|
Social Impact Theory
Social impact theory was created by Bibb Latané in 1981 and consists of four basic rules which consider how individuals can be "sources or targets of social influence". Social impact is the result of social forces including the strength of the source of impact, the immediacy of the event, and the number of sources exerting the impact. The more targets of impact that exist, the less impact each individual target has. Original research According to psychologist Bibb Latané, social impact is defined as any influence on individual feelings, thoughts or behavior that is created from the real, implied or imagined presence or actions of others. The application of social impact varies from diffusion of responsibility to social loafing, stage fright or persuasive communication. In 1981, Latané developed the social impact theory using three key variables: * Strength (S) is a net of all individual factors that make a person influential. It covers stable, trans-situational, intrapersonal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bibb Latané
Bibb Latané (; born July 19, 1937) is an American social psychologist. He worked with John M. Darley on bystander intervention in emergencies. He has also published many articles on social attraction in animals, social loafing in groups, and the spread of social influence in populations. Biography Latané received his B.A. from Yale in 1958 and his Ph.D. (under the mentorship of Stanley Schachter) from the University of Minnesota in 1963. He taught at Columbia University, the Ohio State University, Florida Atlantic University, and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. In the 1980s, he was director of UNC's Institute for Research in Social Science (now the Odum Institute). He is currently director of the Center for Human Science in Chapel Hill, NC, which he founded. Latané's work with Darley involved a series of experiments that staged emergencies so that the social psychologists could observe how the presence of inactive bystanders affect the subjects' helping beh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffusion Of Responsibility
Diffusion of responsibility is a sociopsychological phenomenon whereby a person is less likely to take responsibility for action or inaction when other bystanders or witnesses are present. Considered a form of attribution, the individual assumes that others either are responsible for taking action or have already done so.Ciccarelli, S. K. & White, J. N. (2009). ''Psychology'' (2nd ed.) New Jersey: Pearson Education. . The diffusion of responsibility refers to the decreased responsibility of action each member of a group feels when they are part of a group. For example, in emergency situations, individuals feel less responsibility to respond or call for help if they know that there are others also watching the situation - if they know they are a part of the group of witnesses. In other group settings (in which a group is appointed to complete a task or reach a certain goal), the diffusion of responsibility manifests itself as the decreased responsibility each member feels to con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
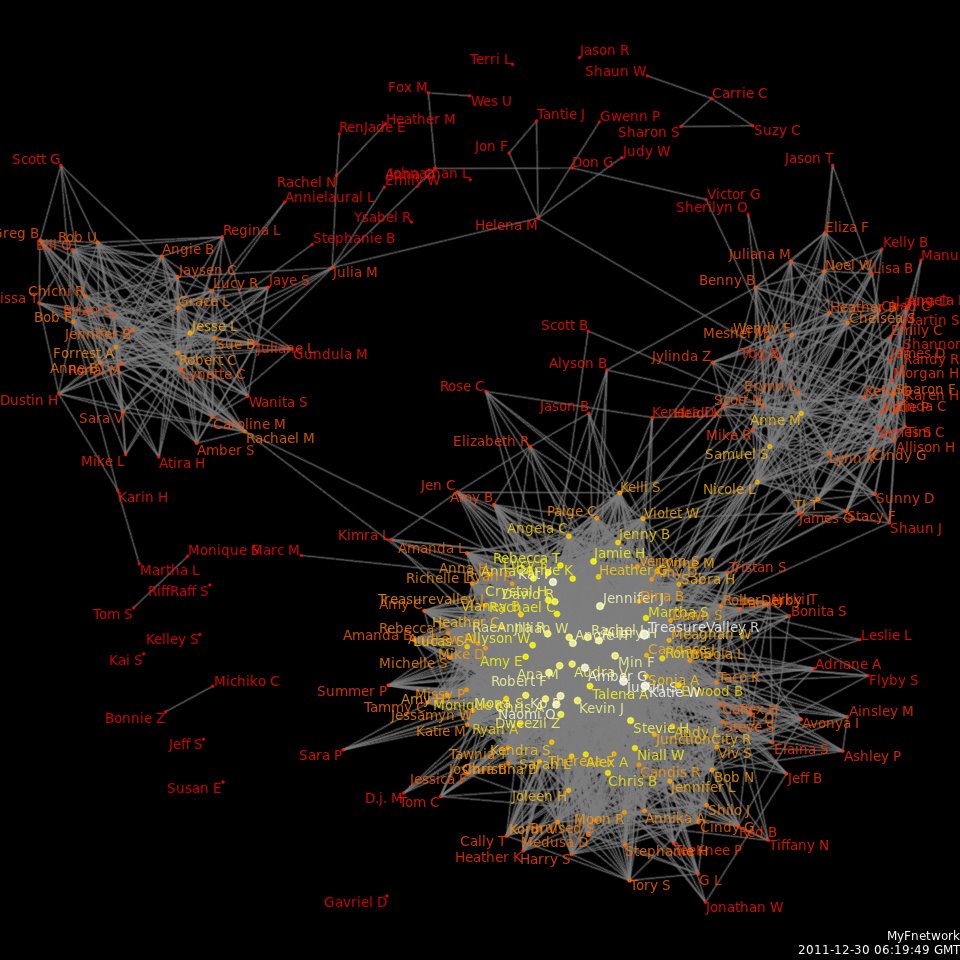
Social Network Analysis
Social network analysis (SNA) is the process of investigating social structures through the use of networks and graph theory. It characterizes networked structures in terms of ''nodes'' (individual actors, people, or things within the network) and the ''ties'', ''edges'', or ''links'' (relationships or interactions) that connect them. Examples of social structures commonly visualized through social network analysis include social media networks, memes spread, information circulation, friendship and acquaintance networks, business networks, knowledge networks, difficult working relationships, social networks, collaboration graphs, kinship, disease transmission, and sexual relationships. These networks are often visualized through ''sociograms'' in which nodes are represented as points and ties are represented as lines. These visualizations provide a means of qualitatively assessing networks by varying the visual representation of their nodes and edges to reflect attributes of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Psychologist
''American Psychologist'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal published by the American Psychological Association. The journal publishes articles of broad interest to psychologists, including empirical reports and scholarly reviews covering science, practice, education, and policy, and occasionally publishes special issues on relevant topics in the field of psychology. The editor-in-chief is Harris Cooper (Duke University). The journal has implemented the Transparency and Openness Promotion (TOP) Guidelines that provide structure to research planning and reporting and aim to make research more transparent, accessible, and reproducible. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 16.358. See also * ''Developmental Psychology'' *''Journal of Abnormal Psychology'' *''Journal of Experimental Psychology The ''Journal of Experimental Psychology'' was a bimonthly peer-reviewed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Personality And Social Psychology
The ''Journal of Personality and Social Psychology'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Psychological Association that was established in 1965. It covers the fields of social and personality psychology. The editors-in-chief are Shinobu Kitayama (University of Michigan; ''Attitudes and Social Cognition Section''), Colin Wayne Leach (Barnard College; ''Interpersonal Relations and Group Processes Section''), and Richard E. Lucas (Michigan State University; ''Personality Processes and Individual Differences Section''). The journal has implemented the Transparency and Openness Promotion (TOP) Guidelines. The TOP Guidelines provide structure to research planning and reporting and aim to make research more transparent, accessible, and reproducible. Contents The journal's focus is on empirical research reports; however, specialized theoretical, methodological, and review papers are also published. For example, the journal's most highly cited paper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basic And Applied Social Psychology
''Basic and Applied Social Psychology'' (''BASP'') is a bi-monthly psychology Scientific journal, journal published by Taylor & Francis. The journal emphasizes the publication of empirical research articles but also publishes literature reviews, criticism, and methodological or theoretical statements spanning the entire range of Social psychology, social psychological issues. In 2015, the journal banned p-values (and related inferential statistics such as confidence intervals) as evidence in papers accepted by the journal, replacing Statistical hypothesis testing, hypothesis testing with "strong descriptive statistics, including effect sizes" on the grounds that "the state of the art [for hypothesis testing] remains uncertain". References External links Official webpage English-language journals Academic journals established in 1980 Social psychology journals Taylor & Francis academic journals Bimonthly journals {{social-psych-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Influence
Social influence comprises the ways in which individuals adjust their behavior to meet the demands of a social environment. It takes many forms and can be seen in conformity, socialization, peer pressure, obedience (human behavior), obedience, leadership, persuasion, sales, and marketing. Typically social influence results from a specific action, command, or request, but people also alter their attitudes and behaviors in response to what they perceive others might do or think. In 1958, Harvard psychologist Herbert Kelman identified three broad varieties of social influence. #Compliance (psychology), Compliance is when people appear to agree with others but actually keep their dissenting opinions private. #Identification (psychology), Identification is when people are influenced by someone who is liked and respected, such as a famous celebrity. #Internalisation (sociology), Internalization is when people accept a belief or behavior and agree both publicly and privately. Morton Deuts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sociological Theories
Sociology is a social science that focuses on society, human social behavior, patterns of social relationships, social interaction, and aspects of culture associated with everyday life. It uses various methods of empirical investigation and critical analysis to develop a body of knowledge about social order and social change. While some sociologists conduct research that may be applied directly to social policy and welfare, others focus primarily on refining the theoretical understanding of social processes and phenomenological method. Subject matter can range from micro-level analyses of society (i.e. of individual interaction and agency) to macro-level analyses (i.e. of social systems and social structure). Traditional focuses of sociology include social stratification, social class, social mobility, religion, secularization, law, sexuality, gender, and deviance. As all spheres of human activity are affected by the interplay between social structure and individual agenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |