|
Son Of Sevenless
In cell signalling, ''Son of Sevenless'' (''SOS'') refers to a set of genes encoding guanine nucleotide exchange factors that act on the Ras subfamily of small GTPases. History and name The gene was so named because the Sos protein that it encoded was found to operate downstream of the '' sevenless'' gene in ''Drosophila melanogaster'' in a Ras/MAP kinase pathway. When ''sevenless'' is mutated or otherwise dysfunctional during development of the fly's ultraviolet light-sensitive compound eye, the seventh, central photoreceptor (R7) of each ommatidium fails to form. Similarly, the mammalian orthologues of Sos, SOS1 and SOS2, function downstream of many growth factor and adhesion receptors. Function Ras-GTPases act as molecular switches that bind to downstream effectors, such as the protein kinase c-Raf, and localise them to the membrane, resulting in their activation. Ras-GTPases are considered inactive when bound to guanosine diphosphate (GDP), and active when bound to guanos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SOS1
Son of sevenless homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SOS1'' gene. Function SOS1 is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) which interacts with RAS proteins to phosphorylate GDP into GTP, or from an inactive state to an active state to signal cell proliferation. RAS genes (e.g., MIM 190020) encode membrane-bound guanine nucleotide-binding proteins that function in the transduction of signals that control cell growth and differentiation. Binding of GTP activates RAS proteins, and subsequent hydrolysis of the bound GTP to GDP and phosphate inactivates signaling by these proteins. GTP binding can be catalyzed by guanine nucleotide exchange factors for RAS, and GTP hydrolysis can be accelerated by GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs). The first exchange factor to be identified for RAS was the S. cerevisiae Cdc25 gene product. Genetic analysis indicated that CDC25 is essential for activation of RAS proteins. In ''Drosophila'', the protein encoded by the 'son of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanosine Diphosphate
Guanosine diphosphate, abbreviated GDP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside guanosine. GDP consists of a pyrophosphate group, a pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase guanine. GDP is the product of GTP dephosphorylation by GTPases, e.g., the G-proteins that are involved in signal transduction. GDP is converted into GTP with the help of pyruvate kinase and phosphoenolpyruvate. See also * DNA *Guanosine triphosphate *Nucleoside *Nucleotide *Oligonucleotide *RNA Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohyd ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Guanosine phosphate2 Nucleotides Phosphate esters Purines Pyrophosphates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Transduction Pathways
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellular response. Proteins responsible for detecting stimuli are generally termed receptors, although in some cases the term sensor is used. The changes elicited by ligand binding (or signal sensing) in a receptor give rise to a biochemical cascade, which is a chain of biochemical events known as a signaling pathway. When signaling pathways interact with one another they form networks, which allow cellular responses to be coordinated, often by combinatorial signaling events. At the molecular level, such responses include changes in the transcription or translation of genes, and post-translational and conformational changes in proteins, as well as changes in their location. These molecular events are the basic mechanisms controlling cell gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution. ::"The chromosomal or genomic location of a gene or any other genetic element is called a locus (plural: loci) and alternative DNA sequences at a locus are called alleles." The simplest alleles are single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP). but they can also be insertions and deletions of up to several thousand base pairs. Popular definitions of 'allele' typically refer only to different alleles within genes. For example, the ABO blood grouping is controlled by the ABO gene, which has six common alleles (variants). In population genetics, nearly every living human's phenotype for the ABO gene is some combination of just these six alleles. Most alleles observed result in little or no change in the function of the gene product it codes for. Howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase
A mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK or MAP kinase) is a type of protein kinase that is specific to the amino acids serine and threonine (i.e., a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase). MAPKs are involved in directing cellular responses to a diverse array of stimuli, such as mitogens, osmotic stress, heat shock and proinflammatory cytokines. They regulate cell functions including proliferation, gene expression, differentiation, mitosis, cell survival, and apoptosis. MAP kinases are found in eukaryotes only, but they are fairly diverse and encountered in all animals, fungi and plants, and even in an array of unicellular eukaryotes. MAPKs belong to the CMGC (CDK/MAPK/GSK3/CLK) kinase group. The closest relatives of MAPKs are the cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). Discovery The first mitogen-activated protein kinase to be discovered was ERK1 ( MAPK3) in mammals. Since ERK1 and its close relative ERK2 ( MAPK1) are both involved in growth factor signaling, the family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PTPN11
Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 11 (PTPN11) also known as protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1D (PTP-1D), Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase-2 (SHP-2), or protein-tyrosine phosphatase 2C (PTP-2C) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PTPN11'' gene. PTPN11 is a protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) Shp2. PTPN11 is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. This PTP contains two tandem Src homology-2 domains, which function as phospho-tyrosine binding domains and mediate the interaction of this PTP with its substrates. This PTP is widely expressed in most tissues and plays a regulatory role in various cell signaling events that are important for a diversity of cell functions, such as mitogenic activation, metabolic control, transcription regulation, and cell migrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KRAS
''KRAS'' ( Kirsten rat sarcoma virus) is a gene that provides instructions for making a protein called K-Ras, a part of the RAS/MAPK pathway. The protein relays signals from outside the cell to the cell's nucleus. These signals instruct the cell to grow and divide ( proliferate) or to mature and take on specialized functions ( differentiate). It is called ''KRAS'' because it was first identified as a viral oncogene in the Kirsten RAt Sarcoma virus. The oncogene identified was derived from a cellular genome, so , when found in a cellular genome, is called a proto-oncogene. The K-Ras protein is a GTPase, a class of enzymes which convert the nucleotide guanosine triphosphate (GTP) into guanosine diphosphate (GDP). In this way the K-Ras protein acts like a switch that is turned on and off by the GTP and GDP molecules. To transmit signals, it must be turned on by attaching (binding) to a molecule of GTP. The K-Ras protein is turned off (inactivated) when it converts the GTP to G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
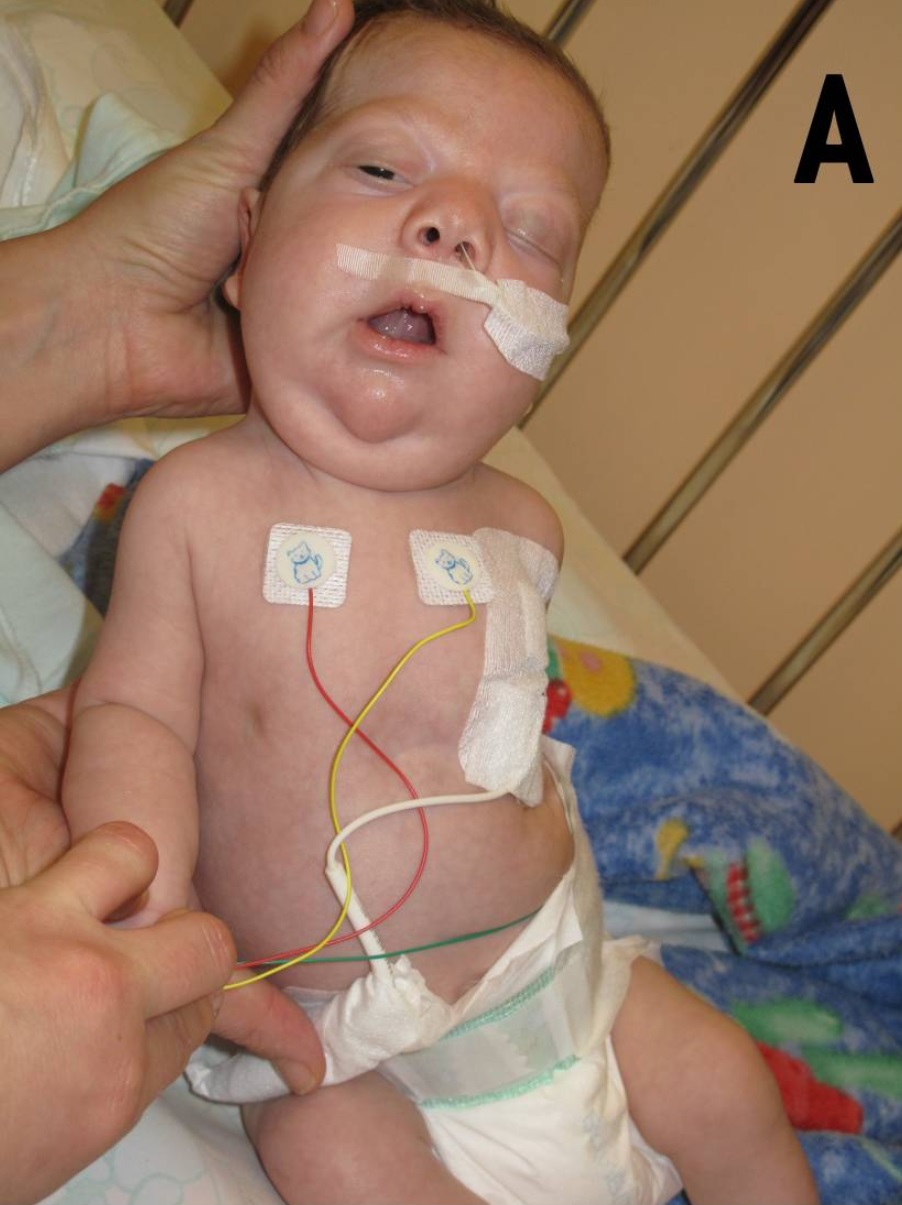
Noonan Syndrome
Noonan syndrome (NS) is a genetic disorder that may present with mildly unusual facial features, short height, congenital heart disease, bleeding problems, and skeletal malformations. Facial features include widely spaced eyes, light-colored eyes, low-set ears, a short neck, and a small lower jaw. Heart problems may include pulmonary valve stenosis. The breast bone may either protrude or be sunken, while the spine may be abnormally curved. Intelligence in the syndrome is often normal. Complications of NS can include leukemia. A number of genetic mutations can result in Noonan syndrome. The condition may be inherited from a person's parents as an autosomal dominant condition or occur as a new mutation. Noonan syndrome is a type of RASopathy, the underlying mechanism for which involves overactivation within the RAS/MAPK cell signaling pathway. The diagnosis may be suspected based on symptoms, medical imaging, and blood tests. Confirmation may be achieved with genetic tes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RasGAP
RAS p21 protein activator 1 or RasGAP (Ras GTPase activating protein), also known as RASA1, is a 120- kDa cytosolic human protein that provides two principal activities: * Inactivation of Ras from its active GTP-bound form to its inactive GDP-bound form by enhancing the endogenous GTPase activity of Ras, via its C-terminal GAP domain * Mitogenic signal transmission towards downstream interacting partners through its N-terminal SH2-SH3-SH2 domains The protein encoded by this gene is located in the cytoplasm and is part of the GAP1 family of GTPase-activating proteins. The gene product stimulates the GTPase activity of normal RAS p21 but not its oncogenic counterpart. Acting as a suppressor of RAS function, the protein enhances the weak intrinsic GTPase activity of RAS proteins resulting in the inactive GDP-bound form of RAS, thereby allowing control of cellular proliferation and differentiation. Mutations leading to changes in the binding sites of either protein are associated wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells ( intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments. In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is surrounded by the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. The cytosol is thus a liquid matrix around the organelles. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others take place within organelles. The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and propert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanosine Triphosphate
Guanosine-5'-triphosphate (GTP) is a purine nucleoside triphosphate. It is one of the building blocks needed for the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process. Its structure is similar to that of the guanosine nucleoside, the only difference being that nucleotides like GTP have phosphates on their ribose sugar. GTP has the guanine nucleobase attached to the 1' carbon of the ribose and it has the triphosphate moiety attached to ribose's 5' carbon. It also has the role of a source of energy or an activator of substrates in metabolic reactions, like that of ATP, but more specific. It is used as a source of energy for protein synthesis and gluconeogenesis. GTP is essential to signal transduction, in particular with G-proteins, in second-messenger mechanisms where it is converted to guanosine diphosphate (GDP) through the action of GTPases. Uses Energy transfer GTP is involved in energy transfer within the cell. For instance, a GTP molecule is generated by one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-Raf
RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase, also known as proto-oncogene c-RAF or simply c-Raf or even Raf-1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''RAF1'' gene. The c-Raf protein is part of the ERK1/2 pathway as a MAP kinase (MAP3K) that functions downstream of the Ras subfamily of membrane associated GTPases. C-Raf is a member of the Raf kinase family of serine/threonine-specific protein kinases, from the TKL (Tyrosine-kinase-like) group of kinases. Discovery The first Raf gene, v-Raf was found in 1983. It was isolated from the murine retrovirus bearing the number 3611. It was soon demonstrated to be capable to transform rodent fibroblasts to cancerous cell lines, so this gene was given the name Virus-induced Rapidly Accelerated Fibrosarcoma (V-RAF). A year later, another transforming gene was found in the avian retrovirus MH2, named v-Mil - that turned out to be highly similar to v-Raf. Researchers were able to demonstrate that these genes encode enzymes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |