|
Solar Eclipse Of September 2, 1997
A partial solar eclipse occurred on Tuesday, September 2, 1997. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. Images Related eclipses Eclipses of 1997 * A total solar eclipse on March 9. * A partial lunar eclipse on March 24. * A partial solar eclipse on September 2. * A total lunar eclipse on September 16. Solar eclipses 1997–2000 Metonic series References External links NASA graphics Photos: APOD Astronomy Picture of the Day (APOD) is a website provided by NASA and Michigan Technological University (MTU). According to the website, "Each day a different image or photograph of our universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written ... 9/3/1997, A Partial Eclipse in Southern Skies, partial eclipse from Kingscote, Kangaroo Islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of the Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six months, during the new moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to the plane of the Earth's orbit. In a total eclipse, the disk of the Sun is fully obscured by the Moon. In partial and annular eclipses, only part of the Sun is obscured. Unlike a lunar eclipse, which may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth, a solar eclipse can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world. As such, although total solar eclipses occur somewhere on Earth every 18 months on average, they recur at any given place only once every 360 to 410 years. If the Moon were in a perfectly circular orbit and in the same orbital plane as Earth, there would be total solar eclipses once a month, at every new moon. Instead, because the Moon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of Australia). The Moon is a planetary-mass object with a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under the geophysical definitions of the term and larger than all known dwarf planets of the Solar System. It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's at , with Jupiter's moon Io being the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density. The Moon orbits Earth at an average distance of , or about 30 times Earth's diameter. Its gravitational influence is the main driver of Earth's tides and very slowly lengthens Earth's day. The Moon's orbit around Earth has a sidereal period of 27.3 days. During each synodic period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More solar e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse Of March 9, 1997
A total solar eclipse occurred on Sunday, March 9, 1997. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible in eastern tip of Kazakhstan, northern tip of Xinjiang and Northeastern China, Northern Mongolia and Russia. Unusual gravity variations This solar eclipse is somewhat special in the sense that some unexplained gravity anomalies of about 7 \times 10−8 m/s2 during the solar eclipse were observed. Attempts (e.g., Van Flandern–Yang hypothesis) to explain these anomalies have not been able to reach a definite conclusion. Images Related eclipses Eclipses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
March 1997 Lunar Eclipse
A partial lunar eclipse took place on Monday, March 24, 1997, the first of two lunar eclipses in 1997. This partial lunar eclipse was nearly total; however, it occurred 3 days after the lunar apogee, so the umbral shadow is smaller. This was the 29th member of Lunar Saros 132, and the last of the first set of partial eclipses. The next event was the April 2015 lunar eclipse, which was the first of 12 total eclipses. This eclipse was the third of an ''almost tetrad'' (that occurred when there were 4 consecutive lunar eclipses that had an umbral eclipse magnitude of 0.9 or greater). The others were 04 Apr 1996 (T), 27 Sep 1996 (T) and 16 Sep 1997 (T). Visibility This eclipse was completely visible from North and South America, and visible setting over Western Europe and Africa. Related eclipses Eclipses of 1997 * A total solar eclipse on March 9. * A partial lunar eclipse on March 24. * A partial solar eclipse on September 2. * A total lunar eclipse on September 16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
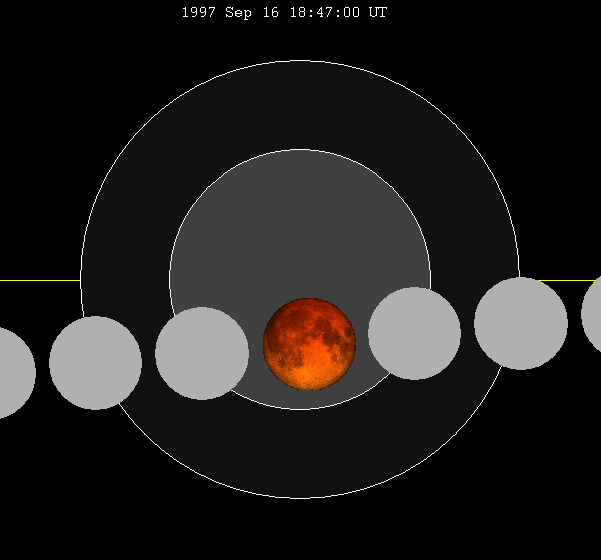
