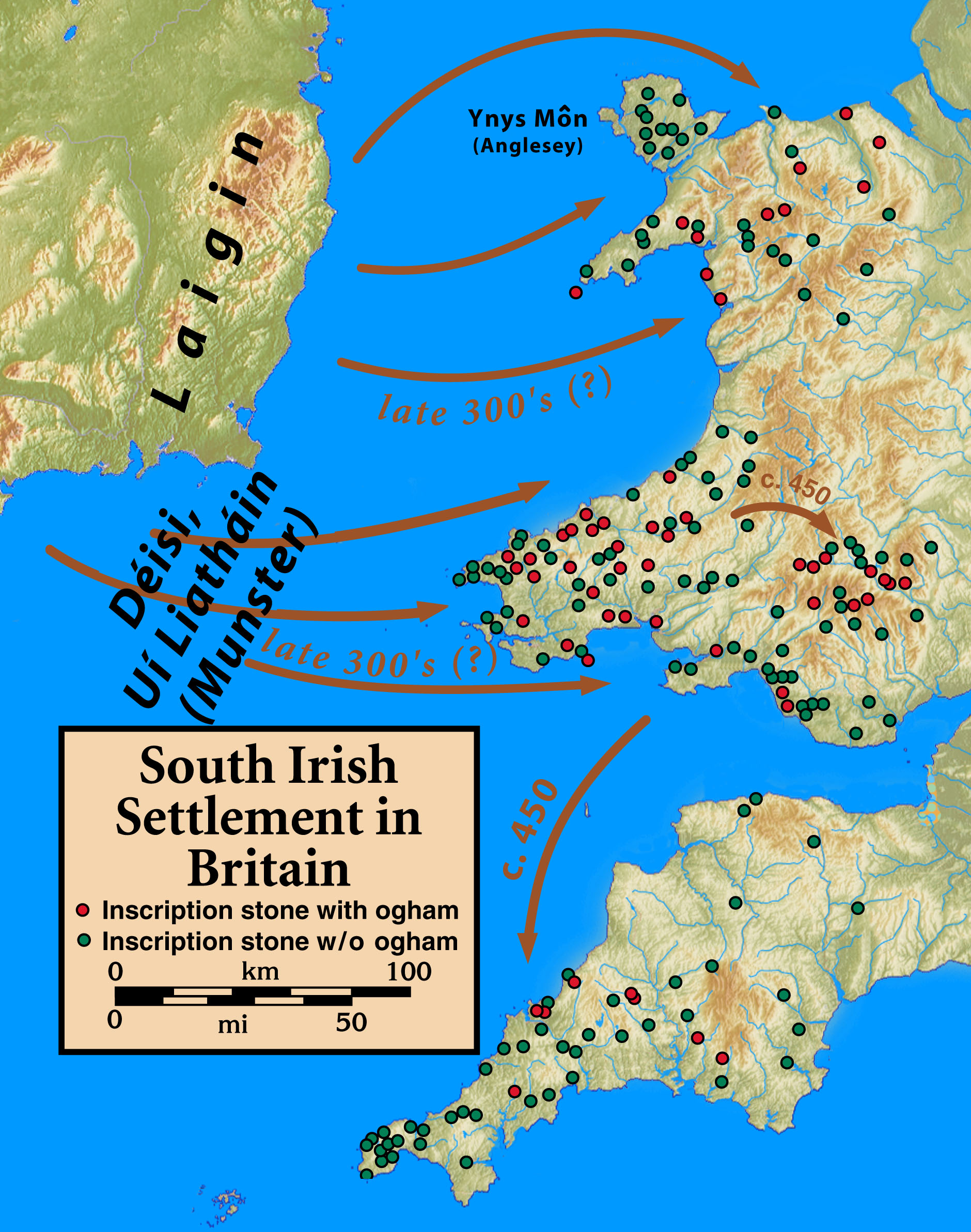 |
Irish Briton
Irish migration to Great Britain has occurred from the earliest recorded history to the present. There has been a continuous movement of people between the islands of Ireland and Great Britain due to their proximity. This tide has ebbed and flowed in response to politics, economics and social conditions of both places. Today, millions of residents of Great Britain are either from Ireland or are entitled to an Irish passport due to having a parent or grandparent who was born in Ireland. The modern era of Irish migration has also seen non-indigenous Asian Irish and black Irish people move to Britain. It is estimated that as many as six million people living in the UK have at least one Irish grandparent (around 10% of the UK population). The Irish diaspora ( ga, Diaspóra na nGael) refers to Irish people and their descendants who live outside Ireland. This article refers to those who reside in Great Britain, the largest island and principal territory of the United Kingdom. Migr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
White British
White British is an ethnicity classification used for the native white population identifying as English, Scottish, Welsh, Cornish, Northern Irish, or British in the United Kingdom Census. In the 2011 census, the White British population was 51,736,290, 81.88% of the UK total population (NB: This total includes the population estimate for Northern Ireland, where only the term 'White' is used in ethnic classification. National identity is listed separately in NI, where 40% classified themselves as British, making up a significant portion of the population, along with those specifying their national identity as Irish). Census classifications For the 2011 census, in England and Wales, the White self-classification option included a subcategory of " English/Welsh/Scottish/ Northern Irish/British". [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |