|
Sooglossoidea
Sooglossoidea is a superfamily of frogs. It contains only two highly divergent families consisting of three genera with two species each, one family being found in southwestern India and the other in the Seychelles. Taxonomy The Sooglossoidea are an ancient division of the Neobatrachia; phylogenetic evidence indicates that they diverged from the rest of the Neobatrachia during the Early Cretaceous, about 125 million years ago, after colonizing Insular India from Africa. One family, the Nasikabatrachidae, remained in India; the other, Sooglossidae, was isolated on the Seychelles Microcontinent (which later turned into an island chain) after it split from India. Both families are thought to have diverged around the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary. Their exact phylogenetic relationships are disputed; previous studies found them to be the second-most basal member of the Neobatrachia, being sister to all other members of the group aside from Heleophrynidae, but more recent stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sooglossoidea
Sooglossoidea is a superfamily of frogs. It contains only two highly divergent families consisting of three genera with two species each, one family being found in southwestern India and the other in the Seychelles. Taxonomy The Sooglossoidea are an ancient division of the Neobatrachia; phylogenetic evidence indicates that they diverged from the rest of the Neobatrachia during the Early Cretaceous, about 125 million years ago, after colonizing Insular India from Africa. One family, the Nasikabatrachidae, remained in India; the other, Sooglossidae, was isolated on the Seychelles Microcontinent (which later turned into an island chain) after it split from India. Both families are thought to have diverged around the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary. Their exact phylogenetic relationships are disputed; previous studies found them to be the second-most basal member of the Neobatrachia, being sister to all other members of the group aside from Heleophrynidae, but more recent stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neobatrachia
The Neobatrachia (New Latin ''neo-'' ("new") + ''batrachia'' ("frogs")) are a suborder of the Anura, the order of frogs and toads. This suborder is the most advanced and apomorphic of the three anuran suborders alive today, hence its name, which literally means "new frogs" (from the hellenic words ''neo'', meaning "new" and ''batrachia'', meaning "frogs"). It is also by far the largest of the three; its more than 5,000 different species make up over 96% of all living anurans. The differentiation between Archaeobatrachia, Mesobatrachia, and Neobatrachia is based primarily on anatomic differences, especially the skeletal structure, as well as several visible characteristics and behaviors. Systematics Separating the Anura into the Archaeo-, Meso- and Neobatrachia is somewhat controversial; as more research is done and more knowledge is gained, it is becoming even less clear, because many characteristics used for this differentiation apply to more than one group. Neobatrachi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely Carnivore, carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order (biology), order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-frog" ''Triadobatrachus'' is known from the Early Triassic of Madagascar, but molecular clock, molecular clock dating suggests their split from other amphibians may extend further back to the Permian, 265 Myr, million years ago. Frogs are widely distributed, ranging from the tropics to subarctic regions, but the greatest concentration of species diversity is in tropical rainforest. Frogs account for around 88% of extant amphibian species. They are also one of the five most diverse vertebrate orders. Warty frog species tend to be called toads, but the distinction between frogs and toads is informal, not from Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy or evolutionary history. An adult frog has a stout body, protruding eyes, anteriorly-attached tongue, limb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasikabatrachus
''Nasikabatrachus'' is a genus of frogs. It is presently treated as the only genus in the family Nasikabatrachidae, though previously it was included in the family Sooglossidae. Two species are recognized, ''Nasikabatrachus bhupathi'' and ''Nasikabatrachus sahyadrensis'', both endemic to southwestern India. Both Nasikabatrachidae and Sooglossidae are thought to be the only extant families of the superfamily Sooglossoidea. With its closest relatives in the Seychelles, ''Nasikabatrachus'' is thought to have evolved separately since the end of the Cretaceous. Its discovery added to the evidence that Madagascar and the Seychelles separated from the India India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...n landmass sometime well after the breakup of Gondwana had started. Reproduction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranoidea
The Ranoidea are a superfamily of frogs in the order Anura. Members of this superfamily are characterised by having the pectoral girdle fused into a single complex unit, having no ribs, and using an axillary grip during amplexus. The larvae have a single spiracle on the left side and complex mouthparts, or in some species, undergo direct development. The taxonomy of these families has been under heavy debate for many years. In recent studies, molecular data has been used to better identify the phylogentic relationships of these frogs, rearranging and introducing new subfamilies to better distinguish between large groups of frogs (Glaw, Vences, 2001). This superfamily contains seventeen different families, each containing at least 2 species (some contain over 300 different species). (See figure 1). Families The families described in this section are based on and Ranixalidae The family of Ranixalidae (leaping frogs) has one genus containing 10 different species. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghost Frog
Heleophrynidae is a family of frogs, commonly known as ghost frogs. They are thought to be the most basal group in the Neobatrachia. The family consists of two genera, ''Heleophryne'' and ''Hadromophryne'', with seven species. Ghost frogs live in swift-moving mountain streams in South Africa. The common name of "ghost frogs" may have been coined because of their occurrence in Skeleton Gorge. Taxonomy The ghost frogs were formerly thought to be closely related to the Sooglossidae of the Seychelles (which are now thought to be a sister group to Ranoidea), or to the Australian Myobatrachidae, which are now thought to be a sister group to Hyloidea. In contrast, more recent taxonomic studies place them as being the most basal extant members of the Neobatrachia and having no close relatives, having diverged from the rest of the Neobatrachia during the Early Cretaceous, about 140 million years ago. Family Heleophrynidae * Genus ''Hadromophryne'' Van Dijk, 2008 ** Natal ghost frog, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sister Group
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree. Definition The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram: Taxon A and taxon B are sister groups to each other. Taxa A and B, together with any other extant or extinct descendants of their most recent common ancestor (MRCA), form a monophyletic group, the clade AB. Clade AB and taxon C are also sister groups. Taxa A, B, and C, together with all other descendants of their MRCA form the clade ABC. The whole clade ABC is itself a subtree of a larger tree which offers yet more sister group relationships, both among the leaves and among larger, more deeply rooted clades. The tree structure shown connects through its root to the rest of the universal tree of life. In cladistic standards, taxa A, B, and C may represent specimens, species, genera, or any other taxonomic units. If A and B are at the same taxonomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous–Paleogene Boundary
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) boundary, formerly known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary (K–T) boundary, is a geological signature, usually a thin band of rock containing much more iridium than other bands. The K–Pg boundary marks the end of the Cretaceous Period, the last period of the Mesozoic Era, and marks the beginning of the Paleogene Period, the first period of the Cenozoic Era. Its age is usually estimated at around 66 million years, with radiometric dating yielding a more precise age of 66.043 ± 0.011 Ma. The K–Pg boundary is associated with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, a mass extinction which destroyed a majority of the world's Mesozoic species, including all dinosaurs except for birds. Strong evidence exists that the extinction coincided with a large meteorite impact at the Chicxulub crater and the generally accepted scientific theory is that this impact triggered the extinction event. The word "Cretaceous" is derived from the Latin "creta" (ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
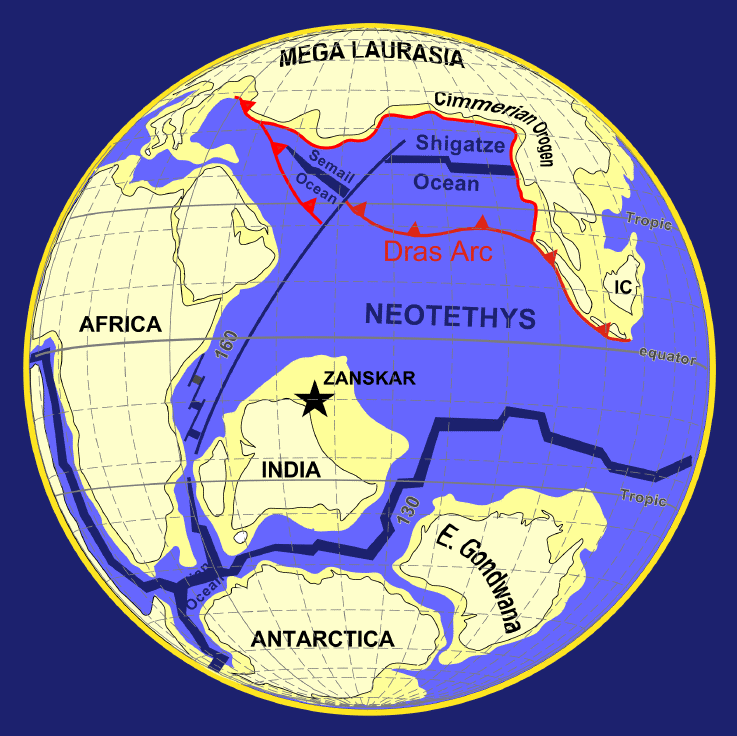
Seychelles Microcontinent
The Seychelles Microcontinent is a microcontinent underlying Seychelles in the western Indian Ocean made of Late Precambrian rock. The granite outcrops of the Seychelles Islands in the central Indian Ocean were amongst the earliest examples cited by Alfred Wegener as evidence for his continental drift theory. Ridge–plume interactions have been responsible for separating a thinned continental sliver from a large continent (i.e. India). The granites of the Seychelles Microcontinent were emplaced 750 Ma, during the late Precambrian. Thermally-induced rifting in the Somali Basin and transform rifting along the Davie Fracture Zone began in the late Permian, 225 million years ago. The Gondwana supercontinent began to break up in the Middle Jurassic, about 167 million years ago. At that time, East Gondwana, comprising Antarctica, Madagascar, India, and Australia, began to separate from Africa. East Gondwana then began to separate about 115–120 million years ago when India began to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area and 20% of its land area.Sayre, April Pulley (1999), ''Africa'', Twenty-First Century Books. . With billion people as of , it accounts for about of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest amongst all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Despite a wide range of natural resources, Africa is the least wealthy continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, behind Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, tribalism, colonialism, the Cold War, neocolonialism, lack of democracy, and corruption. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and the large and young population make Afr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insular India
The term Insular India refers to the isolated landmass which became the Indian subcontinent. Across the latter stages of the Cretaceous and most of the Paleocene, following the breakup of Gondwana, the Indian subcontinent remained an isolated landmass as the Indian Plate drifted across the Tethys Ocean, forming the Indian Ocean. The process of India's separation from Madagascar first began 88 million years ago, but complete isolation only occurred towards the end of the Maastrichtian, a process that has been suggested to be the creation of the Deccan Traps. Soon after, the land mass moved northward rather quickly, until contact with Asia was established 55 million years ago. Even then, both landmasses did not become fully united until around 35 million years ago, and periods of isolation occurred as recently as 24 million years ago. Thus, for a period of 53 million years India has retained a degree of isolation, 11 of which it has been a complete island c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous ( geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma. Geology Proposals for the exact age of the Barremian-Aptian boundary ranged from 126 to 117 Ma until recently (as of 2019), but based on drillholes in Svalbard the defining early Aptian Oceanic Anoxic Event 1a (OAE1a) was carbon isotope dated to 123.1±0.3 Ma, limiting the possible range for the boundary to c. 122–121 Ma. There is a possible link between this anoxic event and a series of Early Cretaceous large igneous provinces (LIP). The Ontong Java-Manihiki-Hikurangi large igneous province, emplaced in the South Pacific at c. 120 Ma, is by far the largest LIP in Earth's history. The Ontong Java Plateau today covers an area of 1,860,000 km2. In the Indian Ocean another LIP began to form at c. 120 Ma, the Kerguelen P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Ranomafana.jpg)

.png)