|
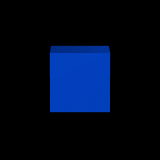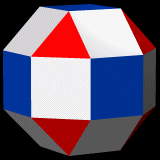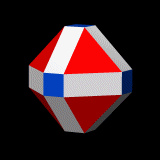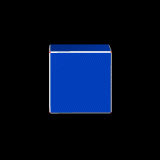
Small Rhombicuboctahedron
In geometry, the rhombicuboctahedron, or small rhombicuboctahedron, is a polyhedron with eight triangular, six square (geometry), square, and twelve rectangle, rectangular faces. There are 24 identical vertices, with one triangle, one square, and two rectangles meeting at each one. If all the rectangles are themselves square (equivalently, all the edges are the same length, ensuring the triangles are equilateral triangle, equilateral), it is an Archimedean solid. The polyhedron has octahedral symmetry, like the Cube (geometry), cube and octahedron. Its dual polyhedron, dual is called the deltoidal icositetrahedron or trapezoidal icositetrahedron, although its faces are not really true trapezoids. Names Johannes Kepler in Harmonices Mundi (1618) named this polyhedron a ''rhombicuboctahedron'', being short for ''truncated cuboctahedral rhombus'', with ''cuboctahedral rhombus'' being his name for a rhombic dodecahedron. There are different truncations of a rhombic dodecahedron int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a ''geometer''. Until the 19th century, geometry was almost exclusively devoted to Euclidean geometry, which includes the notions of point, line, plane, distance, angle, surface, and curve, as fundamental concepts. During the 19th century several discoveries enlarged dramatically the scope of geometry. One of the oldest such discoveries is Carl Friedrich Gauss' ("remarkable theorem") that asserts roughly that the Gaussian curvature of a surface is independent from any specific embedding in a Euclidean space. This implies that surfaces can be studied ''intrinsically'', that is, as stand-alone spaces, and has been expanded into the theory of manifolds and Riemannian geometry. Later in the 19th century, it appeared that geometries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topology
In mathematics, topology (from the Greek language, Greek words , and ) is concerned with the properties of a mathematical object, geometric object that are preserved under Continuous function, continuous Deformation theory, deformations, such as Stretch factor, stretching, Twist (mathematics), twisting, crumpling, and bending; that is, without closing holes, opening holes, tearing, gluing, or passing through itself. A topological space is a set (mathematics), set endowed with a structure, called a ''Topology (structure), topology'', which allows defining continuous deformation of subspaces, and, more generally, all kinds of continuity (mathematics), continuity. Euclidean spaces, and, more generally, metric spaces are examples of a topological space, as any distance or metric defines a topology. The deformations that are considered in topology are homeomorphisms and homotopy, homotopies. A property that is invariant under such deformations is a topological property. Basic exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topologically
In mathematics, topology (from the Greek words , and ) is concerned with the properties of a geometric object that are preserved under continuous deformations, such as stretching, twisting, crumpling, and bending; that is, without closing holes, opening holes, tearing, gluing, or passing through itself. A topological space is a set endowed with a structure, called a ''topology'', which allows defining continuous deformation of subspaces, and, more generally, all kinds of continuity. Euclidean spaces, and, more generally, metric spaces are examples of a topological space, as any distance or metric defines a topology. The deformations that are considered in topology are homeomorphisms and homotopies. A property that is invariant under such deformations is a topological property. Basic examples of topological properties are: the dimension, which allows distinguishing between a line and a surface; compactness, which allows distinguishing between a line and a circle; connectedne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubik's Cube
The Rubik's Cube is a Three-dimensional space, 3-D combination puzzle originally invented in 1974 by Hungarians, Hungarian sculptor and professor of architecture Ernő Rubik. Originally called the Magic Cube, the puzzle was licensed by Rubik to be sold by Pentangle Puzzles in the UK in 1978, and then by Ideal Toy Company, Ideal Toy Corp in 1980 via businessman Tibor Laczi and Seven Towns founder Tom Kremer. The cube was released internationally in 1980 and became one of the most recognized icons in popular culture. It won the 1980 Spiel des Jahres, German Game of the Year special award for Best Puzzle. , 350 million cubes had been sold worldwide, making it the world's bestselling puzzle game and bestselling toy. The Rubik's Cube was inducted into the US National Toy Hall of Fame in 2014. On the original classic Rubik's Cube, each of the six faces was covered by nine stickers, each of one of six solid colours: white, red, blue, orange, green, and yellow. Some later versions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ordinary convex polyhedra and the only one that has fewer than 5 faces. The tetrahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a Euclidean simplex, and may thus also be called a 3-simplex. The tetrahedron is one kind of pyramid, which is a polyhedron with a flat polygon base and triangular faces connecting the base to a common point. In the case of a tetrahedron the base is a triangle (any of the four faces can be considered the base), so a tetrahedron is also known as a "triangular pyramid". Like all convex polyhedra, a tetrahedron can be folded from a single sheet of paper. It has two such nets. For any tetrahedron there exists a sphere (called the circumsphere) on which all four vertices lie, and another sphere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhombicosidodecahedron
In geometry, the rhombicosidodecahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed of two or more types of regular polygon faces. It has 20 regular triangular faces, 30 square (geometry), square faces, 12 regular pentagonal faces, 60 vertex (geometry), vertices, and 120 edge (geometry), edges. Names Johannes Kepler in Harmonices Mundi (1618) named this polyhedron a ''rhombicosidodecahedron'', being short for ''truncated icosidodecahedral rhombus'', with ''icosidodecahedral rhombus'' being his name for a rhombic triacontahedron. There are different truncations of a rhombic triacontahedron into a topology, topological rhombicosidodecahedron: Prominently its rectification (geometry), rectification (left), the one that creates the uniform solid (center), and the rectification of the dual icosidodecahedron (right), which is the core of the dual compound. It can also be called an ''Expansion (geometry), expanded'' or ''Cantellation (geome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P2-A5-P3
P, or p, is the sixteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''pee'' (pronounced ), plural ''pees''. History The Semitic Pê (mouth), as well as the Greek Π or π ( Pi), and the Etruscan and Latin letters that developed from the former alphabet, all symbolized , a voiceless bilabial plosive. Use in writing systems In English orthography and most other European languages, represents the sound . A common digraph in English is , which represents the sound , and can be used to transliterate ''phi'' in loanwords from Greek. In German, the digraph is common, representing a labial affricate . Most English words beginning with are of foreign origin, primarily French, Latin and Greek; these languages preserve Proto-Indo-European initial *p. Native English cognates of such words often start with , since English is a Germanic language and thus has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wings 3D
Wings 3D is a free and open-source subdivision modeler inspired by Nendo and Mirai from Izware. Wings 3D is named after the winged-edge data structure it uses internally to store coordinate and adjacency data, and is commonly referred to by its users simply as Wings. Wings 3D is available for Windows, Linux, and Mac OS X, using the Erlang environment. Overview Wings 3D can be used to model and texture low to mid-range polygon models. Wings does not support animations and has only basic OpenGL rendering facilities, although it can export to external rendering software such as POV-Ray and YafRay. Wings is often used in combination with other software, whereby models made in Wings are exported to applications more specialized in rendering and animation such as Blender. Interface Wings 3D uses context-sensitive menus as opposed to a highly graphical, icon-oriented interface. Modeling is done using the mouse and keyboard to select and modify different aspects of a model's geom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uniform Polyhedron
In geometry, a uniform polyhedron has regular polygons as faces and is vertex-transitive (i.e., there is an isometry mapping any vertex onto any other). It follows that all vertices are congruent. Uniform polyhedra may be regular (if also face- and edge-transitive), quasi-regular (if also edge-transitive but not face-transitive), or semi-regular (if neither edge- nor face-transitive). The faces and vertices need not be convex, so many of the uniform polyhedra are also star polyhedra. There are two infinite classes of uniform polyhedra, together with 75 other polyhedra: *Infinite classes: ** prisms, **antiprisms. * Convex exceptional: ** 5 Platonic solids: regular convex polyhedra, ** 13 Archimedean solids: 2 quasiregular and 11 semiregular convex polyhedra. * Star (nonconvex) exceptional: ** 4 Kepler–Poinsot polyhedra: regular nonconvex polyhedra, ** 53 uniform star polyhedra: 14 quasiregular and 39 semiregular. Hence 5 + 13 + 4 + 53 = 75. There are also many degen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cube
In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. Viewed from a corner it is a hexagon and its net is usually depicted as a cross. The cube is the only regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It has 6 faces, 12 edges, and 8 vertices. The cube is also a square parallelepiped, an equilateral cuboid and a right rhombohedron a 3-zonohedron. It is a regular square prism in three orientations, and a trigonal trapezohedron in four orientations. The cube is dual to the octahedron. It has cubical or octahedral symmetry. The cube is the only convex polyhedron whose faces are all squares. Orthogonal projections The ''cube'' has four special orthogonal projections, centered, on a vertex, edges, face and normal to its vertex figure. The first and third correspond to the A2 and B2 Coxeter planes. Spherical tiling The cube can also be represented as a spherical tiling, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantellation (geometry)
In geometry, a cantellation is a 2nd-order Truncation (geometry), truncation in any dimension that Bevel, bevels a regular polytope at its Edge (geometry), edges and at its Vertex (geometry), vertices, creating a new Facet (geometry), facet in place of each edge and of each vertex. Cantellation also applies to regular tilings and honeycomb (geometry), honeycombs. Cantellating a polyhedron is also rectifying its rectification (geometry), rectification. Cantellation (for polyhedra and tilings) is also called ''Expansion (geometry), expansion'' by Alicia Boole Stott: it corresponds to moving the faces of the regular form away from the center, and filling in a new face in the gap for each opened edge and for each opened vertex. Notation A cantellated polytope is represented by an extended Schläfli symbol ''t''0,2 or ''r''\beginp\\q\\...\end or ''rr''. For Polyhedron, polyhedra, a cantellation offers a direct sequence from a regular polyhedron to its Dual polyhedron, dual. Examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expansion (geometry)
In geometry, expansion is a polytope operation where facets are separated and moved radially apart, and new facets are formed at separated elements ( vertices, edges, etc.). Equivalently this operation can be imagined by keeping facets in the same position but reducing their size. The expansion of a regular polytope creates a uniform polytope, but the operation can be applied to any convex polytope, as demonstrated for polyhedra in Conway polyhedron notation (which represents expansion with the letter ). For polyhedra, an expanded polyhedron has all the faces of the original polyhedron, all the faces of the dual polyhedron, and new square faces in place of the original edges. Expansion of regular polytopes According to Coxeter, this multidimensional term was defined by Alicia Boole StottCoxeter, ''Regular Polytopes'' (1973), p. 123. p.210 for creating new polytopes, specifically starting from regular polytopes to construct new uniform polytopes. The ''expansion'' operation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