September 1997 Lunar Eclipse
A total lunar eclipse took place at the Moon's descending node of the orbit on Tuesday, September 16, 1997, the second of two lunar eclipses in 1997. A shallow total eclipse saw the Moon in relative darkness for 1 hour, 1 minute and 30.8 seconds. The Moon was 19.094% of its diameter into the Earth's umbral shadow, and should have been significantly darkened. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 16 minutes and 28.2 seconds in total. The penumbral eclipse lasted for 5 hours, 8 minutes and 20.1 seconds. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 16 minutes and 28.2 seconds. The total eclipse lasted for 1 hour, 1 minute and 30.8 seconds. Maximum eclipse was at 18:46:39.1 UTC. The moon's apparent diameter was extremely large (6.3% larger than average) because occurred only 3 hours and 21 minutes past perigee. The Moon was only 356,986 km (221,820 mi) of the Earth at greatest eclipse. This eclipse was the fourth and last of an ''almost tetrad'' (that occurred when there were 4 consecuti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APOD
Astronomy Picture of the Day (APOD) is a website provided by NASA and Michigan Technological University (MTU). According to the website, "Each day a different image or photograph of our universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer." The photograph does not necessarily correspond to a celestial event on the exact day that it is displayed, and images are sometimes repeated. However, the pictures and descriptions often relate to current events in astronomy and space exploration. The text has several hyperlinks to more pictures and websites for more information. The images are either visible spectrum photographs, images taken at non-visible wavelengths and displayed in false color, video footage, animations, artist's conceptions, or micrographs that relate to space or cosmology. Past images are stored in the APOD Archive, with the first image appearing on June 16, 1995. This initiative has received support from NASA, the National Science Fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Solar Eclipses
Partial may refer to: Mathematics *Partial derivative, derivative with respect to one of several variables of a function, with the other variables held constant ** ∂, a symbol that can denote a partial derivative, sometimes pronounced "partial dee" **Partial differential equation, a differential equation that contains unknown multivariable functions and their partial derivatives Other uses *Partial application, in computer science the process of fixing a number of arguments to a function, producing another function *Partial charge or net atomic charge, in chemistry a charge value that is not an integer or whole number *Partial fingerprint, impression of human fingers used in criminology or forensic science *Partial seizure or focal seizure, a seizure that initially affects only one hemisphere of the brain * Partial or Part score, in contract bridge a trick score less than 100, as well as other meanings * Partial or Partial wave, one sound wave of which a complex tone is composed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1997 In Science
The year 1997 in science and technology involved many significant events, listed below. Astronomy and space exploration * January 17 – Explosion of a Delta II rocket carrying a military GPS payload shortly after liftoff from Cape Canaveral. * February 13 – Tune-up and repair work on the Hubble Space Telescope is started by astronauts from the Space Shuttle ''Discovery''. * February 27 – GRB 970228, a highly luminous flash of gamma rays, strikes the Earth for 80 seconds, providing early evidence that gamma-ray bursts occur well beyond the Milky Way. * March 8 – Complete solar eclipse. * March 24 – Partial lunar eclipse. * July 4 – ''Mars Pathfinder'' lands on the surface of Mars. * August 25 – Launch of Explorer 71 of the Explorer program of spacecraft. * September 2 – Partial solar eclipse. * September – Total lunar eclipse. * October 15 – Launch of 10-year ''Cassini–Huygens'' spacecraft to Saturn. * October 30 – First successful test flight of the ESA's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |