|
Social Balance Theory
Social balance theory is a class of theories about balance or imbalance of sentiment relation in dyadic or triadic relations with social network theory. Sentiments can result in the emergence of two groups. Disliking exists between the two subgroups within liking agents. Development of the theory This theory evolved over time to produce models more closely resembling real-world social networks. It uses a balance index to measure the effect of local balance on that of a global level and also on a more intimate level, like in interpersonal relationships. Dorwin Cartwright and Frank Harary introduced ''clustering'' to account for multiple social cliques. Davis introduced '' hierarchical clustering'' to account for asymmetric relations. Recent research indicated that hubness in positive and negative subnetworks increases the balance of the signed network. See also * Balance theory * Sociogram A sociogram is a graphic representation of social links that a person has. It is a gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyad (sociology)
In sociology, a dyad is a group of two people, the smallest possible social group. As an adjective, "dyadic" describes their interaction.Macionis, John J., and Linda Marie Gerber. Sociology. 7th ed. Toronto: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2011. 153-54. Print. The pair of individuals in a dyad can be linked via romantic interest, family relation, interests, work, partners in crime, and so on. The relation can be based on equality, but may be based on an asymmetrical or hierarchical relationship (master–servant). The strength of the relationship is evaluated on the basis of time the individuals spend together, as well as on the emotional intensity of their relationship. The term dyad is from . A dyad can be unstable because both persons must cooperate to make it work. If one of the two fails to complete their duties, the group would fall apart. Because of the significance of marriages in society, their stability is very important. For this reason marital dyads are often enforced through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triad (sociology)
Triad refers to a group of three people in sociology. It is one of the simplest human groups that can be studied and is mostly looked at by microsociology. The study of triads and dyads was pioneered by German sociologist Georg Simmel at the end of the nineteenth century. A triad can be viewed as a group of three people that can create different group interactions. This specific grouping is common yet overlooked in society for many reasons. Those being that it is compared to the lives of others, how they shape society, and how communication plays a role in different relationships scenarios. It was derived in the late 1800s to early 1900s and evolved throughout time to shape group interactions in the present. Simmel also hypothesized between dyads and triads and how they may differ. A dyad is a group of two people that interact while a triad is another person added on to create more communicational interactions. For example: adding an extra person, therefore creating a triad, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Network
A social network is a social structure made up of a set of social actors (such as individuals or organizations), sets of dyadic ties, and other social interactions between actors. The social network perspective provides a set of methods for analyzing the structure of whole social entities as well as a variety of theories explaining the patterns observed in these structures. The study of these structures uses social network analysis to identify local and global patterns, locate influential entities, and examine network dynamics. Social networks and the analysis of them is an inherently interdisciplinary academic field which emerged from social psychology, sociology, statistics, and graph theory. Georg Simmel authored early structural theories in sociology emphasizing the dynamics of triads and "web of group affiliations". Jacob Moreno is credited with developing the first sociograms in the 1930s to study interpersonal relationships. These approaches were mathematically formalize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theory
A theory is a rational type of abstract thinking about a phenomenon, or the results of such thinking. The process of contemplative and rational thinking is often associated with such processes as observational study or research. Theories may be scientific, belong to a non-scientific discipline, or no discipline at all. Depending on the context, a theory's assertions might, for example, include generalized explanations of how nature works. The word has its roots in ancient Greek, but in modern use it has taken on several related meanings. In modern science, the term "theory" refers to scientific theories, a well-confirmed type of explanation of nature, made in a way consistent with the scientific method, and fulfilling the criteria required by modern science. Such theories are described in such a way that scientific tests should be able to provide empirical support for it, or empirical contradiction ("falsify") of it. Scientific theories are the most reliable, rigorous, and compr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank Harary
Frank Harary (March 11, 1921 – January 4, 2005) was an American mathematician, who specialized in graph theory. He was widely recognized as one of the "fathers" of modern graph theory. Harary was a master of clear exposition and, together with his many doctoral students, he standardized the terminology of graphs. He broadened the reach of this field to include physics, psychology, sociology, and even anthropology. Gifted with a keen sense of humor, Harary challenged and entertained audiences at all levels of mathematical sophistication. A particular trick he employed was to turn theorems into games—for instance, students would try to add red edges to a graph on six vertices in order to create a red triangle, while another group of students tried to add edges to create a blue triangle (and each edge of the graph had to be either blue or red). Because of the theorem on friends and strangers, one team or the other would have to win. Biography Frank Harary was born in New Yo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cliques
A clique ( AusE, CanE, or ), in the social sciences, is a group of individuals who interact with one another and share similar interests. Interacting with cliques is part of normative social development regardless of gender, ethnicity, or popularity. Although cliques are most commonly studied during adolescence and middle childhood development, they exist in all age groups. They are often bound together by shared social characteristics such as ethnicity and socioeconomic status. Examples of common or stereotypical adolescent cliques include athletes, nerds, and "outsiders". Typically, people in a clique will not have a completely open friend group and can, therefore, "ban" members if they do something considered unacceptable, such as talking to someone disliked. Some cliques tend to isolate themselves as a group and view themselves as superior to others, which can be demonstrated through bullying and other antisocial behaviors. Terminology Within the concepts of sociology, cliqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hierarchical Clustering
In data mining and statistics, hierarchical clustering (also called hierarchical cluster analysis or HCA) is a method of cluster analysis that seeks to build a hierarchy of clusters. Strategies for hierarchical clustering generally fall into two categories: * Agglomerative: This is a " bottom-up" approach: Each observation starts in its own cluster, and pairs of clusters are merged as one moves up the hierarchy. * Divisive: This is a "top-down" approach: All observations start in one cluster, and splits are performed recursively as one moves down the hierarchy. In general, the merges and splits are determined in a greedy manner. The results of hierarchical clustering are usually presented in a dendrogram. The standard algorithm for hierarchical agglomerative clustering (HAC) has a time complexity of \mathcal(n^3) and requires \Omega(n^2) memory, which makes it too slow for even medium data sets. However, for some special cases, optimal efficient agglomerative methods (of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balance Theory
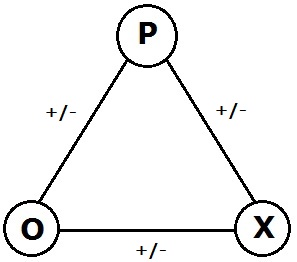
In the psychology of motivation, balance theory is a theory of attitude change, proposed by Fritz Heider. It conceptualizes the cognitive consistency motive as a drive toward psychological balance. The consistency motive is the urge to maintain one's values and beliefs over time. Heider proposed that "sentiment" or liking relationships are balanced if the affect valence in a system multiplies out to a positive result. Structural balance theory in social network analysis is the extension proposed by Frank Harary and Dorwin Cartwright. It was the framework for the discussion at a Dartmouth College symposium in September 1975. P-O-X model For example: a Person (P) who likes (+) an Other (O) person will be balanced by the same valence attitude on behalf of the other. Symbolically, P (+) > O and P X * P (-) > O * O (+) > X Cognitive balance is achieved when there are three positive links or two negatives with one positive. Two positive links and one negative like the example a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
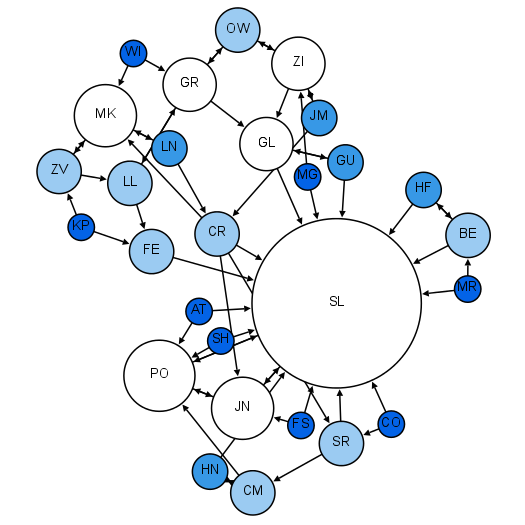
Sociogram
A sociogram is a graphic representation of social links that a person has. It is a graph drawing that plots the structure of interpersonal relations in a group situation. Overview Sociograms were developed by Jacob L. Moreno to analyze choices or preferences within a group. They can diagram the structure and patterns of group interactions. A sociogram can be drawn on the basis of many different criteria: Social relations, channels of influence, lines of communication etc. Those points on a sociogram who have many choices are called stars. Those with few or no choices are called isolates. Individuals who choose each other are known to have made a mutual choice. One-way choice refers to individuals who choose someone but the choice is not reciprocated. Cliques are groups of three or more people within a larger group who all choose each other (mutual choice). Sociograms are the charts or tools used to find the sociometry of a social space. Under the social discipline model, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Networks
A social network is a social structure made up of a set of social actors (such as individuals or organizations), sets of dyadic ties, and other social interactions between actors. The social network perspective provides a set of methods for analyzing the structure of whole social entities as well as a variety of theories explaining the patterns observed in these structures. The study of these structures uses social network analysis to identify local and global patterns, locate influential entities, and examine network dynamics. Social networks and the analysis of them is an inherently interdisciplinary academic field which emerged from social psychology, sociology, statistics, and graph theory. Georg Simmel authored early structural theories in sociology emphasizing the dynamics of triads and "web of group affiliations". Jacob Moreno is credited with developing the first sociograms in the 1930s to study interpersonal relationships. These approaches were mathematically formalize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |