|
South Atlantic Convergence Zone
The South Atlantic convergence zone, or SACZ, is an elongated axis of clouds, precipitation, and convergent winds oriented in a northwest–southeast manner across southeast Brazil into the southwest Atlantic Ocean. By definition, the feature is a monsoon trough. It is strongest in the warm season. Thunderstorm activity along the feature magnifies over three or more days when the Madden–Julian oscillation passes into the region, due to the enhanced upper divergence. Low level winds over Rondônia are tied to the strength of this zone, where westerly wind anomalies correlate to active phases of the South American monsoon, while easterly wind anomalies indicate breaks of activity along the SACZ. The feature is also strongest with negative anomalies in the sea surface temperature Sea surface temperature (SST), or ocean surface temperature, is the ocean temperature close to the surface. The exact meaning of ''surface'' varies according to the measurement method used, but it i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zona De Convergência Do Atlântico Sul
The red-tailed silverside, or zona (''Bedotia geayi'') is a species of Madagascar rainbowfish endemic to the Mananjary River drainage in Madagascar. It is threatened by habitat loss and introduced species. It has often been confused with the related '' B. madagascariensis'', which is common in the aquarium trade.SeriouslyFish: Bedotia madagascarensis.' Retrieved 3 July 2014.Loiselle, P.V.; and Rodriguez, D. (2007). ''A new species of Bedotia (Teleostei: Atherinomorpha: Bedotiidae) from the Rianila drainage of Eastern Madagascar, with redescriptions of Bedotia madagascariensis and Bedotia geayi.'' Zootaxa 1520: 1-18. In addition to meristics, the two can be separated by the exact colour pattern on their tail fin (males of both typically have red in the tail) and the distinct red spot on the lower jaw of breeding male ''B. geayi'' (lacking in ''B. madagascariensis''). ''B. geayi'' was described in 1907 by Jacques Pellegrin from a type collected by the pharmacist and natural histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor (reaching 100% relative humidity), so that the water condenses and "precipitates" or falls. Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation but colloids, because the water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate. Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are called showers. Moisture that is lifted or otherwise forced to rise over a layer of sub-freezing air at the surface may be condense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Meteorological Society
The American Meteorological Society (AMS) is the premier scientific and professional organization in the United States promoting and disseminating information about the Atmospheric sciences, atmospheric, Oceanography, oceanic, and Hydrology, hydrologic sciences. Its mission is to advance the atmospheric and related sciences, technologies, applications, and services for the benefit of society. Background Founded on December 29, 1919, by Charles Franklin Brooks at a meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science in St. Louis and incorporated on January 21, 1920, the American Meteorological Society has a membership of more than 13,000 weather, water, and climate scientists, professionals, researchers, educators, students, and enthusiasts. AMS offers numerous programs and services in the sphere of water, weather and climate sciences. It publishes eleven atmospheric and related oceanic and hydrologic journals (in print and online), sponsors as many as twelve conf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monsoon Trough
The monsoon trough is a portion of the Intertropical Convergence Zone in the Western Pacific,Bin WangThe Asian Monsoon.Retrieved 2008-05-03. as depicted by a line on a weather map showing the locations of minimum sea level pressure, and as such, is a convergence zone between the wind patterns of the southern and northern hemispheres. Westerly monsoon winds lie in its equatorward portion while easterly trade winds exist poleward of the trough. Right along its axis, heavy rains can be found which usher in the peak of a location's respective rainy season. As it passes poleward of a location, hot and dry conditions develop. The monsoon trough plays a role in creating many of the world's rainforests. The term ''monsoon trough'' is most commonly used in monsoonal regions of the Western Pacific such as Asia and Australia. The migration of the ITCZ/monsoon trough into a landmass heralds the beginning of the annual rainy season during summer months. Depressions and tropical cyclones ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are sometimes called thundershowers. Thunderstorms occur in a type of cloud known as a cumulonimbus. They are usually accompanied by strong winds and often produce heavy rain and sometimes snow, sleet, or hail, but some thunderstorms produce little precipitation or no precipitation at all. Thunderstorms may line up in a series or become a rainband, known as a squall line. Strong or severe thunderstorms include some of the most dangerous weather phenomena, including large hail, strong winds, and tornadoes. Some of the most persistent severe thunderstorms, known as supercells, rotate as do cyclones. While most thunderstorms move with the mean wind flow through the layer of the troposphere that they occupy, vertical wind shear sometimes causes a de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
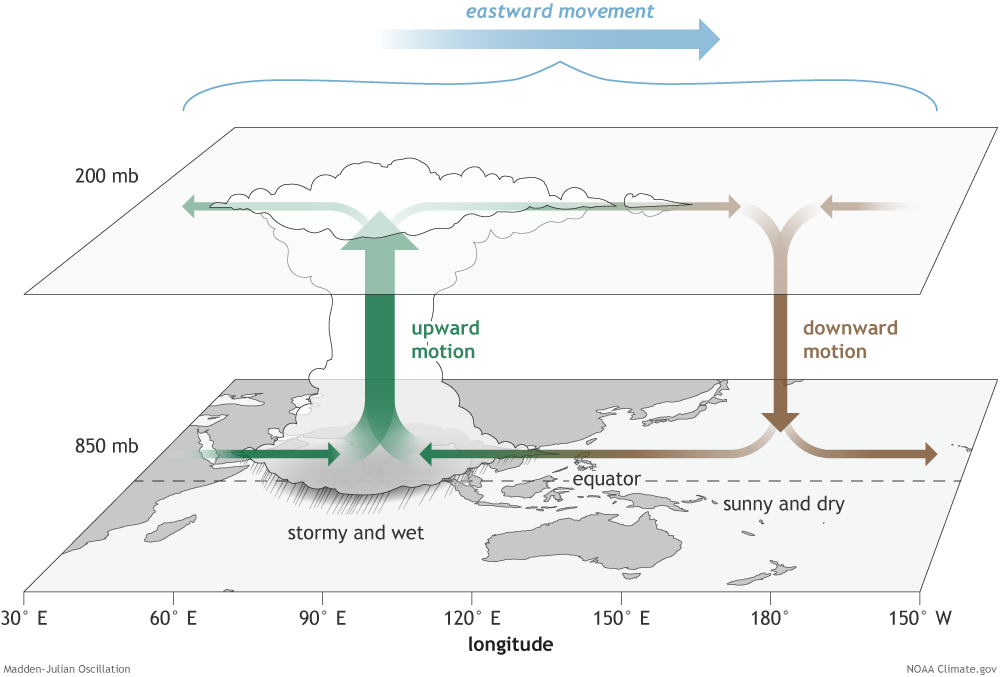
Madden–Julian Oscillation
The Madden–Julian oscillation (MJO) is the largest element of the intraseasonal (30- to 90-day) variability in the tropical atmosphere. It was discovered in 1971 by Roland Madden and Paul Julian of the American National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR). It is a large-scale coupling between atmospheric circulation and tropical deep atmospheric convection. Unlike a standing pattern like the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO), the Madden–Julian oscillation is a traveling pattern that propagates eastward, at approximately , through the atmosphere above the warm parts of the Indian and Pacific oceans. This overall circulation pattern manifests itself most clearly as anomalous rainfall. The Madden–Julian oscillation is characterized by an eastward progression of large regions of both enhanced and suppressed tropical rainfall, observed mainly over the Indian and Pacific Ocean. The anomalous rainfall is usually first evident over the western Indian Ocean, and remains evi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rondônia
Rondônia () is one of the 26 states of Brazil, located in the northern subdivision of the country (central-western part). To the west is a short border with the state of Acre, to the north is the state of Amazonas, in the east is Mato Grosso, and in the south and southwest is Bolivia. Rondônia has a population of 1,815,000 as of 2021. It is the fifth least populated state. Its capital and largest city is Porto Velho. The state was named after Cândido Rondon, who explored the north of the country during the 1910s. The state, which is home to 0.8% of the Brazilian population, is responsible for 0.6% of the Brazilian GDP. Geography Rondonia was originally home to over 200,000 km2 of rainforest, but has become one of the most deforested places in the Amazon. By 2003 around 70,000 km2 of rainforest had been cleared. The area around the Guaporé River is part of the Beni savanna ecoregion. The Samuel Dam is located in the state, on the Jamari River. History Dem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscillation of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) between its limits to the north and south of the equator. Usually, the term monsoon is used to refer to the rainy phase of a seasonally changing pattern, although technically there is also a dry phase. The term is also sometimes used to describe locally heavy but short-term rains. The major monsoon systems of the world consist of the West African, Asia–Australian, the North American, and South American monsoons. The term was first used in English in British India and neighboring countries to refer to the big seasonal winds blowing from the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea in the southwest bringing heavy rainfall to the area. Etymology The etymology of the word monsoon is not wholl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Climate
The ''Journal of Climate'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal published semi-monthly by the American Meteorological Society. It covers research that advances basic understanding of the dynamics and physics of the climate system on large spatial scales, including variability of the atmosphere, oceans, land surface, and cryosphere; past, present, and projected future changes in the Climate, climate system; and climate simulation and prediction. See also *List of scientific journals in earth and atmospheric sciences A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby unio ... External links * Climatology journals Publications established in 1988 English-language journals American Meteorological Society academic journals {{climate-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Surface Temperature
Sea surface temperature (SST), or ocean surface temperature, is the ocean temperature close to the surface. The exact meaning of ''surface'' varies according to the measurement method used, but it is between and below the sea surface. Air masses in the Earth's atmosphere are highly modified by sea surface temperatures within a short distance of the shore. Localized areas of heavy snow can form in bands downwind of warm water bodies within an otherwise cold air mass. Warm sea surface temperatures are known to be a cause of tropical cyclogenesis over the Earth's oceans. Tropical cyclones can also cause a cool wake, due to turbulent mixing of the upper of the ocean. SST changes diurnally, like the air above it, but to a lesser degree. There is less SST variation on breezy days than on calm days. In addition, ocean currents such as the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO), can affect SST's on multi-decadal time scales, a major impact results from the global thermohaline ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Meteorology
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is referred to by different names, including hurricane (), typhoon (), tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean, and a typhoon occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean, South Pacific, or (rarely) South Atlantic, comparable storms are referred to simply as "tropical cyclones", and such storms in the Indian Ocean can also be called "severe cyclonic storms". "Tropical" refers to the geographical origin of these systems, which form almost exclusively over tropical seas. "Cyclone" refers to their winds moving in a circle, whirling round ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Dynamics
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences (which include atmospheric chemistry and physics) with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not begin until the 18th century. The 19th century saw modest progress in the field after weather observation networks were formed across broad regions. Prior attempts at prediction of weather depended on historical data. It was not until after the elucidation of the laws of physics, and more particularly in the latter half of the 20th century the development of the computer (allowing for the automated solution of a great many modelling equations) that significant breakthroughs in weather forecasting were achieved. An important branch of weather forecasting is marine weather forecasting as it relates to maritime and coastal safety, in which weather effects also include atmospheric interactions with large bodies of water. Meteorological phenom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |