|
Smarty (template Engine)
Smarty is a web template system written in PHP. Smarty is primarily promoted as a tool for separation of concerns. Smarty is intended to simplify compartmentalization, allowing the front-end of a web page to change separately from its back-end. Ideally, this lowers costs and minimizes the efforts associated with software maintenance. Smarty generates web content through the placement of special ''Smarty tags'' within a document. These tags are processed and substituted with other code. Tags are directives for Smarty that are enclosed by template delimiters. These directives can be variables, denoted by a dollar sign ($), functions, logical or loop statements. Smarty allows PHP programmers to define custom functions that can be accessed using Smarty tags. Smarty example Since Smarty separates PHP from HTML, there are two files — one contains the presentation code: an HTML template, including Smarty variables and tags - - which might look like this: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Template Engine (web)
A web template system in web publishing allows web designers and developers to work with ''web templates'' to automatically generate custom web pages, such as the results from a search. This reuses static web page elements while defining dynamic elements based on web request parameters. Web templates support static content, providing basic structure and appearance. Developers can implement templates from content management systems, web application frameworks, and HTML editors. Overview A ''web template system'' is composed of the following: * A template engine: the primary processing element of the system; * '' Content resource'': any of various kinds of input data streams, such as from a relational database, XML files, LDAP directory, and other kinds of local or networked data; * '' Template resource'': ''web template''s specified according to a template language; The template and content resources are processed and combined by the template engine to mass-produce web doc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU Lesser General Public License
The GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) is a free-software license published by the Free Software Foundation (FSF). The license allows developers and companies to use and integrate a software component released under the LGPL into their own (even proprietary) software without being required by the terms of a strong copyleft license to release the source code of their own components. However, any developer who modifies an LGPL-covered component is required to make their modified version available under the same LGPL license. For proprietary software, code under the LGPL is usually used in the form of a shared library, so that there is a clear separation between the proprietary and LGPL components. The LGPL is primarily used for software libraries, although it is also used by some stand-alone applications. The LGPL was developed as a compromise between the strong copyleft of the GNU General Public License (GPL) and more permissive licenses such as the BSD licenses and the MI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
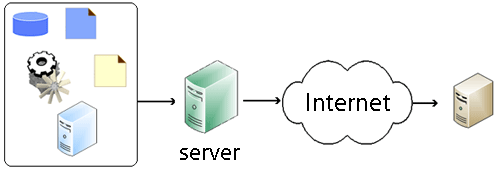
Web Template System
A web template system in web publishing allows web designers and developers to work with ''web templates'' to automatically generate custom web pages, such as the results from a search. This reuses static web page elements while defining dynamic elements based on HTTP request, web request parameters. Web templates support static content, providing basic structure and appearance. Developers can implement templates from content management systems, web application frameworks, and HTML editors. Overview A ''web template system'' is composed of the following: * A Template processor, template engine: the primary processing element of the system; * ''Content resource'': any of various kinds of input data streams, such as from a relational database, XML files, Lightweight Directory Access Protocol, LDAP directory, and other kinds of local or Computer networking, networked data; * ''Template resource'': ''web template''s specified according to a template language; The template and con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Separation Of Concerns
In computer science, separation of concerns (sometimes abbreviated as SoC) is a design principle for separating a computer program into distinct sections. Each section addresses a separate '' concern'', a set of information that affects the code of a computer program. A concern can be as general as "the details of the hardware for an application", or as specific as "the name of which class to instantiate". A program that embodies SoC well is called a modular program. Modularity, and hence separation of concerns, is achieved by encapsulating information inside a section of code that has a well-defined interface. Encapsulation is a means of information hiding. Layered designs or packaging by feature in information systems are another embodiment of separation of concerns (e.g., presentation layer, business logic layer, data access layer, persistence layer). Separation of concerns results in more degrees of freedom for some aspect of the program's design, deployment, or usage. Comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encapsulation (computer Science)
Encapsulation may refer to: Chemistry * Molecular encapsulation, in chemistry, the confinement of an individual molecule within a larger molecule * Micro-encapsulation, in material science, the coating of microscopic particles with another material Biology * Cell encapsulation, technology made to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications Computing and electronics * An alternate term for conformal coating or potting, which protects electronic components * Encapsulation (networking), the process of adding control information as it passes through the layered model * Encapsulation (computer programming) In software systems, encapsulation refers to the bundling of data with the mechanisms or methods that operate on the data. It may also refer to the limiting of direct access to some of that data, such as an object's components. Essentially, enca ..., the combination of program code and data, and/or restriction (hide) of access t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Maintenance
Software maintenance is the modification of software after delivery. Software maintenance is often considered lower skilled and less rewarding than new development. As such, it is a common target for outsourcing or offshoring. Usually, the team developing the software is different from those who will be maintaining it. The developers lack an incentive to write the code to be easily maintained. Software is often delivered incomplete and almost always contains some bugs that the maintenance team must fix. Software maintenance often initially includes the development of new functionality, but as the product nears the end of its lifespan, maintenance is reduced to the bare minimum and then cut off entirely before the product is withdrawn. Each maintenance cycle begins with a change request typically originating from an end user. That request is evaluated and if it is decided to implement it, the programmer studies the existing code to understand how it works before implementing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable (programming)
In computer programming, a variable is an abstract storage location paired with an associated symbol, symbolic name, which contains some known or unknown quantity of Data (computer science), data or Object (computer science), object referred to as a ''value (computer science), value''; or in simpler terms, a variable is a named container for a particular set of bits or Data type, type of data (like Integer (computer science), integer, Floating-point arithmetic, float, String (computer science), string, etc...). A variable can eventually be associated with or identified by a memory address. The variable name is the usual way to Reference (computer science), reference the stored value, in addition to referring to the variable itself, depending on the context. This separation of name and content allows the name to be used independently of the exact information it represents. The identifier in computer source code can be Name binding, bound to a Value (computer science), value during R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delimiter
A delimiter is a sequence of one or more Character (computing), characters for specifying the boundary between separate, independent regions in plain text, Expression (mathematics), mathematical expressions or other Data stream, data streams. An example of a delimiter is the comma character, which acts as a ''field delimiter'' in a sequence of comma-separated values. Another example of a delimiter is the time gap used to separate letters and words in the transmission of Morse code. In mathematics, delimiters are often used to specify the scope of an Operation (mathematics), operation, and can occur both as isolated symbols (e.g., Colon (punctuation), colon in "1 : 4") and as a pair of opposing-looking symbols (e.g., Angled bracket, angled brackets in \langle a, b \rangle). Delimiters represent one of various means of specifying boundaries in a data stream. String literal#Declarative notation, Declarative notation, for example, is an alternate method (without the use of delimiter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conditional (programming)
In computer science, conditionals (that is, conditional statements, conditional expressions and conditional constructs) are programming language constructs that perform different computations or actions or return different values depending on the value of a Boolean expression, called a ''condition''. Conditionals are typically implemented by selectively executing instructions. Although dynamic dispatch is not usually classified as a conditional construct, it is another way to select between alternatives at runtime. Terminology Conditional statements are imperative constructs executed for side-effect, while conditional expressions return values. Many programming languages (such as C) have distinct conditional statements and conditional expressions. Although in pure functional programming, conditional expressions do not have side-effects, many languages with conditional expressions (such as Lisp) support conditional side-effects. If–then(–else) The if–then or if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Flow
In computer science, control flow (or flow of control) is the order in which individual statements, instructions or function calls of an imperative program are executed or evaluated. The emphasis on explicit control flow distinguishes an ''imperative programming'' language from a ''declarative programming'' language. Within an imperative programming language, a ''control flow statement'' is a statement that results in a choice being made as to which of two or more paths to follow. For non-strict functional languages, functions and language constructs exist to achieve the same result, but they are usually not termed control flow statements. A set of statements is in turn generally structured as a block, which in addition to grouping, also defines a lexical scope. Interrupts and signals are low-level mechanisms that can alter the flow of control in a way similar to a subroutine, but usually occur as a response to some external stimulus or event (that can occur asynchr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Logic
In computer software, business logic or domain logic is the part of the program that encodes the real-world business rules that determine how data can be created, stored, and changed. It is contrasted with the remainder of the software that might be concerned with lower-level details of managing a database or displaying the user interface, system infrastructure, or generally connecting various parts of the program. Details and example Business logic: * Prescribes how business objects interact with one another * Enforces the routes and the methods by which business objects are accessed and updated Business rules: * Model real-life business objects (such as accounts, loans, itineraries, and inventories) Business logic comprises: * Workflows that are the ordered tasks of passing documents or data from one participant (a person or a software system) to another. Business logic should be distinguished from business rules. Business logic is the portion of an enterprise system which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Of Web Template Engines
The following table lists the various web template engines used in Web template systems and a brief rundown of their features. See also * Template processor * Web template system A web template system in web publishing allows web designers and developers to work with ''web templates'' to automatically generate custom web pages, such as the results from a search. This reuses static web page elements while defining dynami ... * JavaScript templating * :Template engines Java template engine performance report in spring boot Notes References {{DEFAULTSORT:Web template engines Scripting languages * Computing comparisons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |