|
Soudan 2
Soudan 2 was a particle detector located in the Soudan Mine in Northern Minnesota, United States, that operated from 1989 to 2001. It was a 960-ton iron tracking calorimeter whose primary purpose was to search for proton decay, although its data was also used to investigate the properties of neutrinos. It found no evidence of proton decay, but it did help confirm Super-Kamiokande's atmospheric neutrino result, supporting the theory of neutrino oscillation. The Soudan Mine is also home to the MINOS and CDMS detectors. History Soudan 2 was the successor to the Soudan 1, a similar 30 ton detector also intended to search for proton decay. The excavation for Soudan 2 was done in 1984–1985. Installation was started in 1986 and was completed in 1993. The experiment was run from April 1989 to June 2001, beginning with a partial detector of 275 tons.http://www.slac.stanford.edu/spires/find/experiments/www2?expt=SOUDAN "Results From The Soudan Prototype Proton Decay Experimen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
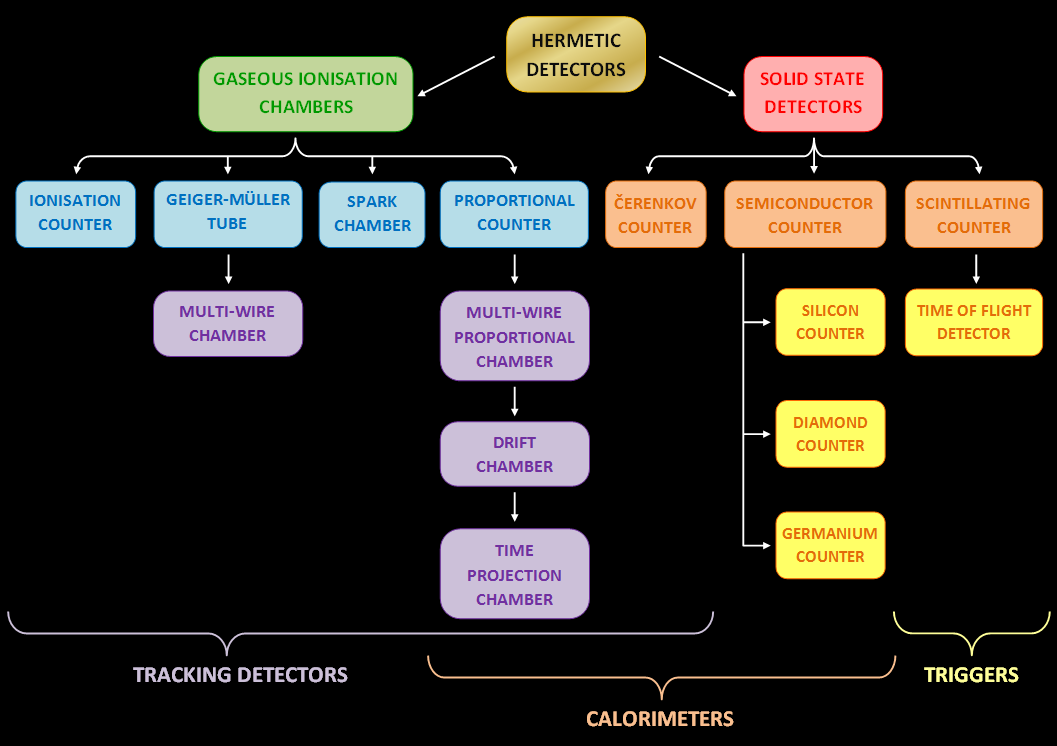
Particle Detector
In experimental and applied particle physics, nuclear physics, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify ionizing particles, such as those produced by nuclear decay, cosmic radiation, or reactions in a particle accelerator. Detectors can measure the particle energy and other attributes such as momentum, spin, charge, particle type, in addition to merely registering the presence of the particle. Examples and types Many of the detectors invented and used so far are ionization detectors (of which gaseous ionization detectors and semiconductor detectors are most typical) and scintillation detectors; but other, completely different principles have also been applied, like Čerenkov light and transition radiation. Historical examples *Bubble chamber * Wilson cloud chamber (diffusion chamber) * Photographic plate ;Detectors for radiation protection The following types of particle detector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soudan Mine
The Lake Vermilion-Soudan Underground Mine State Park is a Minnesota state park at the site of the Soudan Underground Mine, on the south shore of Lake Vermilion, in the Vermilion Range (Minnesota). The mine is known as Minnesota's oldest, deepest, and richest iron mine, and now hosts the Soudan Underground Laboratory. As the Soudan Iron Mine, it has been designated a U.S. National Historic Landmark. History In the late 19th century, prospectors searching for gold in northern Minnesota discovered extremely rich veins of hematite at this site, often containing more than 65% iron. An open pit mine began operation in 1882, and moved to underground mining by 1900 for safety reasons. From 1901 until the end of active mining in 1962, the Soudan Mine was owned by the United States Steel Corporation's Oliver Iron Mining division. By 1912 the mine was at a depth of 1,250 feet (381 m). When the mine closed, level 27 was being developed at 2,341 feet (713.5 m) below the surface and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calorimeter (particle Physics)
In particle physics, a calorimeter is an experimental apparatus that measures the energy of particles. Most particles enter the calorimeter and initiate a particle shower and the particles' energy is deposited in the calorimeter, collected, and measured. The energy may be measured in its entirety, requiring total containment of the particle shower, or it may be sampled. Typically, calorimeters are segmented transversely to provide information about the direction of the particle or particles, as well as the energy deposited, and longitudinal segmentation can provide information about the identity of the particle based on the shape of the shower as it develops. Calorimetry design is an active area of research in particle physics. Types of calorimeters Electromagnetic versus hadronic An electromagnetic calorimeter is one specifically designed to measure the energy of particles that interact primarily via the electromagnetic interaction, while a hadronic calorimeter is one designed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton Decay
In particle physics, proton decay is a hypothetical form of particle decay in which the proton decays into lighter subatomic particles, such as a neutral pion and a positron. The proton decay hypothesis was first formulated by Andrei Sakharov in 1967. Despite significant experimental effort, proton decay has never been observed. If it does decay via a positron, the proton's half-life is constrained to be at least years. According to the Standard Model, the proton, a type of baryon, is stable because baryon number (quark number) is conserved (under normal circumstances; see chiral anomaly for an exception). Therefore, protons will not decay into other particles on their own, because they are the lightest (and therefore least energetic) baryon. Positron emission and electron capture – forms of radioactive decay which sees a proton become a neutron – are not proton decay, since the proton interacts with other particles within the atom. Some beyond-the-Standard Model Gran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrinos
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is a fermion (an elementary particle with spin of ) that interacts only via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass is so small ('' -ino'') that it was long thought to be zero. The rest mass of the neutrino is much smaller than that of the other known elementary particles excluding massless particles. The weak force has a very short range, the gravitational interaction is extremely weak due to the very small mass of the neutrino, and neutrinos do not participate in the strong interaction. Thus, neutrinos typically pass through normal matter unimpeded and undetected. Weak interactions create neutrinos in one of three leptonic flavors: electron neutrinos muon neutrinos (), or tau neutrinos (), in association with the corresponding charged lepton. Although neutrinos were long believed to be massless, it is now known that there are three discrete neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Super-Kamiokande
Super-Kamiokande (abbreviation of Super-Kamioka Neutrino Detection Experiment, also abbreviated to Super-K or SK; ja, スーパーカミオカンデ) is a Neutrino detector, neutrino observatory located Kamioka Observatory, under Mount Ikeno near the city of Hida, Gifu, Hida, Gifu Prefecture, Japan. It is located underground in the Mozumi Mining, Mine in Hida's Kamioka area. The observatory was designed to detect high-energy neutrinos, to search for proton decay, study solar neutrino, solar and Neutrino#Atmospheric neutrinos, atmospheric neutrinos, and keep watch for supernovae in the Milky Way Galaxy. It consists of a cylindrical stainless steel tank about in height and diameter holding 50,000 metric tons (55,000 US tons) of ultrapure water. Mounted on an inside superstructure are about 13,000 photomultiplier tubes that detect light from Cherenkov radiation. A neutrino interaction with the electrons or nuclei of water can produce an electron or positron that moves faster t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MINOS
In Greek mythology, Minos (; grc-gre, Μίνως, ) was a King of Crete, son of Zeus and Europa. Every nine years, he made King Aegeus pick seven young boys and seven young girls to be sent to Daedalus's creation, the labyrinth, to be eaten by the Minotaur. After his death, Minos became a judge of the dead in the underworld. The Minoan civilization of Crete was named after him by the archaeologist Sir Arthur Evans. Etymology "Minos" is often interpreted as the Cretan word for "king", or, by a euhemerist interpretation, the name of a particular king that was subsequently used as a title. According to La Marle's reading of Linear A, which has been heavily criticised as arbitrary, we should read ''mwi-nu ro-ja'' (Minos the king) on a Linear A tablet. La Marle suggests that the name'' mwi-nu'' (Minos) is expected to mean 'ascetic' as Sanskrit ''muni'', and fits this explanation to the legend about Minos sometimes living in caves on Crete. The royal title ''ro-ja'' is rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryogenic Dark Matter Search
The Cryogenic Dark Matter Search (CDMS) is a series of experiments designed to directly detect particle dark matter in the form of Weakly Interacting Massive Particles (or WIMPs). Using an array of semiconductor detectors at millikelvin temperatures, CDMS has at times set the most sensitive limits on the interactions of WIMP dark matter with terrestrial materials (as of 2018, CDMS limits are not the most sensitive). The first experiment, CDMS I, was run in a tunnel under the Stanford University campus. It was followed by CDMS II experiment in the Soudan Mine. The most recent experiment, SuperCDMS (or SuperCDMS Soudan), was located deep underground in the Soudan Mine in northern Minnesota and collected data from 2011 through 2015. The series of experiments continues with SuperCDMS SNOLAB, an experiment located at the SNOLAB facility near Sudbury, Ontario in Canada that started construction in 2018 and is expected to start data taking in early 2020s. Background Observations of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soudan 1
Soudan 1 was a particle detector located in the Soudan Mine in Northern Minnesota, United States, which operated for a year in 1981–82. It was a 30-ton tracking calorimeter whose primary purpose was to search for proton decay. It set a lower limit on the lifetime of the proton of 1.6×1030 years as well as upper limits on the density of magnetic monopoles. It also served as a prototype for the following Soudan 2 and MINOS experiments. Design and operation Soudan 1 was installed 590 meters below the surface and brought into routine operation in August 1981 by high-energy physics research groups from the University of Minnesota and Argonne National Laboratory. The detector was a 3×3×2m3 block of iron oxide-loaded concrete instrumented with 3456 gas proportional tubes. It was surrounded on five sides by a veto shield of solid scintillator, which was completed in October 1981. This allowed events which might otherwise have looked like proton decay, but were actually c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Minnesota
The University of Minnesota, formally the University of Minnesota, Twin Cities, (UMN Twin Cities, the U of M, or Minnesota) is a public land-grant research university in the Twin Cities of Minneapolis and Saint Paul, Minnesota, United States. The Twin Cities campus comprises locations in Minneapolis and Falcon Heights, a suburb of St. Paul, approximately apart. The Twin Cities campus is the oldest and largest in the University of Minnesota system and has the ninth-largest main campus student body in the United States, with 52,376 students at the start of the 2021–22 academic year. It is the flagship institution of the University of Minnesota System, and is organized into 19 colleges, schools, and other major academic units. The Minnesota Territorial Legislature drafted a charter for the U of M as a territorial university in 1851, seven years before Minnesota became a state. Today, the university is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |