|
Social Impact
Social impact may refer to: * Social impact assessment * Social impact theory * Social influence Social influence comprises the ways in which individuals adjust their behavior to meet the demands of a social environment. It takes many forms and can be seen in conformity, socialization, peer pressure, obedience, leadership, persuasion, s ... {{disambiguation Social science disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
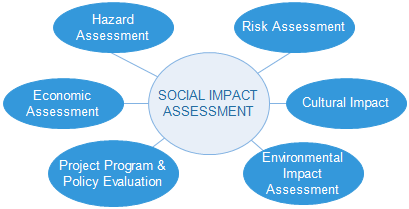
Social Impact Assessment
Social impact assessment (SIA) is a methodology to review the social effects of infrastructure projects and other development interventions. Although SIA is usually applied to planned interventions, the same techniques can be used to evaluate the social impact of unplanned events, for example, disasters, demographic change, and epidemics. SIA is important in applied anthropology, as its main goal is to be able to deliver positive social outcomes and eliminate any possible negative or long term effects. Overview The origins of SIA largely derives from the environmental impact assessment (EIA) model, which first emerged in the 1970s in the U.S. In the United States under the National Environmental Policy Act. Social impact assessments are federally mandated and performed in conjunction with environmental impact assessments. SIA has been incorporated into the formal planning and approval processes in several countries, in order to categorize and assess how major developments m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Impact Theory
Social impact theory was created by Bibb Latané in 1981 and consists of four basic rules which consider how individuals can be "sources or targets of social influence". Social impact is the result of social forces including the strength of the source of impact, the immediacy of the event, and the number of sources exerting the impact. The more targets of impact that exist, the less impact each individual target has. Original research According to psychologist Bibb Latané, social impact is defined as any influence on individual feelings, thoughts or behavior that is created from the real, implied or imagined presence or actions of others. The application of social impact varies from diffusion of responsibility to social loafing, stage fright or persuasive communication. In 1981, Latané developed the social impact theory using three key variables: * Strength (S) is a net of all individual factors that make a person influential. It covers stable, trans-situational, intrapersonal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Influence
Social influence comprises the ways in which individuals adjust their behavior to meet the demands of a social environment. It takes many forms and can be seen in conformity, socialization, peer pressure, obedience, leadership, persuasion, sales, and marketing. Typically social influence results from a specific action, command, or request, but people also alter their attitudes and behaviors in response to what they perceive others might do or think. In 1958, Harvard psychologist Herbert Kelman identified three broad varieties of social influence. #Compliance is when people appear to agree with others but actually keep their dissenting opinions private. # Identification is when people are influenced by someone who is liked and respected, such as a famous celebrity. # Internalization is when people accept a belief or behavior and agree both publicly and privately. Morton Deutsch and Harold Gerard described two psychological needs that lead humans to conform to the expectat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |