|
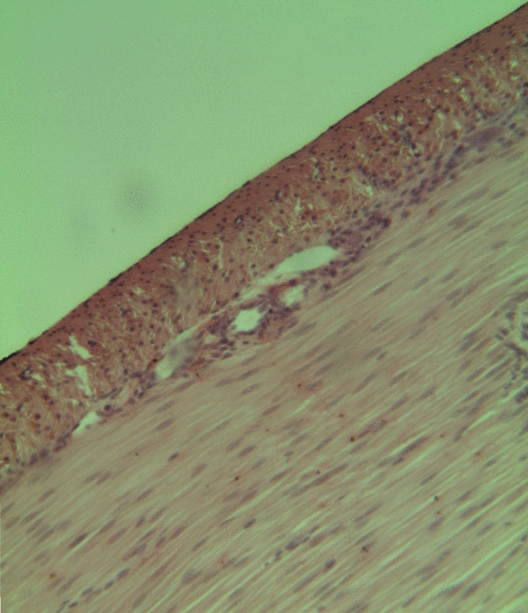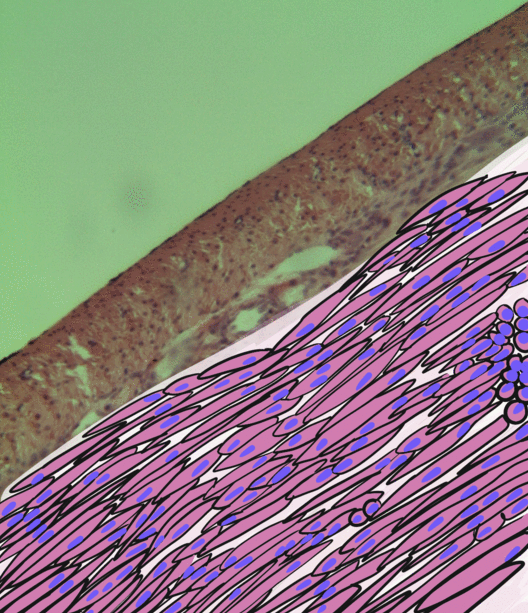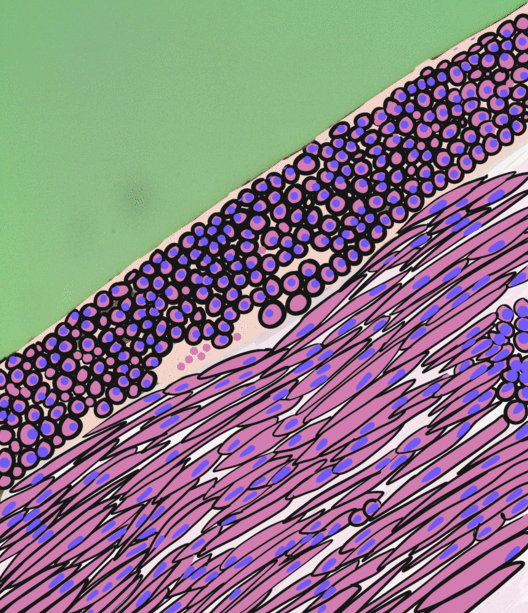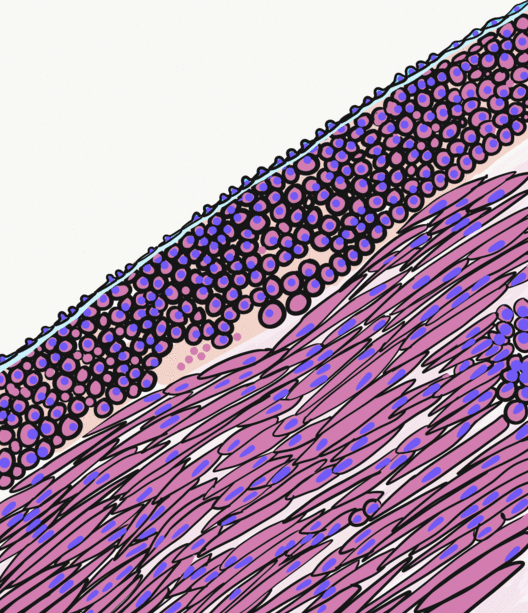
Small Intestinal Submucosa
The submucosa (or tela submucosa) is a thin layer of tissue in various organs of the gastrointestinal, respiratory, and genitourinary tracts. It is the layer of dense irregular connective tissue that supports the mucosa (mucous membrane) and joins it to the muscular layer, the bulk of overlying smooth muscle (fibers running circularly within layer of longitudinal muscle). The submucosa ('' sub-'' + ''mucosa'') is to a mucous membrane what the subserosa ('' sub-'' + ''serosa'') is to a serous membrane. Structure Blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves (all supplying the mucosa) will run through here. In the intestinal wall, tiny parasympathetic ganglia are scattered around forming the submucous plexus (or "Meissner's plexus") where preganglionic parasympathetic neurons synapse with postganglionic nerve fibers that supply the muscularis mucosae. Histologically, the wall of the alimentary canal shows four distinct layers (from the lumen moving out): mucosa, submucosa, muscular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucous Membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated. Structure The mucosa is composed of one or more layers of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, and an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue. The type of cells and type of mucus secreted vary from organ to organ and each can differ along a given tract. Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory and reproductive trac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts as a syncytium. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines, bladder and uterus; in the walls of passageways, such as blood, and lymph vessels, and in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems. In the eyes, the ciliary muscles, a type of smooth muscle, dilate and contract the iris and alter the shape of the lens. In the skin, smooth muscle cells such as those of the arrector pili cause hair to stand erect in response to cold temperature or fear. Structure Gross anatomy Smooth muscle is grouped into two types: single-unit smooth muscle, also known as visceral smooth muscle, and multiunit smooth muscle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submucosal Gland
Submucosal glands can refer to various racemose exocrine glands of the mucous type. These glands secrete mucus to facilitate the movement of particles along the body's various tubes, such as the throat and intestines. The mucosa is the lining of the tubes, like a kind of ''skin''. ''Submucosal'' means that the actual gland resides in the connecting tissue below the mucosa. The submucosa is the tissue that connects the mucosa to the muscle outside the tube. The glands themselves are quite complex. The mucus factory is at the bottom, in the submucosa, it is composed of many little sacs (acini) where the mucus originates. Each sac (acinus) has one end that can open and close (dilate) to allow the mucus out. The acini empty into little tubes (tubules) that lead to a reservoir (collecting duct) that has a portal through the ''skin'' (mucosa) that can open and close allowing the mucus into the main tube. The submucosal glands are a companion to goblet cells which also produce mucus, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adventitia
The adventitia () is the outer layer of fibrous connective tissue surrounding an organ. The outer layer of connective tissue that surrounds an artery, or vein – the tunica externa, is also called the ''tunica adventitia''. To some degree, its role is complementary to that of the serosa, which also provides a layer of tissue surrounding an organ. In the abdomen, whether an organ is covered in adventitia or serosa depends upon whether it is peritoneal or retroperitoneal: * intraperitoneal organs are covered in serosa (a layer of mesothelium, the visceral peritoneum) * retroperitoneal organs are covered in ''adventitia'' (loose connective tissue) In the gastrointestinal tract, the muscular layer is bounded in most cases by serosa. However, at the oral cavity, thoracic esophagus, ascending colon, descending colon and the rectum, the muscular layer is instead bounded by adventitia. The muscular layer of the duodenum is bounded by both tissue types. Generally, if it is a part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscularis Mucosae
The lamina muscularis mucosae (or muscularis mucosae) is a thin layer (lamina) of muscle of the gastrointestinal tract, located outside the lamina propria, and separating it from the submucosa. It is present in a continuous fashion from the esophagus to the upper rectum (the exact nomenclature of the rectum's muscle layers is still being debated). A discontinuous muscularis mucosae–like muscle layer is present in the urinary tract, from the renal pelvis to the bladder; as it is discontinuous, it should not be regarded as a true muscularis mucosae. In the gastrointestinal tract, the term ''mucosa'' or ''mucous membrane'' refers to the combination of epithelium, lamina propria, and (where it occurs) muscularis mucosae.H.G. Burkitt et al., ''Wheater's Functional Histology, 3rd ed.'' The etymology suggests this, since the Latin names translate to "the mucosa's own special layer" (''lamina propria mucosae'') and "muscular layer of the mucosa" (''lamina muscularis mucosae''). The mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postganglionic
In the autonomic nervous system, fibers from the ganglion to the wikt:effector, effector organ are called postganglionic fibers. Neurotransmitters The neurotransmitters of postganglionic fibers differ: * In the parasympathetic division, neurons are ''cholinergic''. That is to say acetylcholine is the primary neurotransmitter responsible for the communication between neurons on the parasympathetic nervous system, parasympathetic pathway. * In the sympathetic division, neurons are mostly ''adrenergic'' (that is, epinephrine and norepinephrine function as the primary neurotransmitters). Notable exceptions to this rule include the sympathetic innervation of sweat glands and Arrector pili muscle, arrectores pilorum muscles where the neurotransmitter at both pre and post ganglionic synapses is acetylcholine. Another notable structure is the medulla of the adrenal gland, where chromaffin cells function as modified post-ganglionic nerves. Instead of releasing epinephrine and norepineph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preganglionic
In the autonomic nervous system, fibers from the CNS to the ganglion are known as preganglionic fibers. All preganglionic fibers, whether they are in the sympathetic division or in the parasympathetic division, are cholinergic (that is, these fibers use acetylcholine as their neurotransmitter) and they are myelinated. Sympathetic preganglionic fibers tend to be shorter than parasympathetic preganglionic fibers because sympathetic ganglia are often closer to the spinal cord than are the parasympathetic ganglia. Another major difference between the two ANS (autonomic nervous systems) is divergence. Whereas in the parasympathetic division there is a divergence factor of roughly 1:4, in the sympathetic division there can be a divergence of up to 1:20. This is due to the number of synapses formed by the preganglionic fibers with ganglionic neurons. See also * Postganglionic fibers In the autonomic nervous system, fibers from the ganglion to the effector organ are called p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submucous Plexus
The submucosal plexus (Meissner's plexus, plexus of the submucosa, plexus submucosus) lies in the submucosa of the intestinal wall. The nerves of this plexus are derived from the myenteric plexus which itself is derived from the plexuses of parasympathetic nerves around the superior mesenteric artery. Branches from the myenteric plexus perforate the circular muscle fibers to form the submucosal plexus. Ganglia from the plexus extend into the muscularis mucosae and also extend into the mucous membrane. They contain Dogiel cells. The nerve bundles of the submucous plexus are finer than those of the myenteric plexus. Its function is to innervate cells in the epithelial layer and the smooth muscle of the muscularis mucosae. 14% of submucosal plexus neurons are sensory neurons - Dogiel type II, also known as enteric primary afferent neurons or intrinsic primary afferent neurons. History Meissners' plexus was described by German professor Georg Meissner George Meissner (19 Novemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasympathetic
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for regulating the body's unconscious actions. The parasympathetic system is responsible for stimulation of "rest-and-digest" or "feed and breed" activities that occur when the body is at rest, especially after eating, including sexual arousal, salivation, lacrimation (tears), urination, digestion, and defecation. Its action is described as being complementary to that of the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for stimulating activities associated with the fight-or-flight response. Nerve fibres of the parasympathetic nervous system arise from the central nervous system. Specific nerves include several cran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerves
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system. A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses called action potentials that are transmitted along each of the axons to peripheral organs or, in the case of sensory nerves, from the periphery back to the central nervous system. Each axon, within the nerve, is an extension of an individual neuron, along with other supportive cells such as some Schwann cells that coat the axons in myelin. Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the endoneurium. The axons are bundled together into groups called Nerve fascicle, fascicles, and each fascicle is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the perineurium. Finally, the entire nerve is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the epineurium. Nerve cells (often called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphatic Vessels
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessels are lined by endothelial cells, and have a thin layer of smooth muscle, and adventitia that binds the lymph vessels to the surrounding tissue. Lymph vessels are devoted to the propulsion of the lymph from the lymph capillaries, which are mainly concerned with the absorption of interstitial fluid from the tissues. Lymph capillaries are slightly bigger than their counterpart capillaries of the vascular system. Lymph vessels that carry lymph to a lymph node are called afferent lymph vessels, and those that carry it from a lymph node are called efferent lymph vessels, from where the lymph may travel to another lymph node, may be returned to a vein, or may travel to a larger lymph duct. Lymph ducts drain the lymph into one of the subclavian ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Vessels
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Blood vessels are needed to sustain life, because all of the body's tissues rely on their functionality. There are five types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the arterioles; the capillaries, where the exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues occurs; the venules; and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart. The word ''vascular'', meaning relating to the blood vessels, is derived from the Latin ''vas'', meaning vessel. Some structures – such as cartilage, the epithelium, and the lens and cornea of the eye – do not contain blood vessels and are labeled ''avascular''. Etymology * artery: late Middle English; from Latin ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |